Ashton Mills. Wipe It Free: Secure Wiping Software. www.cso.com.au
Any company wants to have confirmation that its confidential data will not fall into the wrong hands, and a home user should not leave traces of personal information and transactions credit cards, because attackers can take advantage of them.
Before you transfer the computer to strangers, you should make sure that all data from it is deleted in compliance necessary measures security. In this case, simply deleting data or formatting a disk partition is not enough - the units and zeros that make up the information do not disappear anywhere, and they can be easily restored using specialized tools.
Naturally, demand creates supply, and therefore many tools have already been created for safely erasing information from disks. Moreover, to perform the relevant operations it is not at all necessary to purchase expensive software, which will undoubtedly please accountants and financiers. A lot of free tools have been developed that do for the user everything that he needs. However, as will be noted later, paid tools also find their customers.
Software designed for reliable information deletion is divided into two large classes based on processing of the file system or the disk itself. It is clear that in the second case the disk is erased, and in general, such a method would be preferable if guarantees are needed. Even when a program efficiently overwrites a file by overwriting it many times, a copy of this file or data can be saved in a page file, in syslog data, or in temporary files. However, it all depends on what level of security is needed.
This review will cover both very popular tools and programs that you probably never heard of. We hope that this will help you navigate the world of affordable tools and understand how they work.
The popular CCleaner tool designed to delete temporary files, clear browser cache, files system logs and other garbage, copes well with its tasks.
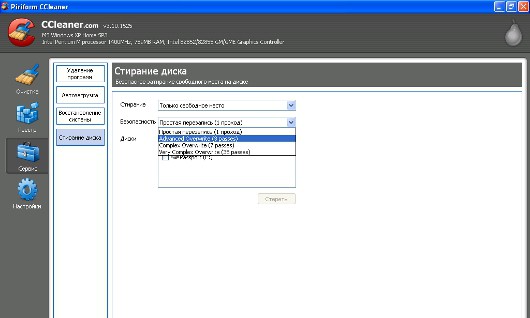
In addition, he has the Drive Wiper tool in the Tools section, which frees up space or the entire disk using four methods, from single-pass dubbing to the Gutman 35-pass algorithm. CCleaner is inferior in functionality to the other products included in this review, but it does its job quite well. In addition, it is distributed free of charge.
Slimware Slimcleaner Shredder
Slimcleaner is the actual Slimlean CCleaner equivalent with the Shredder tool.
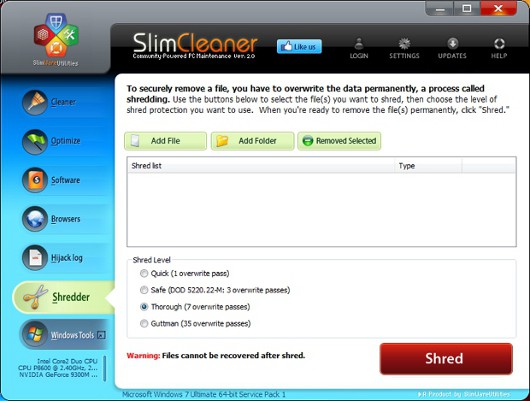
The user can choose the appropriate method of erasure, starting from a single-pass and ending with the Gutman 35-pass algorithm (see the section "Gradations of safe deletion"). Before pressing the Shred button, it is proposed to make a list of deleted items, which includes files and folders located in different places. Although there is no obvious way to erase everything from the disk, you can achieve the corresponding effect by selecting Folder and clicking on the root of the disk. However, this procedure is not equivalent to completely erasing the disk, since the file system structures are preserved in this case. A good product and again - free.
Darik "s Boot and Nuke
Darik's Boot and Nuke utility creates a Linux-based boot disk, the sole purpose of which is to erase the entire drive to a state where even the most cautious forensics will not produce any result.
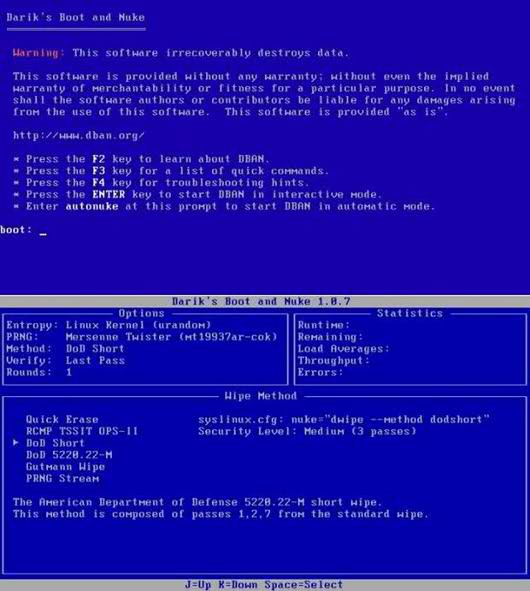
It is also allowed to erase data from multiple disks at once. Their total number is limited only by the number of system interfaces and PCI bus bandwidth. It really can be very useful. Boot and Nuke erase methods range from a simple one-pass to a 35-pass Gutman algorithm. The program supports various standards (for example, the US Department of Defense “short” erase standard) and pseudorandom number generator (PRNG) streams generated using the Mersenne Whirlwind algorithm. This is not to say that everything was done very beautifully (after loading the disc, only ASCII text code will appear on the screen), but after completing all the procedures, the "enthusiasts" who retain the hope of recovering the destroyed information can only sympathize and wish good luck. The Linux-based Boot and Nuke boot disk is free.
Active @ KillDisk
The Active @ KillDisk utility, according to its developers, supports 17 different security standards (the “Gradations for Safe Deletion” section explains why most of them are not needed), including the popular methods used by the military.
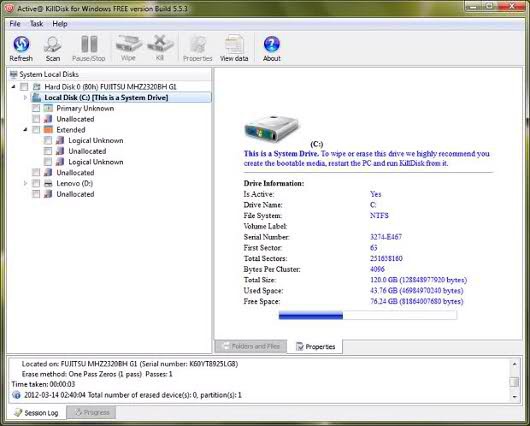
Unlike other tools, KillDisk comes in versions for Windows and for DOS. The first one can be used both directly in the operating system environment, and with boot disk. This allows you to erase data on the drive where Windows is located. This utility helps clean up free space. It contains a built-in disk viewer that helps you compare clusters before and after the procedure. In the free demo mode, only single pass dubbing is supported. All other methods require the purchase of the Pro version, which has an initial price of $ 50 for personal use and $ 1,500 for corporate use.
Disk wipe
The impressive compact utility Disk Wipe fully lives up to its expectations. It does not require installation and works in offlineby supporting seven methods. These include the Gutman 35-pass algorithm, technologies that meet the requirements of the British and Russian standards, as well as the US military standard. Like Active @ KillDisk, Disk Wipe has built-in disk viewers, and its volume does not exceed 1 MB.
As an additional option, formatting the disk and writing to it a new file system are offered. There are no tools for working with individual files or folders here, but you should not expect such options from a utility called Disk Wipe.
Acronis Drive Cleanser
Acronis is known for its popular apps for reserve copyoriented both to corporate clients and home users. In addition, its product range includes Drive Cleanser, designed to safely remove information from disk.

It is a little sad that during the installation process you will need an additional driver and you will have to reboot the system - and all this for a simple disk cleanup? In fairness, it should be noted that the utility is highly flexible, supporting not only the fast execution of standard algorithms and data deletion according to the Gutman method and the standard of the US Department of Defense, but also uses its own technology to erase information and determine the data written to the disk. In addition, you can create a boot disk with the means of reliable deletion of information placed on it (approximately the same thing was observed in the Darik application). Drive Cleanser software has a 15-day trial period. For the right to use the utility without restrictions on one computer, customers will have to pay $ 61.
East Tec Dispose Secure
Developed by East Tec's Dispose Secure software, like the other tools described here, you can create a boot disk. Its main advantage is the ability to manage information from networked computers from a single console.
All supported standard methods cleaning, as well as several new combinations, for example, the original method 3 + 7 + 3. In Network Sanitiser mode, data is deleted remotely from other machines with their MAC address or via network connection. This allows you to simultaneously access the disks of several machines at once, without leaving your workplace. The trial version clears only a quarter of the disk. A fully functional option that allows you to reliably remove from the disk all previously recorded data on it, can be purchased for $ 24.
Iolo drive scubber
Iolo Drive Scubber has a simple and nice interface. In most modes, a button is displayed on the screen that allows you to get additional information, which serves as a good help for beginners. The utility runs both in Windows and from pre-created bootable media. Thanks to this, you can delete data from those disks on which the operating system is deployed.
It supports simultaneous erasing of multiple disks at once and overwriting free space, not busy files. It is worth noting that this product belongs to the few that offer only one method that meets the DoD 5220.22-M standard. The user can independently set the number of passes and define their own patterns. In Desktop Incinerator mode, the utility acts as the Recycle Bin, supporting algorithms for the reliable destruction of deleted files. The trial version features are limited to three launches. A full-featured version with a license to use on three machines costs $ 50.
Clean disk security
Despite its big name, the Clean Disk Security utility cannot clean disks and erase individual files. It got into the review because it is close to CCleaner in functionality - cleaning the Recycle Bin, browser cache, browsing history, cookies, etc. are supported.
The user gets the opportunity to reliably destroy the data after they are deleted, which CCleaner can not do. Simple cleaning in several passes is supported, as well as two other modes, including data deletion using the Gutman method. Although the application cannot be used to clean the entire computer, it can come in handy for those who want to securely delete personal account information. Clean Disk Security belongs to the category of shareware software.
Jetico bcipe
BCWipe software is integrated directly into the Windows shell, which allows you to safely delete files and folders through the right-click context menu or through the Task Manager.

The tools built into the Task Manager provide scheduled deletion, cleaning free space and selected files and folders. A fairly wide range of methods is supported, including the popular military and Gutman algorithms. Additionally, you can clear the FAT and NTFS directories, as well as the space reserved by the system. The delivery includes a real-time paging file encryption mechanism. Fans Apple company Jetico offers a Mac version. The demo version can be downloaded from the developer's site. The full-featured version is priced at $ 50.
MiniTool Drive Wipe
The simplicity of the proposed tool should be especially noted here. The MiniTool Drive Wipe interface has only two buttons - Wipe Partition and Wipe Disk. After clicking on them, a dialog box with an image of the disk partition table is displayed. Depending on the selected mode, you can mark individual partitions on disks or entire disks.
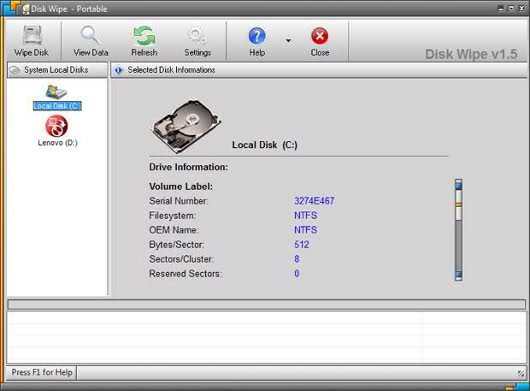
Then you need to choose one of five methods (among others, the US Department of Defense standard with three and seven passes is supported), click the execute button and wait for the process to complete. The tool is supplied free of charge, it is intended solely for personal use. Its use for commercial purposes is prohibited.
Lavasoft file shredder
Lavasoft Utility File shredder, as its name implies, is designed to work with files and the file system - the functions of cleaning disks and their partitions are not supported. But the set of operations with files and folders is very diverse. Three basic algorithms and 13 are offered by default. various methods, including popular military standards, and, of course, the Gutman algorithm.

The utility has assistants for cleaning files and folders, Recycle Bin, free disk space and system fileswhich include temporary files, browser cache, and cookies. Perhaps the functionality of File Shredder is not as wide as that of the other tools considered in our review, but the helpers noticeably simplify the work with this utility. The software has a trial period, after which you will have to pay $ 30 for a fully functional version.
Eraser
Like File Shredder, Eraser supports 13 algorithms that meet the requirements of various military standards, as well as a simple one-pass method for recording pseudorandom data (its usefulness is explained in the "Gradation of Safe Deletion" section).
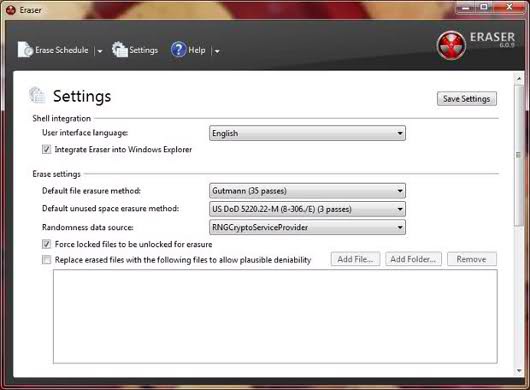
Jobs related to deleting information can be run in advance certain time or after rebooting the system. Supports cleaning files, folders, Recycle Bin and free space. The interface is nothing special, but at the same time, Eraser has several unique features. When cleaning files and free space, it is acceptable to use two different methods. For example, free space can be processed by quick simple rewriting, and files can be destroyed by executing a slow multi-pass algorithm.
When erasing, locked files (as a rule, these are currently used or system files) can be automatically unlocked.
Of particular interest is the function that helps the user to hide his actions, replacing for disguise deleted files some other. Finally, the Eraser tool is not just free - it comes with open source.
Which utility is better?
The answer to this question is determined by your needs, and in order to get it, you need to do with each of the utilities all the operations that you might potentially need. Our subjective choices were awarded Gold, Silver and Bronze Prizes.
No special need to buy for money software for reliable data deletion, unless you need a commercial license or some specific functions (for example, the function of clearing information over the network, or encrypting the paging file. In general, all methods have already been tested, proved their worth and meet the requirements of the standards, which they are based.
Do not even torment your disk for four days with 35 passes of rewriting, achieving absolute reliability. The author himself, who proposed a comprehensive 35-pass algorithm, which is mainly used now, argued that overwriting with random data in one pass is quite enough for modern disks.
So we choose our programs to taste and go! Have a good work!
Graduation Safe Removal
Most programs designed to safely delete data support several different methods. They differ in the number of passes to overwrite a file or disk, the nature of the data used when overwriting, or a combination of these two parameters.
This method was first proposed by Peter Gutman and Colin Plum in 1996 to erase information recorded on magnetic tape in the MFM and RLL formats. Combinations of random data and data templates were selected specifically to exclude the possibility of restoring previously recorded information on the tape even using special equipment (which intercepts and analyzes analog signals and, by comparing them with digital, tries to recognize what was previously stored on the medium.
The Gutman and Plum method is often used without taking into account the specifications of modern discs. Users still prefer to perform all 35 passes, whereas even many years ago in most cases, according to the authors of the method themselves, only ten were enough. The number of passes was determined by the type of medium, and most of them were intended for certain coding mechanisms used when recording information on hard disks that time. With increasing recording density, the method ceased to be relevant.
In a study published in 2006 by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, one pass is enough to prevent data recovery on modern hard drives.
At the same time, there are a number of standards defined by government and military organizations around the world, in particular the Australian Radio Defense Administration and the US Department of Defense, which take data security seriously. For reliable erasure of information (apparently, in order to exclude accidents during the destruction of information), the US Department of Defense recommends three passes, and the Australian Radio Defense Authority advises to refuse to overwrite data altogether. From the point of view of safety, the demagnetization procedure is considered correct (for more details, see the section “Demagnetization”), and ideally, the physical destruction of the medium. Naturally, both of these methods are more effective, but they also have an obvious drawback - hDD after performing such operations it becomes unusable.
Erase on Linux
As you would expect, erasing data in the Linux environment is done through free tools, and they are part of any popular Linux distribution.
There are several options, but the simplest of them are the two presented below.
Erasing a single file is done using the shred command, which, like the ones discussed here windows utilities, performs repeated rewriting of the data (the number of repetitions is set by the user) by randomly selected patterns (this includes a number of Gutman sequences). In addition, the file is renamed many times to remove information in the catalog tables, and zeros are written in its place. The shred command may look like this: shred –zvun10 / home / CSO / testfile. The file is deleted, overwritten ten times, and at the end its contents are replaced with zeros. Moreover, all information about the progress of the command is displayed on the screen. By the way, the Shred utility was written by Colin Plum.
Erasing the entire disk is done by the dd command, which has a very long history. This tool supports a variety of modes, ranging from mirroring disks to create snapshots of partitions to low-level reading. You can clear the disk by entering the command: dd if \u003d / dev / urandom of \u003d / dev / sda bs \u003d 1M. The if and of parameters determine the input and output files (in this case we are talking about the whole device), and bs is the block size. Specified command reads random data from the / dev / urandom file and writes it directly to disk until it is full. Another option is to use / dev / zero as the input file. And then the disk will be filled with zeros.
It must be remembered that the corresponding commands should not be entered in the Linux environment for the disk on which the system is recorded. You can boot from a Linux Live CD (for example, from the popular Ubuntu Live CD) and run the command in relation to the Windows drives connected to the computer.
Demagnetization
Of course, the use of software is not the only way to destroy information. To more reliably remove information from media with magnetic properties, it is worth using a magnet.
Moreover, it must be very powerful. During demagnetization, powerful magnets move around the device, creating moving magnetic fields that effectively destroy the data stored on the media. The advantage of demagnetization is that the impact is on the entire surface of the disk, including partition tables, boot sectors, and low-level formatting information. As a result, the disk is put into an inoperable state (since the low-level formatting data has been deleted), and it can only be restored by the manufacturer, but provided that the magnetic pulses did not damage the engine. Commercial demagnetization systems cost from 30 thousand to 140 thousand dollars.
The question remains, will it be possible to demagnetize the disk using a powerful magnet on its own? In most cases, the answer is yes. Magnets made of neodymium, rare earth metal, sold in electronic stores, create very powerful force fields, thousands of times greater than the weight of the magnets themselves. Applying them to a drive is very effective, but, like commercial demagnetization systems, they can render the drive unusable.
Testing methodology
Before each test, a formatted disk was installed on the PC, onto which sample files were copied. For programs that erase individual files and disks as a whole, sectors were marked where the files were located. The computer booted from the Linux Live CD, after which the hdparm command was entered with the --fibmap and --readsector options. This made it possible to find and read sectors of the drive in which the files were physically located.
Then the files or the disk were erased in the Windows environment, the computer was loaded from the Linux disk again, and the sectors were read again. Thus, it was possible to verify that those sectors in which the files were located no longer contain the previous data, or rather, include random or zeroed information.
The duration of the erasing procedure was not measured, since all products are performed at a good level and their performance is limited only by the speed of the input / output subsystem.
Solid State Drive Features
In the past few years, solid state drives (SSDs) are gaining increasing popularity among both corporate and home users. They work quickly, quietly and consume less electricity, however, their inherent design features affect their safety. Unlike traditional spinning plates, NVRAM memory, on the basis of which solid-state drives are built, can withstand a limited number of write cycles. In practice, the service life of SSDs still remains quite decent - long-term studies that accurately calculate the number of recording cycles during the service period have not yet been carried out. In addition, manufacturers use special firmware to extend their life. This technology, called wear leveling, is to evenly distribute recording cycles between all memory cells.
In practice, this means that when overwriting a file using the operating system, the new file is saved in a different place. And even if you “delete” the file from the disk, recovering it will not be difficult. Secure file deletion and free space deletion are not applicable to SSDs for the same reason. The transferred sectors that the operating system sees are not related to the initial physical placement of data in the NAND chip.
Unfortunately, with increased security requirements, this task actually has no solution. The only way is connected with the so-called safe erase mode. All manufacturers support this feature. solid state drives. It consists in restoring the factory state of the device (unless, of course, taking into account the degree of wear and tear) and writing zeros to all cells. In this case, you get everything or nothing, since selective safe erasing of files, folders or partitions, unlike disks with rotating plates by solid-state disks, is not supported.
In addition to the fact that SSDs are notable for the complexity of recording algorithms, many of them have a special memory area, the dimensions of which sometimes reach several gigabytes. It is used by garbage collection procedures or procedures for allocating new sectors in the event of failure of individual cells. This area also contains old data that can be recovered with the necessary tools.
Contrary to popular belief, in fact, the contents of the memory cells are not erased by the TRIM command, and a special flag is set in the cluster drive circuit. It indicates that the cells do not need to perform the full cycle of read / modify / write operations that are usually initiated when information is written to the cell that already contains data. Until these cells are written new information, they will store old data.
Based on all of the above, we can conclude that if security is more important to you than speed, then using solid-state drives will not be the best solution.
If you regularly deal with files containing private, important or secret information, remember (this has already been discussed) that even after deleting these files and cleaning the Recycle Bin, the files themselves can remain on the hard drive for an indefinitely long time. If someone steals your computer or gets access to it, then, having the appropriate programs, it can easily restore these files.
IN operating system Mac OS X Leopard and newer, you can use the Empty Trash Securely Feature: select Finder About Preferences About Advanced to increase security by writing to abracadabra files. You might think that this is a great defense, but as it turned out, data recovery specialists using sophisticated equipment can still recover, at least partially, the original files.
It turns out, it is impossible to delete files absolutely safe? Fortunately, mac computer It has a powerful tool that allows you to repeatedly erase the data of deleted files, so that no one can ever recover them. This tool is called Clear free place"(Erase Free Space), and it should be run from time to time to ensure the reliability of deletion of files containing important data. Here's what to do.
1. If you are using an earlier version of Mac OS X than Lion, insert the installation DVD or flash drive.
2. Restart your Mac while holding down the Option key. The boot menu appears on the screen.
3. On Mac OS X Lion, double-click the “Disk Recovery” icon (Recovery HD). In earlier versions, double-click the installation DVD or flash drive icon and then click the Continue arrow.
4. On Mac OS X Lion, click “ Disk utility"(Disk Utility), and then -" Continue "(Continue). In earlier mac versions OS X select “Utilities” О “Disk Utility”. The Disk Utility application launches.
5. In the list of drives, click Macintosh HD.
6. Click on the “Erase” tab.
7. Click on “Erase Free Space”. The disk utility displays the Erase Free Space Options dialog box.
8. Using the slider, specify how many times you want to overwrite the free space on your hard drive:
- Fast (Fastest) the method is “Zero Out Deleted Files”. Free space is overwritten once. This is the fastest, but also the least secure method, and a sophisticated user after it will be able to recover part of the data.
- "Middle" (Middle) method - “Three-pass Erase of Deleted Files” (3-Pass Erase of Deleted Files). Deletes the deleted files three times. This means that erasing a loss is three times longer than zeroing, but it is more reliable. This method It combines comfort and safety in the best way.
- The Most Secure method - “seven-pass erase of deleted files” (7-Pass Erase of Deleted Files). Free space is overwritten on disk seven times. This means that erasing is performed more than two times slower than with the three-pass method, and is much slower than with zeroing. Most likely, this procedure will take several hours, but will provide the highest reliability of deleting deleted files (necessary, for example, in state organizations).
9. Click on “Erase Free Space”. The disk utility will start cleaning.
To prepare a concrete surface for further use, processing with special grouting tools is necessary. Rubbing the hardener into the cement also does not do without special equipment. When leveling, trowel discs will allow you to get rid of bumps, curvatures and sagging of different sizes. The choice of such discs will depend on the type of grouting technique, as well as the scope of the tools. Components of different diameters (610-1200 millimeters) are on the market.
By trowel discs are meant parts of machines designed to smooth out irregularities on concrete. Tools are available in the form of plates, which are installed on two- or single-rotor equipment. They are necessary for coarse grouting on concrete or when working with industrial cement floors. In addition, various modifications of the tools allow finishing concrete. All discs manufactured by leading manufacturers are able to withstand heavy loads.
Usually, specialists first smooth out the bumps and sag that formed after using the vibrating device with the help of discs, after which they use special blades or knives. They will help give concrete a smooth and shiny finish. Among the advantages of components, experts mention their durability: it can process up to 1500 square meters of surfaces. To extend the life of the drive, there are special fuses on the disk. However, manufacturers do not equip them with all models. For additional smoothing use blades. Such tools are divided by diameter, as well as by the number of fixtures.
Grout disc dimensions
Components are selected depending on the type of equipment. Their sizes are 300-1800 millimeters. In addition, the discs are both completely flat and slightly convex.
Manufacturer's examples and specifications

Conclusion
When carrying out various construction works: pouring screeds, cement floor and pavement, it is necessary to use special grouting equipment. Using such devices, you can achieve a perfectly smooth surface.
Many users, browsing through the numerous menus and settings of the CCleaner application, suddenly stumble upon the “Erasing disks” section. The question naturally arises: erasing cCleaner drives what is it? Moreover, from the menu items themselves, little can be understood. So…
Erase CCleaner drives - what is it?
This mysterious function is located on the "Service" tab, in the "Erase Disks" item. A tooltip at the top of the window gives a meager and uninformative message: "Reliably overwriting all content or free disk space." In fact, this very useful feature, which is likely to be useful to those who want the deleted information to be truly deleted from hard drive a computer.
The fact is that the erased file, even if it passed the Recycle Bin or was deleted from it, for some time still remains recorded on the hard drive. Just the user sees this place as free. However with special utilities you can “stretch” and restore erased files. But this can be done only until the moment when new information is not written over the deleted file. In this case, no utilities will help. CCleaner allows you to repeatedly overwrite a deleted file so that no recovery utility gets to it.
How to Use Erase CCleaner Disks
The following options are available in the drop-down menu:
- only free space. The visible free space is overwritten. Wherein visible files will not be affected. However, previously deleted files are wiped clean;
- whole disk. In this case, absolutely all files on the selected drive are deleted. But this function should not be confused with disk formatting.

Wiping Methods:
- simple dubbing in one pass. For most cases this is quite enough;
- DOD 5220.22-M - three times erasure is assumed for greater reliability;
- NSA - mashing in seven passes;
- finally, the most reliable - Gutmann - in 35 passes.
It is also suggested that you select the drive that you want to erase. At the same time, although the erasing process does not take up a lot of system resources, it can take quite a lot of time, depending on the chosen method, computer power, and disk capacity. And now, knowing about erase CCleaner drives - what is it for the function, you can use it at your own discretion and not be afraid for the secrecy of your data deleted from the computer.
We often talk a lot about information security. We discuss the topic of protection against viruses, trojans. We consider various software and compare it with each other. We use keyloggers, firewalls, we use cryptography and various password systems. But information, no matter how we defend it in such ways, sometimes still leaks into the wrong hands. One way to obtain confidential (and secret) information is to restore it from formatted disks on which this information was previously located.
Many people know that neither reformatting nor formatting of disks provides a complete deletion of information stored on such media. If you understand the reformatting process, it turns out that this process destroys the links to partitions in the disk partition table without affecting the data itself. You can find many programs (once very useful program was Tiramisu), which will help restore seemingly permanently lost data, including after accidentally reformatting the disk.
Not completely destroys data and formatting of storage media, including low-level. Yes, with ordinary programs, after such a procedure, you may not recover information, but there are others that don’t software methods. For example, the use of magnetic microscopy technology. How long? Expensive? Of course. But information sometimes costs significantly more than the time and money spent on its recovery. (This method can even be used for discs whose plates have been subjected to mechanical stress.)
Therefore, in cases where the information should in no case fall into the wrong hands, the storage media should be subjected to the procedure of irreversible deletion and destruction of data. This procedure is called disk cleanup. It is believed that after cleaning the media will no longer be of any interest and even developed technical means will not be able to remove any information from them. Many countries have adopted specific standards that define algorithms for cleaning media. I will give an excerpt from the documentation for the program, which will be discussed below.
- US DoD 5220.22-M - US Department of Defense standard;
- uS Naval Standards NAVSO P-5239-26:
- NAVSO P-5239-26 for RLL-encoded devices;
- NAVSO P-5239-26 for MFM-encoded devices;
- british Standard HMG Infosec No.5;
- german standard VSItR;
- australian ASCI 33;
- russian GOST R 50739-95;
- peter Gutman's algorithm;
- bruce Schneier algorithm;
- paragon algorithm:
- each sector is overwritten with an absolutely random 512-bit string, new for each sector, using CSPRNG (cryptographically secure random number generator);
- each cleared sector is overwritten by its binary complement;
- each sector is overwritten with a 512-bit string (CSPRNG), again completely random, different from the one used in the first pass, and new for each sector;
- each cleaned sector is filled with the value 0xAA. Upon completion of the operation, the resulting data area is checked.
I will not give more detailed description algorithms, users of the Paragon Disk Wiper program will find additional information in its documentation. The program implements almost all of the above algorithms, and it is also possible to determine your own mashing algorithm. The choice of algorithm depends on the version of the program. There are two of them - personal and professional. In the personal one, the Paragon algorithm is implemented, in the professional - ten different algorithms. This is the main difference between the versions.
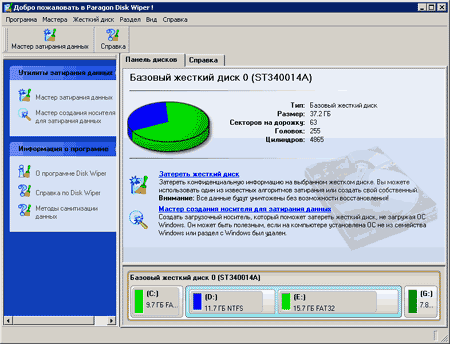
The main features of the program are overwriting the disk, for which the basic version of the program or specially created using it can be used bootable media (CD-ROM, floppy disks) for working in DOS-mode, as well as the implementation of the basic functions for initializing, splitting and formatting disks. The program can work under any windows versions and supports everything file systems. Cleaning can be applied both to hard and floppy disks, and to flash disks.
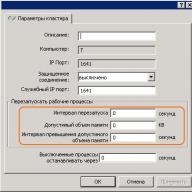
Work with the program is performed through its main window. Its main field is intended for outputting information about physical and logical drives connected to your computer. Their list is located at the bottom of the main window. On the top line are physical disks, on the bottom is their division into logical disks. Both formatted and unformatted partitions are displayed. When you select a physical or logical drive, information about it will be displayed at the top of the main window.
For a physical disk, its type is displayed in the window title, and the size, number of heads, cylinders and sectors are displayed as information. For logical drives, the amount of information displayed is greater. Displays data on the file system, number boot sectors, file system version, disk size, used and free space. Additional Information - Does it logical drive active and visible.
Cleaning can be performed both for a physical disk and for a logical partition. To facilitate the work in the program, special wizards are implemented, which step by step guide the user through all stages of preparation for the task.

Consider the process of preparing to clean the disk (partition). At the first step, you can choose the cleaning option - either wipe the partition completely, or clean only the free space. The second option, perhaps, will be claimed more often - without deleting all the information, you can destroy all deleted information without the possibility of its recovery. To test the work, I would suggest first to use just such an opportunity. The next step suggests choosing the algorithm that will be used for cleaning. The default algorithm can be defined in the program settings. Then it will be proposed as the main one.
In the personal version, only two options are available - either use the Paragon algorithm, or define your own cleaning algorithm. Choosing a standard algorithm, you will be taken to a page where detailed information about the principle of its operation will be displayed and the possibility of some changes will be provided, in particular, you can completely or partially disable verification of the operation performed. You can play with this for test runs, but in real conditions it is better to use the full capabilities of the selected algorithm. On the same page, the estimated time of the operation is determined and displayed.
When choosing the option of assigning your own algorithm, a window will open in which you will need to enter your own characteristics. The user can define up to four data masks, the number of passes for each mask and for a group of masks. To determine the mashing mask, the user will need to specify a two-digit number in hexadecimal form (the default value is "00"). In addition to masks and the number of passes, you can set the algorithm to check for the presence of the remaining data as a percentage of the total number of sectors checked.

By selecting or assigning an algorithm, you can start the work, but the wizard will once again ask for your confirmation - do you really want to complete the task. Who knows, maybe at the last moment you will recall that among the information being cleared there remains what needs to be left. Then you have last opportunity refuse stripping and check again whether the operation can be performed.
The wipe disk wizard can be launched in various ways: through the context menu of a logical or physical disk, through the main window with information about the selected disk (partition), through the main menu or through the toolbar. The difference can only be that when you start the wizard from the main menu in the first step, you will need to select the drive with which you are going to work, but when working through the context menu, it is not necessary.

In the case when you need to destroy data boot partition or destroy data on a disk from which the OS is no longer loaded, you can use another program feature - loading it from a boot disk or diskette. To do this, you will first need to create such a disk. To this end, you can use the Media Creation Wizard to erase data. He will offer to choose the medium - a CD-ROM or a floppy disk, and then either use the standard image of the disk or diskette that comes with the program, or use the image you have emergency disk. If there was any information on the disk, then it will first be destroyed (of course, this applies only to CD / RW disks) and floppy disks.
Now a little about working with disk partitions. As already noted, the program implements the ability to create, delete, format logical partitions, assign and delete partition letters, and check the surface. But there are some limitations when creating partitions. In particular, current version programs cannot create new partitions on dynamic drives. Only hard disks that use the DOS partitioning scheme are supported (in Windows 2000 and XP, such disks are called primary disks). Accordingly, the restrictions imposed by the DOS scheme also apply.
Partitioning is performed using the graphical interface, in which the program initially offers some agreed parameters. Often these values \u200b\u200bsuit the user, but any available values \u200b\u200bcan be changed. After creating a section, it is formatted. The program offers a choice of various options: file systems FAT16 / FAT32, NTFS and HPFS, ReiserFS and Linux Swap v. 2. Then you can assign a drive letter. Similarly, you can perform the reverse operations - delete the letter ("unmount" the disk), delete the partition. These actions are performed both from the disk context menu and from the "Section" submenu of the main program menu. Another feature of the program is to view sectors of partitions or disk.
In conclusion, I would like to note the qualitatively executed interface of the program - it is pleasant and convenient to work with it. Perhaps only one remark. Help about the program opens in the same field of the window, where information about disks and partitions is also displayed, so it will not work at the same time to read the help and perform operations. But the need for this exists only at the initial stage of familiarization, then you will no longer need help.