Self firmware a phone or tablet is a risky activity, especially if the procedure is performed by the user for the first time. As a result of inept actions or software errors, the device may stop turning on, and then you have to look for ways to restore it.
Why a fight could happen
There are several reasons why the firmware is unsuccessful:
- Crash update (the phone was disconnected from the computer, the battery was exhausted).
- Incorrect firmware version.
- User errors during flashing.
Problems after the upgrade can be fixed.
In the worst case, the phone will turn into a "brick", but even from this state Android device is being restored.
Failure after official update
If you used official tools to update Android, then restore the phone after unsuccessful firmware You can use the utility from the manufacturer. Download the necessary software on the company’s website, in the “Support” or “Service” section. In addition, you will need mobile device drivers that must be installed on the computer.
- Connect the phone to the computer.
- Find the section that allows you to perform the recovery and start rolling back the changes made.
Each manufacturer has its own update program, so carefully look at all the items and menus. If you have an LG phone, then in the LG Mobile Support Tool in the "Advanced Features" section, you will see the option "Restore after an update error."
After starting this tool, the utility will download the suitable one from the Internet. android version and return the phone or tablet to a healthy state.
Problems after custom firmware
If Android problems arose after installing custom firmware through Recovery mode, then you can restore the phone by updating it again. If you installed the firmware yourself, then you should already know how to open Recovery mode. It usually starts by simultaneously pressing the power button and volume key.
Navigation by recovery menu carried out by volume keys and power button. If you did an Android backup before unsuccessful firmware, then use the “Backup and restore” item to restore the phone to the previously saved state. If there is no backup:
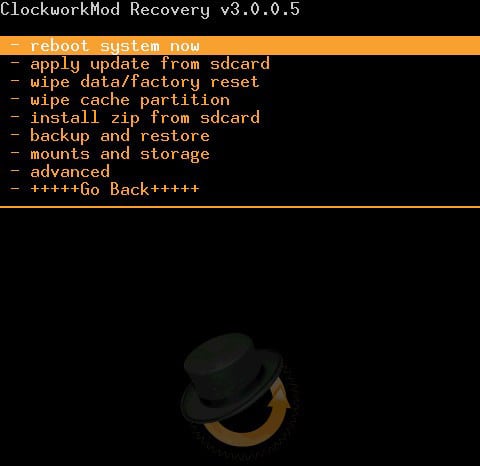
After the installation is complete, the phone should start working correctly. You can install another version of the firmware, if the first one failed, just replace the archive on the SD card and follow the recommendations above.
Firmware reset
If after repeated flashing the phone is working, it is recommended to reset android settings to the factory state. This procedure will correct the errors that occur and return the original version of the operating system:
When resetting, all data from the memory will be deleted, so first move needed files to a computer or other drive. The system will be restored to the factory state, all errors must be corrected.
If your gadget on the Android platform has stopped turning on, it means that you performed some action that led to such problems. Perhaps you installed a conflicting application or a virus program, incorrectly updated the device, received Root rights, or deleted, changed system files. There may be a lot of reasons, and now it’s not so important for us why it happened. In this article, we will solve the problem of not turning on the mobile gadget on the Android operating system using the new firmware.
Solution
If everything is fine with the bootloader, there is nothing complicated in solving the problem. But first you need to make sure that this is so. Click on “Power” and watch the reaction of the screen. If everything is in order with the bootloader, you will see an exclamation mark, Android or a lying robot on the screen. If there is a reaction, it’s all about the operating system, which means that new firmware will solve the problem.If you don’t see anything on the screen, connect your smartphone or tablet to the computer and press “Power” or the combination of Power + volume control button (decrease). The computer should see that the mobile gadget is connecting to it. In this case, there is also a chance to update the software.
Recovery using the manufacturer's program
The easiest way to restore a device that does not turn on is to download the utility for installing drivers and updating the OS on the manufacturer’s official website. Not for all models of smartphones and tablets, this option is suitable. But if your device is manufactured by LG, do the following:
If custom Recovery CWM is installed
There is another opportunity to update the software for the "dead" Android. But in order to use it, you must have access to Recovery. To open the special mode, press the “Power” and “Volume -” keys simultaneously.If Recovery started on the device, do the following:

Via custom Windows application for firmware
You can use the unofficial program. Follow the instructions to install the software.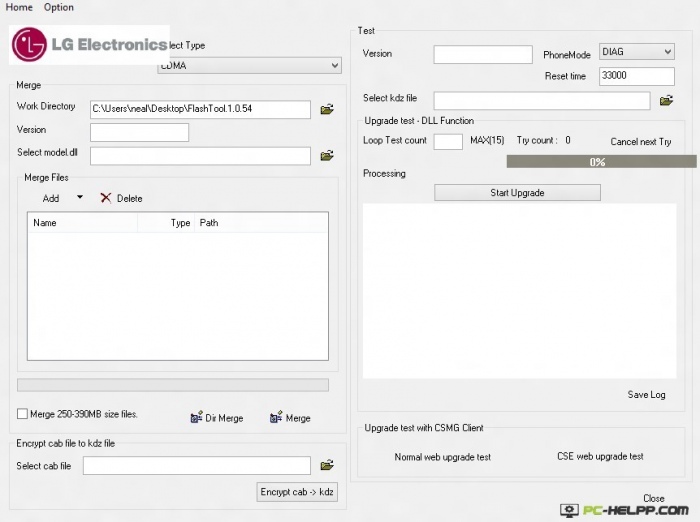
Execution steps
- Download the program (flasher) to the PC.
- Download the firmware for the device.
- Connect the device to the PC and click “Power” + “Vol -”.
- Select a file with Android using the utility and install.
Many users are looking forward to when manufacturers release a new firmware update for their Android smartphone. As a rule, bugs are fixed in them. previous versions OS, new features are added and overall work is optimized. But what if, after the update, the phone began to work worse than it originally worked? Let's consider in more detail why and how to restore the phone after an unsuccessful Android firmware.
Self-firmware Android device is always a risky event, the consequences of which are borne by the user himself. Unless, of course, we are talking about installing a standard official update by air or using a proprietary program on a computer. In this case, the responsibility for the consequences of the update lies with the developer, so you can safely contact the service center under warranty. But before you panic and everyone possible ways To try to restore the original firmware, you need to understand whether the failure really occurred. There are several main reasons that can lead to failure during a flashing:
- Emergency interruption (the phone was disconnected from the computer, the smartphone’s battery was exhausted, etc.)
- Unsuitable OS version.
- Incorrect settings, user errors.
Any of the above problems can cause malfunctioning mobile device, constant system crashes, etc. In the event that the phone does not turn on or starts to work worse than before installing the update, you need to proceed with active recovery actions.
How to roll back firmware
If the update fails, the question arises, how to return the old OS? Depending on whether you used the official or custom version of the firmware, the recovery options will be different. We consider both cases in more detail.
Failure caused by official developer firmware installation
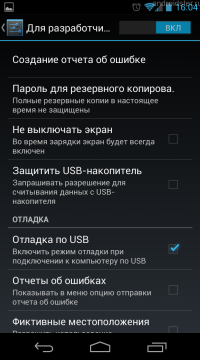
Enable USB debugging
![]()
Settings menu
This does not happen often, but in some situations, the phone may not work correctly when installing the official update. To roll back and restore the factory version of the mobile phone’s operating system in this case is quite simple. To do this, the user will need a computer with installed drivers on mobile device and special program. Depending on the manufacturer of your smartphone or tablet, the required utility must be downloaded from the official website of the developer. Further steps for installing native firmware can be written in two points:
- Connect the mobile device to a desktop computer or laptop via a USB cable.
- Run the program, find the recovery section in it and start the rollback of the changes made.
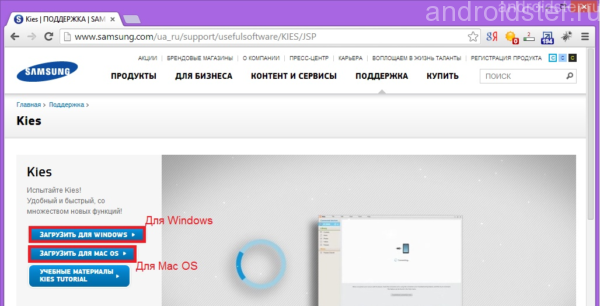
Website with samsung program Kies
After that, the program will automatically search and install the required OS version and return the mobile to original condition.
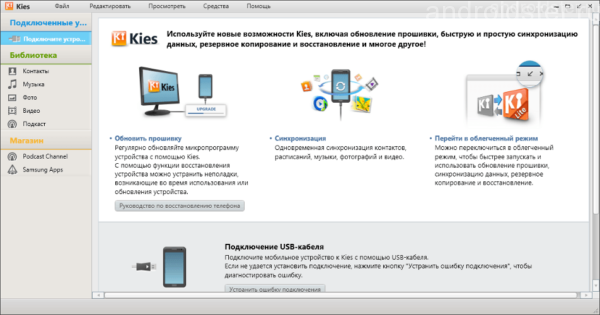
The program interface on the computer
Failure caused by installing custom (custom) firmware
In this case, a second update from Recovery mode will help. In order to enter recovery mode, turn off the mobile device and simultaneously hold down the key combination. In most cases, these are buttons: power + volume down.
Management in the Recovery menu is carried out with the same keys: volume and power on. In the event that you made a backup of the system before flashing, then just select the “Backup and restore” item. If backup was not done, then the recovery procedure will take a little longer. You must complete the following steps:
- Reset all settings by selecting “wipe data / factory reset”.
- Format the cache partition by clicking on the “wipe cache partition”.
- Try reinstalling the firmware by selecting “install zip from sdcard” and clicking on the file with the previously created archive on the memory card.
After that, the phone should work fine. You can also try to download and install in a similar way a different version of the OS. For more information on how to roll back the newly installed firmware, see the training video below.
How to return factory firmware?
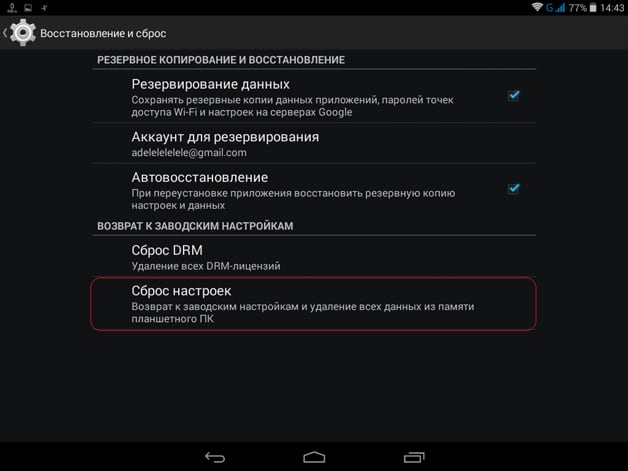
If you want to return the factory version of the OS, correcting the accumulated system errors, then you can do this directly from the menu of the main settings of the smartphone. This will require:
- Turn on the mobile device, go to the main settings (through the application menu or by clicking on the hexagon icon in the upper right corner when lowering the curtain).
- Find the “restore and reset” tab, and then click on “reset settings” ( Hard reset) and agree to the necessary conditions.
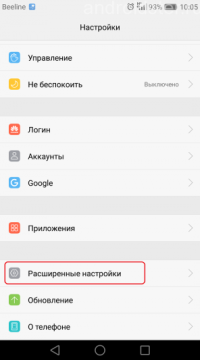
Settings menu
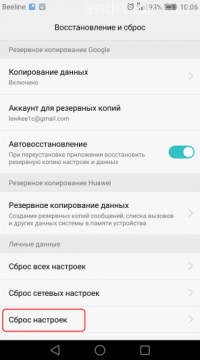
Reset to factory settings
After successfully completing this operation, your phone or tablet will return to the OS factory settings. We recommend that before resetting, backing up important data, or saving it to a separate medium, as it will be deleted from memory.
In the training video, presented below, the procedure for resetting a mobile gadget running on Android OS bases to the factory ones is described.
Most of the articles in the X-Mobile rubric are devoted to hacks and tweaks that require root privileges, firmware modifications, or their replacement with custom ones. However, not every reader is ready to expose their smartphone to such operations, fearing that they can turn the device into a brick or lead to instability in work. Today I will debunk these myths and show that even in the most stalemate situation, bringing a smartphone back to life is not so difficult.
Destroying Myths
Let's talk about what it is all about “turning a smartphone into a brick” and what other pitfalls a user can wait on the way to change the system and install custom firmware. What kind of glitches can I catch at the same time, and is it possible to kill a smartphone by reflashing it incorrectly? Will you lose the guarantee forever or can the smartphone be returned to its previous state? Can custom firmware really let the smartphone owner in the most inopportune moment and are they worth it?
Myth 1. Incorrect flashing can kill a smartphone
A smartphone can be killed by falling from the fifth floor, but not a flashing. The main problem that anyone who wants to reflash a smartphone faces is that a failure may occur during the installation of the firmware, which will lead to its inoperability, and the smartphone will actually turn into a brick.
All this is true, but only on paper. To understand why, it’s enough to understand how the process of flashing the smartphone works and what system components are used. To be able to install third-party firmware on your smartphone, you need to unlock the bootloader (not in all cases), get root, and install a custom recovery console (ClockworkMod or TWRP) that can install firmware with any digital signature.
The recovery console is stored in a separate section of the internal NAND memory and is in no way associated with the installed operating system. After installing a modified version of the console, it will be possible to flash custom firmware or even another OS (Firefox OS, for example). If a failure occurs during the installation of the firmware, the smartphone will not be able to download it, however, the recovery console will remain in place, and all that needs to be done is to boot into recovery again and reinstall the firmware.
In addition, any custom recovery console contains a backup / restore function that allows you to do backup main firmware and restore it unchanged (with all applications, settings and data) in the event that something goes wrong. In fact, the smartphone can be returned to its original state.
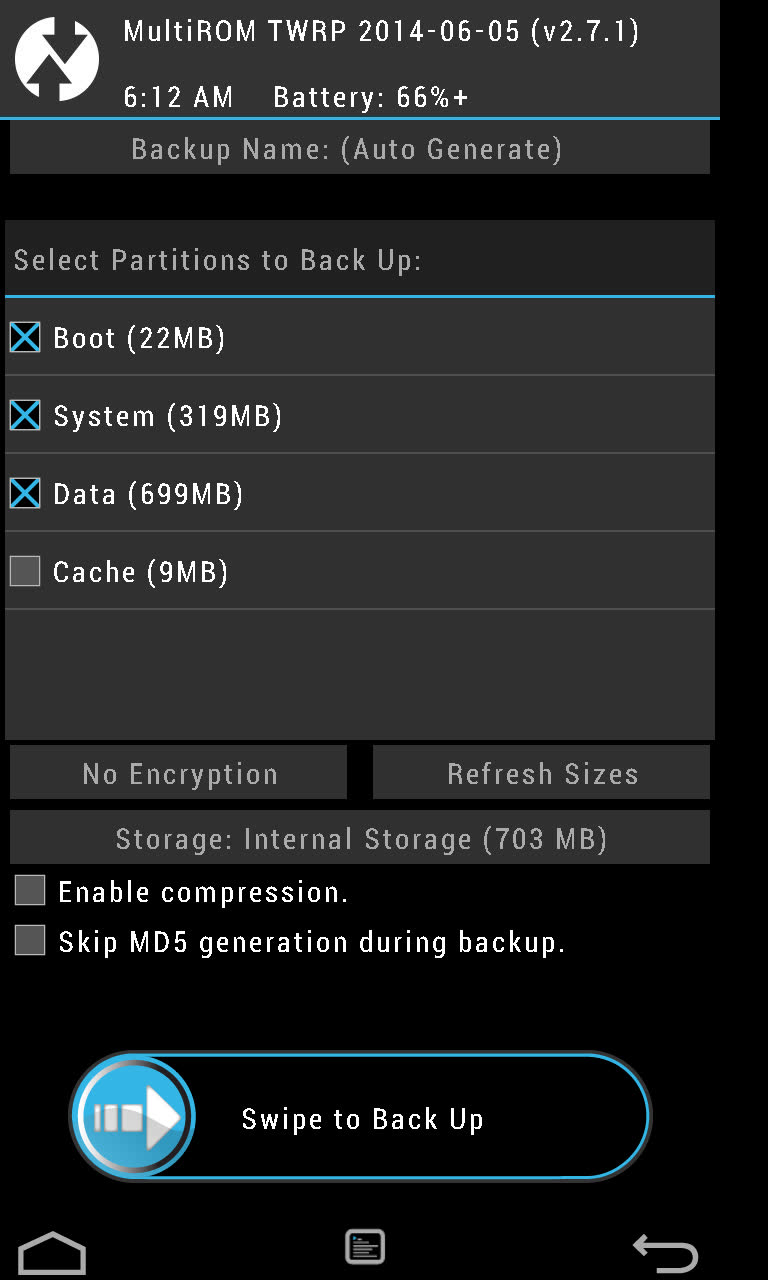
You may ask: what will happen if a failure occurs during the installation of the recovery console itself? Nothing, in this case the opposite situation will turn out, when the operating system itself will remain in place, and the console will be lost. To deal with it, just re-flash recovery directly from Android.
Hypothetically, one can imagine a situation where both the firmware and the recovery console will be killed (although this is rather difficult to do), but even in this case, the primary bootloader will always remain in place, stitched into the permanent memory of the smartphone.
Conclusion: it is impossible to kill a smartphone by installing third-party firmware through a custom recovery console. Either recovery or the primary bootloader will always remain in place.
Myth 2. Custom firmware is unreliable
Firmware firmware is different. On the expanses of the World Wide Web, you can find a huge number of Android assemblies for every taste and color, and most of them are really slag, which can lead to instabilities in the smartphone and loss of functionality. Therefore, the first thing to remember is that you should only deal with serious custom firmware developed by large teams of experienced developers. First of all, these are CyanogenMod, Paranoid Android, AOKP, OmniROM and MIUI.
The second one. There are two types of firmware: officially supported and ported by third-party developers. The same CyanogenMod, for example, has the official version for the Nexus 4 smartphone, but does not have one for Motorola Defy. But for Defy there is an unofficial port of CyanogenMod 11 from the developer with the nickname Quarx. Their difference lies in the fact that the CyanogenMod team is responsible for the support and proper operation of the first, while the second is for Quarx personally. Official firmware versions are usually usually fully functional, but the correctness of the second depends on a third-party developer.
Well, the third. There are stable and developing firmware versions. Stable versions of CyanogenMod have an M index (CyanogenMod 11.0 M7, for example). This version of the firmware usually does not contain bugs. Developed versions (in the case of CyanogenMod it is daily nightly builds) may contain errors, and therefore are not recommended for everyday use.
Conclusion: if you install a stable official version of “normal” firmware on your smartphone, the risk of encountering bugs is minimal. Everything else is for experimenters.
Myth 3. Software that requires root privileges can turn a smartphone on.
In theory, an application with root privileges can do anything with the smartphone’s firmware, including erasing it completely. Therefore, with such software you must be extremely careful. The software that we talk about on the pages of the magazine is completely safe and tested on its own skin. In addition, for the entire time using smartphones on Android (and this is starting from version 1.5), I never I have not encountered a situation where root-based software would kill a smartphone.
Software distributed through Google play, usually completely corresponds to the declared characteristics, and if he led to a brick or left a backdoor in the bowels of a smartphone, he would not have lasted a week. In any case, here you need to follow the rule “trust, but verify” and carefully read the instructions for using root-applications.
Myth 4. Root rights make a smartphone vulnerable to viruses
The smartphone is vulnerable to viruses not by root privileges, but by the bugs used to receive them. Rooting tools and viruses can use the same Android vulnerabilities to gain root privileges, so the fact of having root on the device does not change anything. A competently written virus will not request rights standard wayBy betraying his presence, he will instead take advantage of the same vulnerability to get them covertly.
Moreover, having root, you get the opportunity to install the latest version of Android (in the form of custom firmware), in which these bugs are already fixed. Also, do not forget that most custom firmware allows you to disable root or create white lists of applications that can use these rights.
Myth 5. A rooted smartphone may fail
The software designed to get root does four simple things: it launches an exploit that allows you to obtain root privileges in the system, mounts the / system partition in write mode, copies the su binary required for obtaining root privileges to the / system / xbin directory, and installs the SuperSU or SuperUser application, which will receive control whenever an application asks for root privileges using su.
None of these steps can lead to a crash or kill a smartphone. The only thing that can happen is that the exploit will cause a segmentation error and the smartphone will go into reboot, after which it will continue to work normally.
Myth 6. Having received root and installing custom firmware, I will lose the guarantee.
The warranty is lost not from the very fact of getting root, but because of its discovery by the service center. Most devices can be removed from root privileges using the Universal Unroot application or by reinstalling the stock firmware using the official application from the manufacturer.
There are, however, two exceptions to this rule. The first is the Knox system, pre-installed on new smartphones and samsung tabletssuch as Galaxy S4, S5, Note 3 and Note 10.1. Knox provides enhanced Android security by responding to any firmware modifications and installing third-party kernels and firmware. In the event that the user performs these actions, the system sets a trigger that confirms the fact of modification. The trigger is implemented in hardware (eFuse chip), so resetting it to its original position will not work. On the other hand, it is not clear whether the service center will refuse to repair the device on this basis. Second: the eFuse chip is also installed on some other devices (for example, smartphones from LG), and it also allows you to accurately determine whether the smartphone was rutted or reflash.
If we talk about custom firmware, everything is more complicated. Usually, a flashing operation requires unlocking the bootloader, and this can be done either using special exploits or using the web service of the smartphone manufacturer. In any case, the unlocked bootloader will accurately indicate that the smartphone did not belong to the blonde.
On some smartphones, it is possible to lock the bootloader back, but you should learn about this separately, and also keep in mind that a newly locked bootloader will most likely receive the status of Re-locked, not Locked, as it was originally (this happens on HTC smartphones, eg). The exception is only smartphones and tablets of the Nexus line, the bootloader of which can be locked and unlocked in three clicks without dancing with a tambourine, and no one will find fault with anything.
INFO
On Linux, ADB and Fastboot can be installed separately from the Android SDK. On Ubuntu: sudo apt-get install android-tools-fastboot. In Fedora: sudo yum install android-tools.
To prevent Knox from interfering with root applications, it can be disabled using the following command from the terminal: su pm disable com.sec.knox.seandroid.
conclusions
Obtaining root and flashing the smartphone are absolutely safe operations that can not brick the smartphone for purely technical reasons. The only exception is trying to hack bootloader in order to unlock it. In this case, the eFuse chip may work (if there is one in the smartphone) and block the ability to turn on the smartphone.
Fortunately, today, smartphone manufacturers either choose not to block the ability to turn on a smartphone with a hacked bootloader (by setting a trigger that indicates the fact of an action such as Knox does), or they implement a special web service that allows you to safely unlock the bootloader with a loss of warranty on your smartphone, which eliminates the need for users to risk breaking the bootloader.
Problems that may occur during flashing
So, now let's talk about what problems can arise when getting root and flashing and how to deal with them.
Scenario one: after a failed flashing, the smartphone stopped loading
Unsuccessful flashing can be caused by several factors: the battery is dead, and the firmware is only half full, the firmware was unsuccessful or intended for another model of smartphone. In the end, the smartphone simply did not have enough space that could happen when trying to install the latest version of Android on a smartphone three to four years ago.
Outwardly, all these problems usually manifest themselves either in the endless reset of the smartphone to the initial logo of the manufacturer, or in the so-called boot-loop, when the loading animation spins on the screen for more than five to ten minutes. There may be problems with the screen (colorful ripples) and a broken touch screen, which also impede the use of the smartphone.
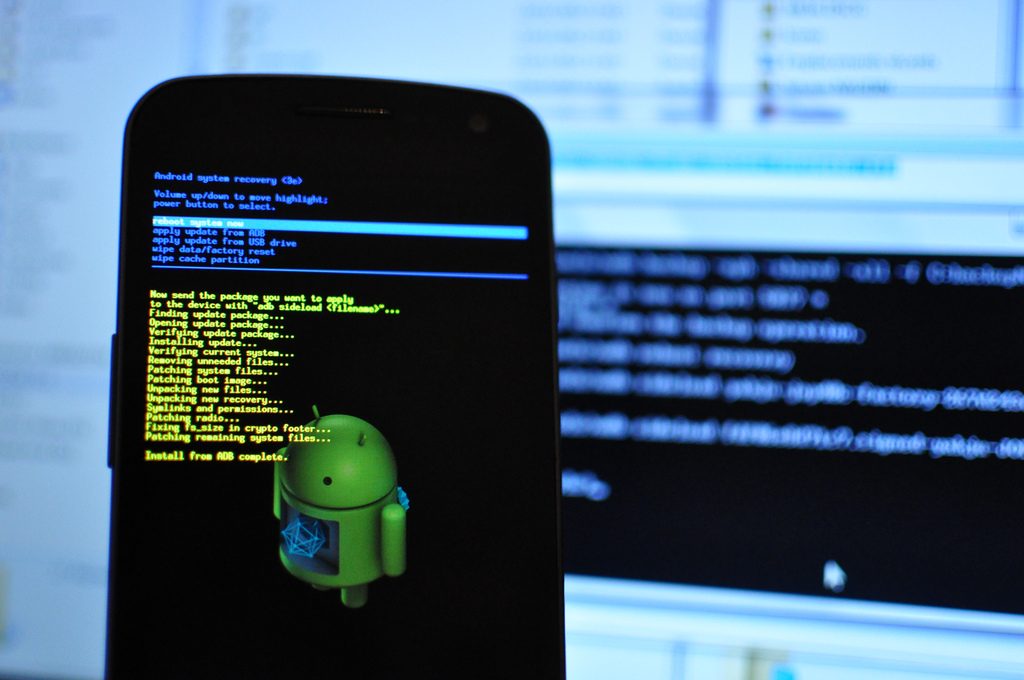
In all these cases, it’s enough to do one simple thing: turn off the smartphone by long pressing the power button, then turn on the volume down button while holding down (some smartphones use a different combination), and after getting into recovery, reinstall the firmware (Install zip from sdcard - \u003e Chooze zip from sdcard) or restore a backup (Backup and restore -\u003e Restore). Everything is easy and simple.
Scenario two: firmware works, but recovery is not available
This can happen after an unsuccessful installation or upgrade of the recovery console. The problem is that after rebooting the smartphone and turning it on with the volume down button held down, a black screen appears, after which the smartphone either resets or hangs.
Solving this problem is not easy, but very simple. You can install the recovery console on the vast majority of smartphones using the TWRP Manager, ROM Manager or ROM Installer applications. They themselves determine the model of the smartphone, download and flash the desired recovery, without requiring a reboot. If, with their help, it is not possible to restore the console, just find the instructions on the Web for install recovery on your device.
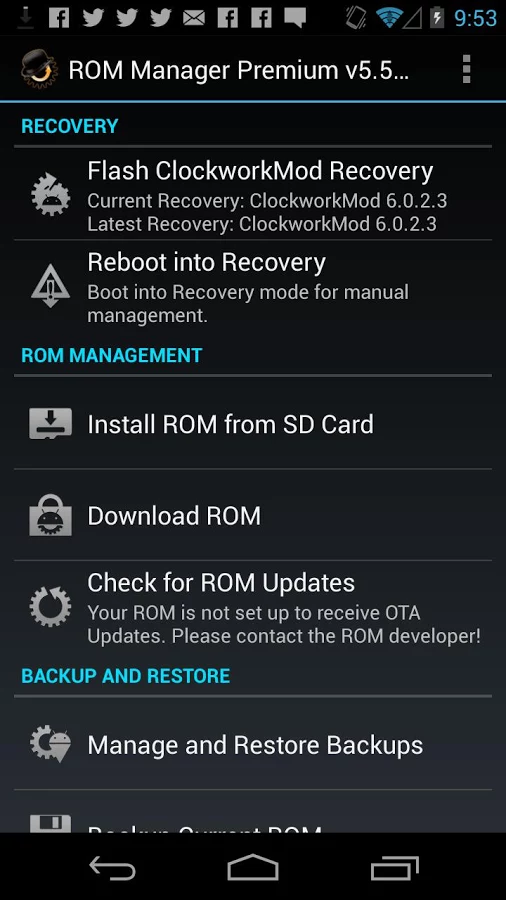
Scenario three: neither firmware nor recovery is available
Honestly, it’s hard for me to imagine such a scenario, but, as practice confirms, it is quite real. There are two ways to get out of this situation: use fastboot to upload recovery to your smartphone or use the tool from the manufacturer to install the stock firmware. We will consider the second method in more detail in the next section, but I will talk about fastboot here.
Fastboot is a tool that works directly with the primary bootloader of the device and allows uploading firmware, recovery and unlocking the bootloader to the smartphone (in devices of the Nexus line). Fastboot support is available in many smartphones and tablets, but some manufacturers block the possibility of its use. So you have to consult about its availability with the Internet.
To access fastboot, you will need drivers and an Android SDK. When they are installed, open command line, go to the SDK installation directory, then to the platform-tools directory, turn off the smartphone, turn it on with the volume buttons held down (both) and connect it using the USB cable to the PC. Next you need to find recovery image in the .img format for your device and execute the command:
$ fastboot flash recovery image.img
Or even make the smartphone boot recovery without actually installing it:
$ fastboot boot image.img
In the same way, you can flash official firmware update:
$ fastboot update update file.zip
You can find a recovery suitable for your device either on the TWRP website or in the XDA-Developers and w3bsit3-dns.com forums.
Returning the smartphone to its original state
In this section, I will talk about ways to return a smartphone to a clean drain, no matter what condition it is in. These instructions can be used both for scraping the smartphone, and to remove traces of rooting and flashing. Unfortunately, I can’t talk about all the possible models, so I will focus on the four most popular flagships: Nexus 5 (this instance I call the control), Galaxy S5, LG G2 and Sony Xperia Z2.
Nexus 5 and other google phones
Returning Nexus devices to their original state is easier than any other smartphone or tablet. In fact, it is so simple that there’s nothing to talk about. In fact, all that needs to be done is to install the ADB / fastboot drivers (even they are not needed on Linux), download the archive with the firmware and run the script. Step by step the whole operation looks like this:
- from here.
- Download and install the Android SDK.
- Download the archive with firmware for the desired device from the Google site.
- Turn off the device, turn it on with the volume buttons held down (both) and connect using a USB cable.
- Unpack the archive with firmware and run the flash-all.bat (Windows) or flash-all.sh (Linux) script and wait for the operation to complete.
- We launch the command line, go to the directory with the Android SDK, then platfrom-tools and execute the fastboot oem lock command to lock the bootloader.
For those who are interested in what the script does, here is a list of commands:
Fastboot flash bootloader bootloader-NAME-DEVICE-VERSION.img fastboot reboot-bootloader fastboot flash radio radio-NAME-DEVICE-VERSION.img fastboot reboot-bootloader fastboot flash system system.img fastboot reboot-bootloader fastboot flash userdata userdata recovery recovery.img fastboot flash boot boot.img fastboot erase cache fastboot flash cache cache.img
Galaxy S5
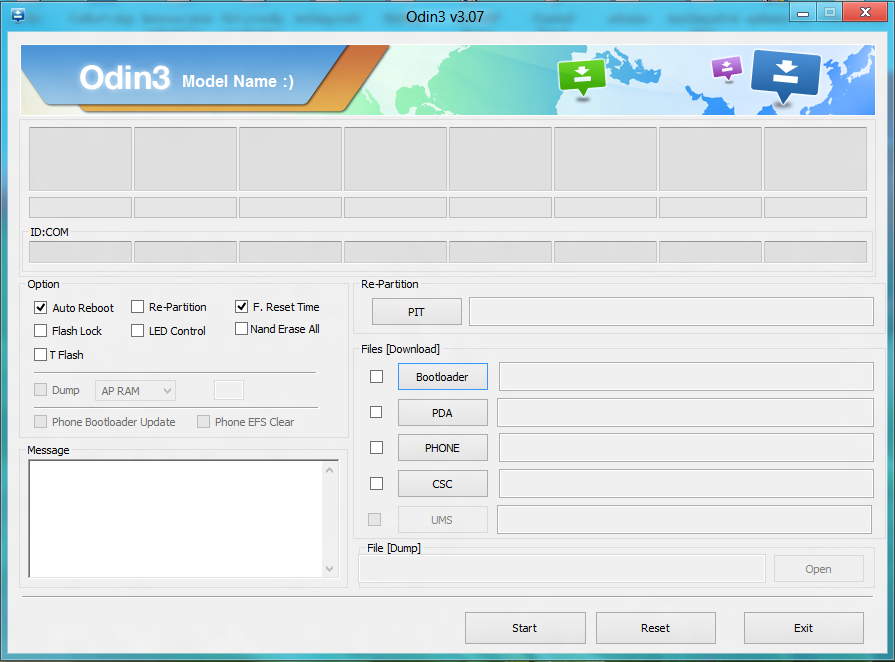
With galaxy smartphone S5 is a bit more complicated, but overall quite simple. This time, you will need the Samsung application Odin, with which the smartphone will be flashed. Sequencing:
- Download and install latest version Samsung USB drivers from here.
- Download and install the latest version of Odin from here.
- We go to samfirmware.com, enter the search model SM-G900F, find the firmware marked Russia, download and unpack.
- Turn off the smartphone and turn on with the volume down and Home buttons held down, wait five seconds until a warning message appears.
- Press the volume up button to put the smartphone in Odin mode.
- We connect the smartphone using a USB cable.
- Launch Odin, press the PDA button and select the file with the extension tar.md5 inside the directory with the unpacked firmware.
- Press the Start button in Odin and wait until the firmware process is completed.
As I said, this operation will return the smartphone to its original state, but will not reset the trigger, installed by system Knox (if it was in standard firmware). Therefore, the service center may refuse to repair.
LG G2
Restoring the LG G2 to its factory state will also not cause any special problems. The number of steps in this process is somewhat larger, but by themselves they do not require special training and knowledge. So what to do to return the factory firmware to G2:
- Download and install the ADB Driver Installer from here.
- Download the official firmware (Europe Open 32G or Europe Open) from here.
- Download and install LG Mobile Support Tool, as well as FlashTool (goo.gl/NE26IQ).
- Turn off the smartphone, hold down the volume up button and insert the USB cable.
- We expand the FlashTool archive and run the UpTestEX.exe file.
- In the window that opens, select Select Type -\u003e 3GQCT, Phone Mode -\u003e DIAG, in the Select KDZ file option, select the firmware downloaded in the second step.
- Click the CSE Flash button at the bottom of the screen.
- In the window that opens, click Start.
- In the next window, select the country and language and click Ok.
- We are waiting for the firmware to finish, and then turn the smartphone off and on.
It's all. But keep in mind that, as in the case of Samsung, the smartphone will still have the status of Rooted, and this can not be fixed.
Sony Xperia Z2
Now about how to return to factory state smartphone Sony Xperia Z2. As in the previous two cases, this will require stock firmware and the official firmware utility. You run the utility on the PC, connect the smartphone with a USB cable and start the update process. Step by step it all looks like this:
- Download and install the ADB Driver Installer from here.
- We reset the smartphone to the factory settings.
- Download and install the Flash Tool from the official Sony website and the latest firmware from here.
- Copy the firmware file to the C: / Flashtool / Firmwares directory.
- Turn off the smartphone and turn on the volume down and Home keys with the keys held down.
- We connect the smartphone to the PC using the USB cable and run the Flash Tool.
- Press the button with the lightning icon in the Flash Tool. In the window that opens, select Flashmode, double-click on the firmware in the list that opens.
WARNING
In many smartphones, an unlocked bootloader will not allow an update by air.
In 90% of cases, unlocking the bootloader will entail the deletion of all data from the smartphone, including the memory card.
conclusions
Smartphone firmware, and even more so getting root access, are not at all as scary and dangerous operations as they might seem at first glance. If you do everything right and do not resort to tools that unlock the smartphone bootloader bypassing the manufacturer’s tools, you won’t be able to brick the smartphone. Yes, in some cases it will be necessary to tinker to get everything back in place, but what is better - to use a locked smartphone, which does not allow to do half of the things that it is capable of, or get full control over the device? Finally, reinstalling windows nobody scares anyone on a PC.
Today we will learn how to restore the phone after unsuccessful firmware. This does not require much time, just downloading the necessary software and a few additional steps.
Restoring with official support
If you tried to update Android using the official firmware, then utilities from the manufacturer will help in the recovery.
- look at the company's website, download drivers and other software there
- connect the computer to the phone
- restore the device to its original state
In the software of each company, a certain section is responsible for this, but it is usually not difficult to find it.
Enable Recovery
If you tried to install third-party firmware on the device, then at best it will be possible to restore the system by resetting the settings. It can be started by simultaneously pressing the volume and power buttons. Combinations may vary on different devices. Select the line “wipe data”, then start zeroing the contents of the device. You can try to install operating system again, select "choose zip from sdcard" for this. We find the archive with the firmware, start the installation process on a new one. It is better to use a different version, as the old version can lead to the same problems.
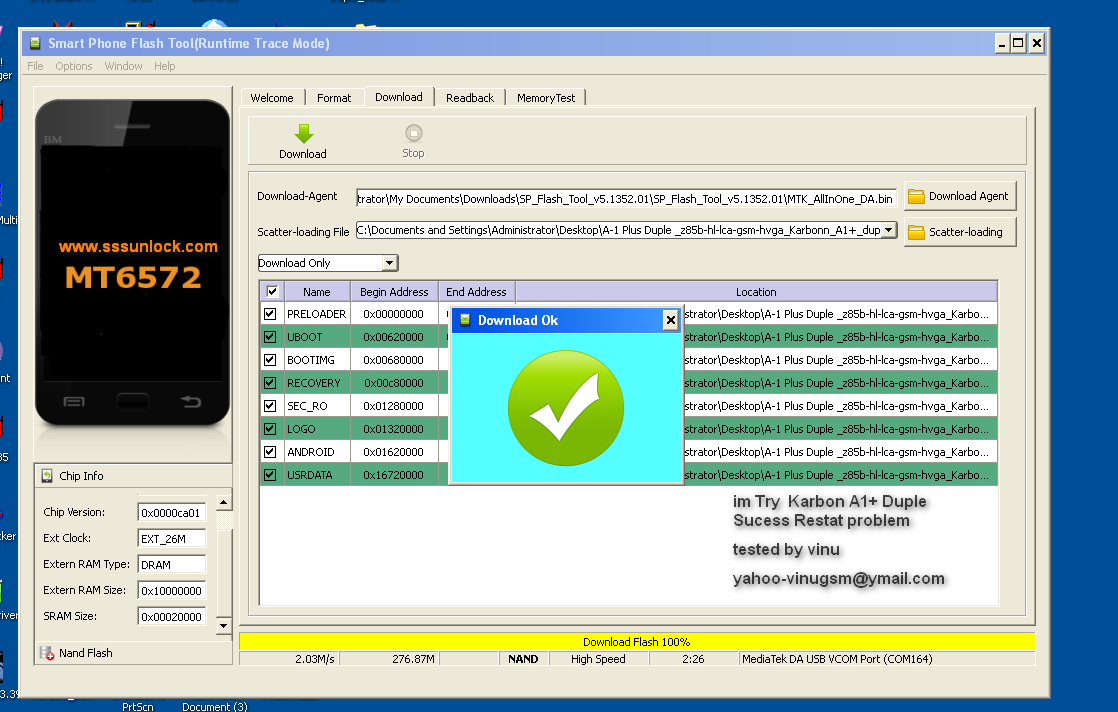
Using the Flash Tool
This program will help you in all those cases when you need to return the mobile device to its original state. The method is applicable on almost all smartphones. First download and install the ADB Driver Installer. Copy the firmware file to the Firmwares folder located in the Flashtool directory. We take the device and connect to the PC using the USB cable. Now press the button with the lightning icon in the Flash Tool, and then select the device firmware in the program.
Note that in cases where root is installed on your smartphone, installing the official firmware will be problematic, usually such actions will lead to crashes.
In addition to video from detailed instructions on the "rollback" of the firmware.