Linux is an operating system created by Linus Torvalds. There are a lot of Linux users today, but there are also many who know little about this operating system. There are those who tried to work in Linux, but were not used to this OS. In this case, it is useful to learn how to remove Linux. Now we will describe to you several options for removing this OS.
How to remove Linux? Before deleting, you should keep in mind that not only the operating system will be deleted, but also information from hard drive, so first you need to save the necessary data on other media. After that, we begin the process of uninstalling Linux.
Turn off the Swap and Native segments. To do this, use the integrated Fdisk program. To boot the computer, use the installation diskette or the Linux disk. At the command line, type Fdisk and press Enter. Then, to get information about any of the sections, enter "p" and press Enter. To turn off the segments there, type "d" and press Enter again. After this action, a window will appear asking you to delete the partition. To delete, enter 1, etc. Thus, delete all segments in this operating system. At the command line, enter "w" and Enter. The computer will give an error. Do not attach any importance to this. You need to do work with the command line. To do this, type "q" and press Enter.
There is another method that tells you how to remove Linux from your computer. This method is suitable for you if you want to install Windows. Install from boot windows drive and proceed to install this operating system. During the installation process, you will see information about the disk segments that are there, indicating their types. Then you will need to continue the installation, following the instructions of the program- windows installation. To delete the main boot record, it is possible to execute the fdisk / mbr command after booting from a floppy disk or Windows disk, which will make it possible to return the main boot record to the disk windows record. If you figured this out, then easily answer the question of how to remove Linux from your laptop, because the procedure is the same.
Linux Mint
How to remove Linux Mint? You can turn off segments using the Fdisk program. Remove the Linux native, swap, and boot partition. Boot the device from a floppy disk. Type fdisk on the command line. Press the Enter button. For information about segments, type “p” at the command line, then press Enter. At the top are information about the main partition of the hard drive. Type “d” at the command line. Press the Enter button. A window appears in which you need to specify the number of the section to be deleted.
Linux Ubuntu
How to remove Linux Ubuntu? If the user wants to remove Ubuntu, it is necessary to format the partition of the disk on which the operating system is installed. After that, you need to install the boot of the user computer from the drive in the BIOS. As part of the Microsoft OS installation, you need to take the terms of the agreement, then click on the “Next” button, find the installation section that covers the previously installed Ubuntu operating system, you need to format it (it's better to do this in file format nTFS systems) Here's how to remove Linux, then, if you wish, you can install another OS, for example, Windows.
Using the Ubuntu distribution example. In this article, we will consider the reverse process, which sooner or later will have to be resorted to by those users whom Linux did not like. How to remove Linux installed on the same Windows computer? How to return windows bootloader?
To completely get rid of Linux, you need to restore the Windows bootloader, delete the Linux files and solve the problem with further fate disk space, which was reserved for the installation of this operating system (the swap section and the section with the files of Linux itself). Below we’ll look at 3 ways to remove Linux and return the Windows boot loader. Two of them are methods for computers based on the regular BIOS; they will differ in the tools used. The third way is to remove the Linux bootloader from the boot list of computers with the UEFI BIOS. All the operations described below are carried out inside Windows.
1. Bootice Utility and Windows Disk Management
For the first method of uninstalling Linux and restoring the Windows boot loader, you will need two utilities - a third-party free Bootice and a regular diskmgmt.msc (disk management).
1.1. Recovering Windows Bootloader with Bootice
First of all, download the Bootice utility from its official website. For computers based on the regular BIOS, the 32- or 64-bit edition of the utility does not matter. After unpacking Bootice, run it. On the first tab, select from the drop-down list the desired hDDif there are several connected. And press the button "Process MBR".
In the window that appears for Windows 7, 8.1 and 10, select the option “Windows NT 6.x MBR”. In the case of Windows XP, you need to choose the option above - “Windows NT 5.x MBR”. Next, click the "Install / Config" button.
We confirm.
Windows bootloader restored.
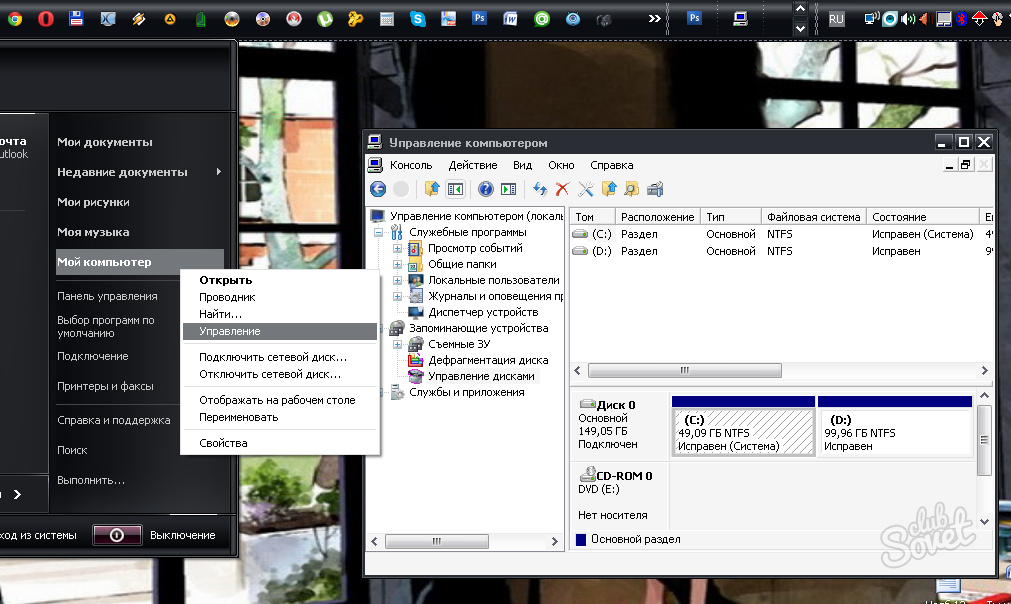
1.2. Removing Linux Partitions in Windows Disk Management
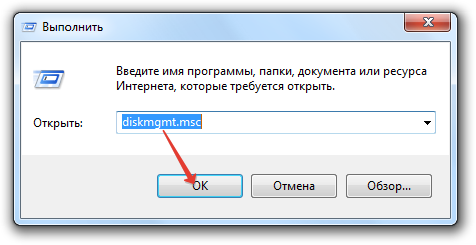
After restoring the Windows boot loader, we go to the standard disk management utility. We press the Win + R keys and enter its name:
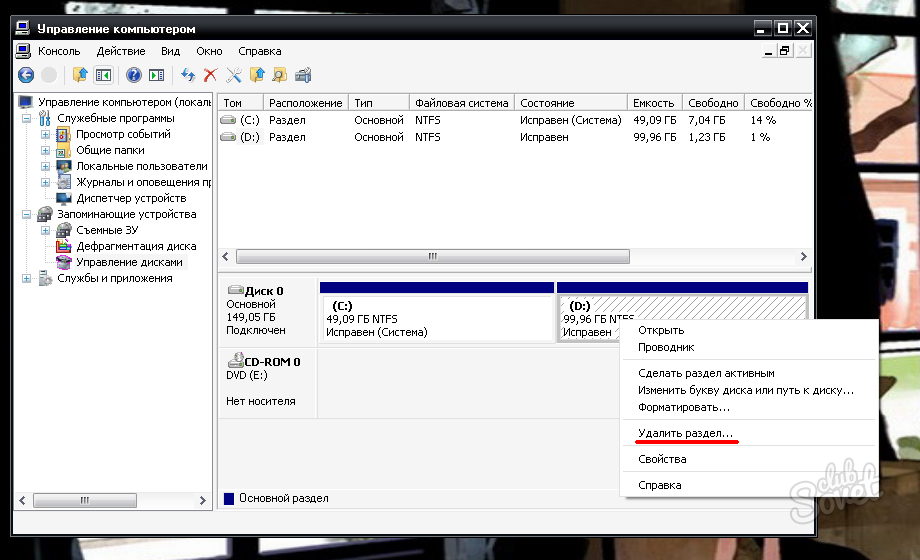
In the utility window, delete two Linux partitions - specially prepared before installing it manually or automatically created by this system. In the latter case, as a rule, the Linux partitions on the hard drive are located immediately behind the Windows system partition. Not understanding the Linux file system, its partitions the Windows operating system does not give letters, and, accordingly, they can not be displayed in Explorer. But in any case, it is better to focus on these signs, and on the size of the Linux partitions. To delete Linux partitions on each of them, you need to call the context menu and select "Delete volume".
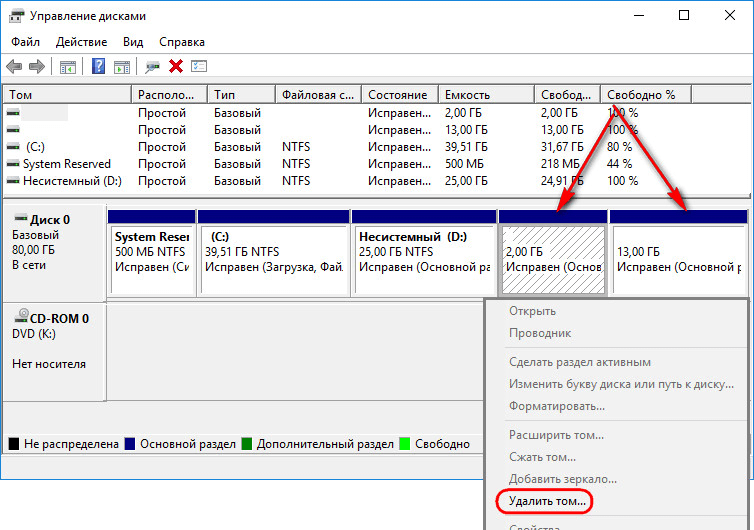
The free disk space can then be created here in the disk management utility into a partition or several partitions acceptable for Windows (in the NTFS file system format). Details on creating simple partitions using regular windows tools can be read in.
2. AOMEI Partition Assistant program
An alternative way to get rid of Linux and return the Windows boot loader for users of computers based on the regular BIOS can offer a functional program for working with disk space AOMEI Partition Assistant. All the necessary tools for these purposes are available in the free edition of the Standard Edition program. In the AOMEI Partition Assistant window on the side toolbar, in the "Disk Operations" section, select "MBR Recovery".
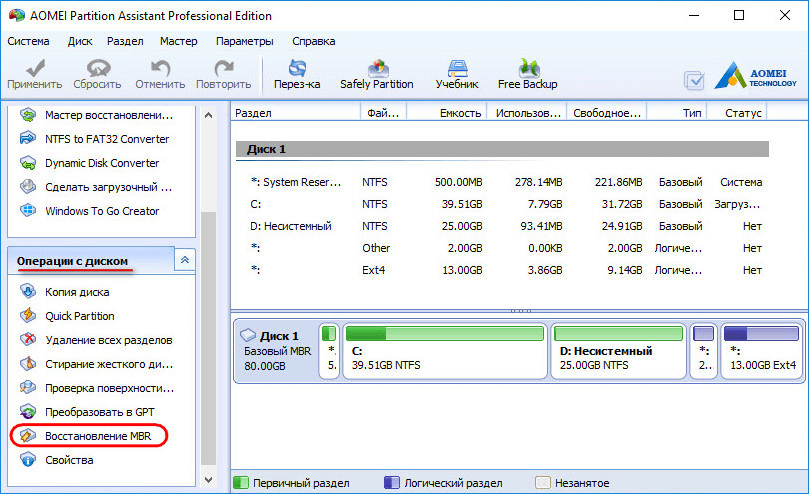
In the window that appears, select the bootloader type for the corresponding versions of Windows from the drop-down list.
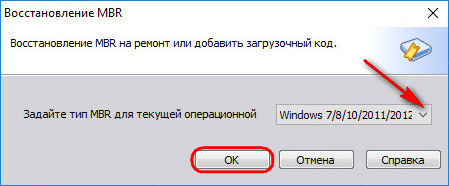
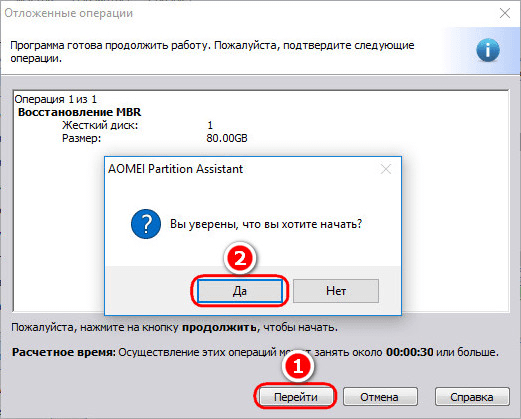
The program will warn that after the planned operation, Linux will stop loading. Click "Yes."
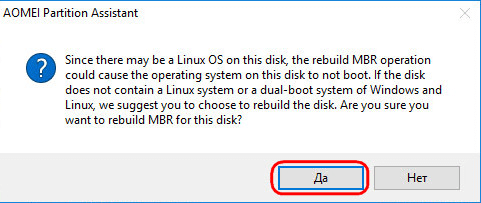
Then we apply the operation with the green button at the top of the Apply window.
We go through a couple of steps in order to confirm intentions.
All operation is applied.
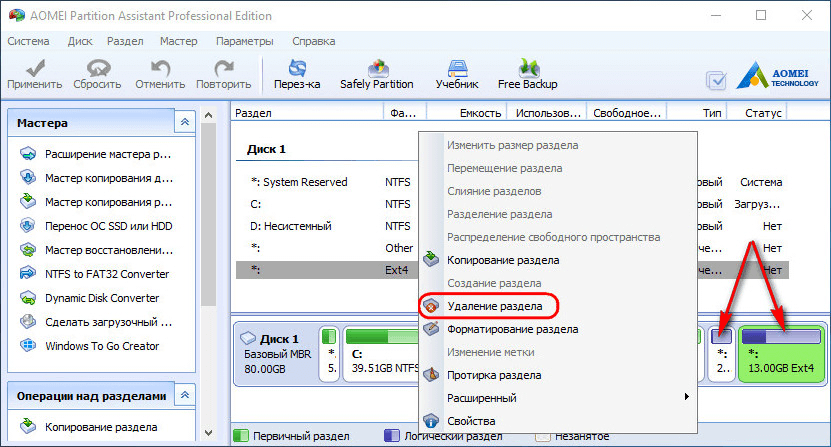
Deletion of each section is confirmed.
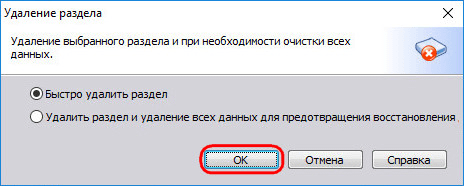
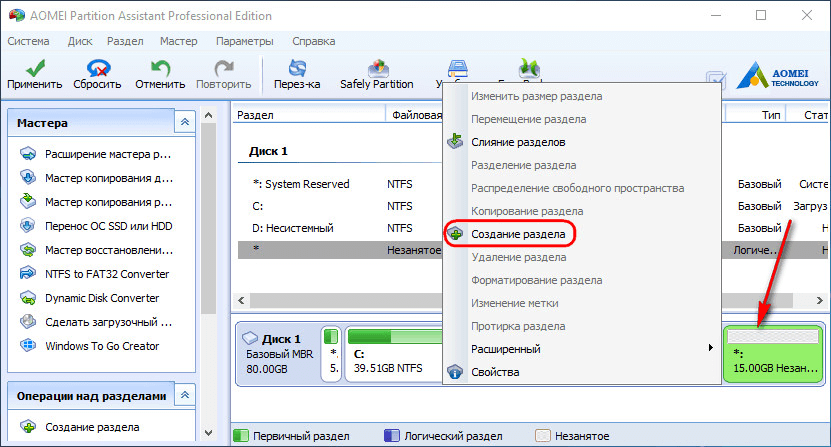
And we make up the free space in a section (or sections) with a file system that is understandable for Windows. In the context menu on unallocated space select "Create Partition".
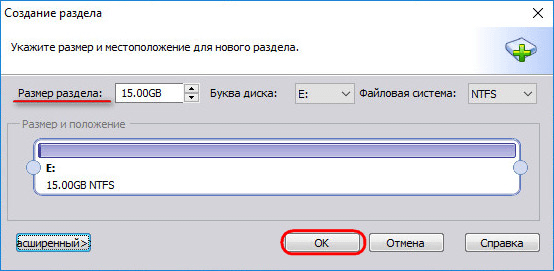
If only part of the space is reserved for the partition, specify the desired size. Click OK.
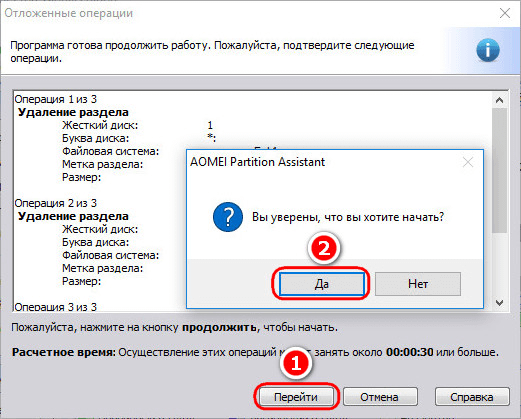
We apply the planned operations.

3. Removing the Linux boot loader in the UEFI BIOS boot queue
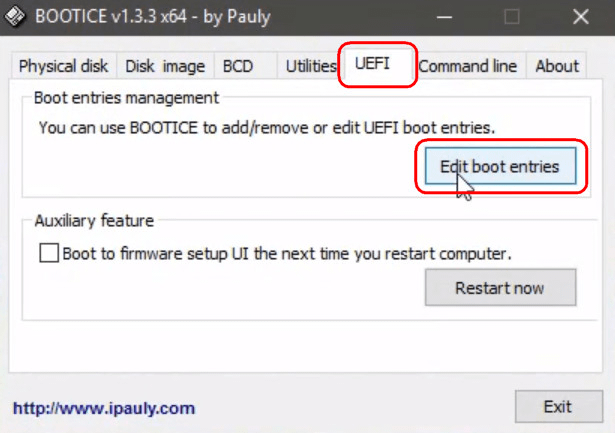
To remove the Linux bootloader on computers with UEFI BIOS, we will resort to the help of the Bootice utility mentioned in Section 1 of the article. But in this case, you need to download its 64-bit edition. This provides for a special tab "UEFI". We go to this tab, click the "Edit boot entries" button.
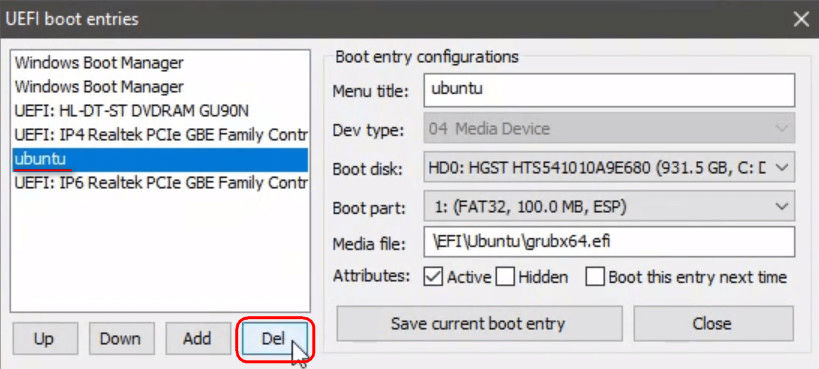
On the left we choose linux bootloader, in this case, Ubuntu. And press the “Del” button below.
The bootloader has been removed from the UEFI boot queue.
The operations for deleting Linux partitions and creating new partitions with a file system understandable for Windows can be performed using any of the methods described above - in p. 1.2 and 2 articles.
I think that many of the users install Linux as a second system next to Windows.
Although I personally don’t like this option, it’s quite viable and very popular. And I do not like this option because of potential problems that you will certainly encounter, for example, when reinstalling Windows.
For a better understanding of the situation, I will delve a little into the theory, namely, the process of loading the operating system.
So, when you turn on the computer, control is transferred to the BIOS and after standard self-tests, then the so-called content is read MBR (Master boot record - home boot record) It is always in the same place - in the first sector of the first hard drive of the computer.
MBR occupies a total of 512 bytes and contains all the service information about the medium, for example, about partitions or the type of file system. Most MBR takes the bootloader, on which lies the responsibility for further loading the computer.
Typically, operating systems do not have enough 512 bytes to load normally, so MBR they put instructions to start the bootloader of the operating system itself and give it all the permissions.
The most popular bootloader in Linux is GRUB2 (GRand Unified Bootloader) It is this program that is fully responsible for the entire process linux boot on computer.
Well, now, in fact, about the problem ...
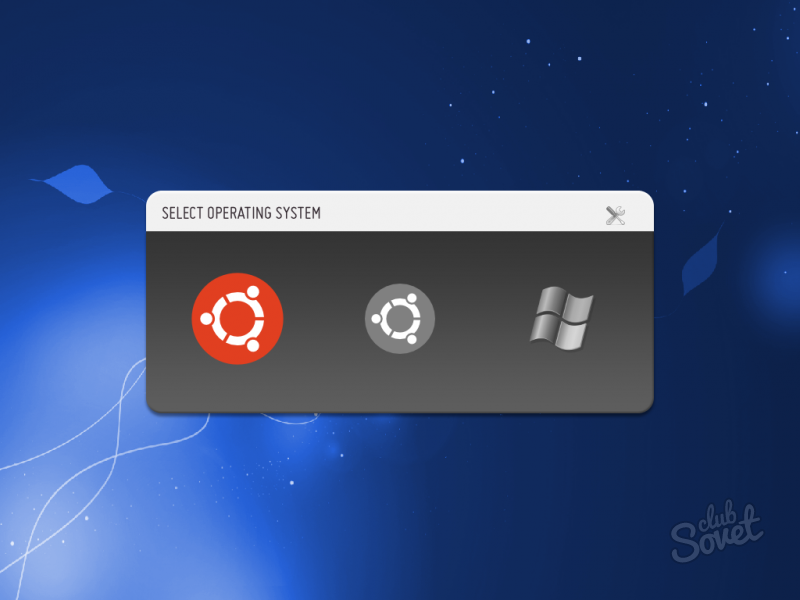
Windows was installed on the computer and we installed Linux as the second operating system. When installing Linux, I discovered another operating system and put it on my list, which allowed us to select the operating system with which we want to work from the special menu when starting up the computer.
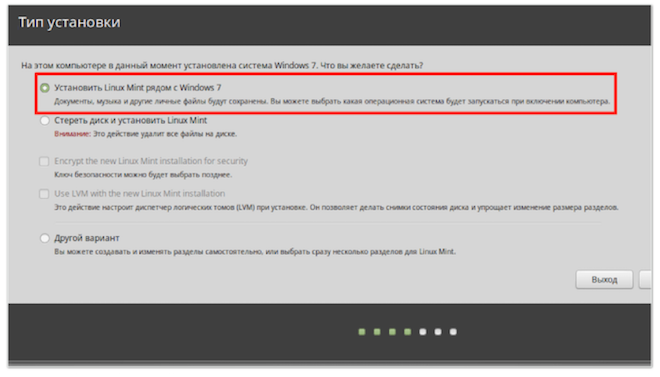
But for some reason, you decide to reinstall Windows. Windows Installer erases MBR and writes there his data, which means instructions Grub disappear and the ability to run Linux also becomes unavailable.
Quite logical ways out of the situation are two:
- save contents MBR before reinstalling windows and then restore her
- after reinstalling Windows install again Grub.
These options are both viable, and for each option there are several implementation methods. Many methods use exclusively Terminal, which is the norm for most Linux users, but for a beginner, all these actions will be incomprehensible, but personally I think that in such situations it is necessary to have full view about what you do. Therefore, I will talk about restoring the bootloader with special utilityhaving a more familiar graphic interface for beginners.
So, we reinstalled Windows and Linux stopped loading. We will need a bootable USB flash drive, with Linux, which we created when installing the operating system, as well as an Internet connection, since we need to download the recovery utility.
We boot from the flash drive and launch the Terminal.
Now we will consider another useful terminal command - add-apt-repository. It allows you to connect to any additional repository. In our case, we need a program Boot repair and we will connect to one of the Linux Ubuntu repositories to download and install the utility from there.
Here is a list of the commands that we will use:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa: yannubuntu / boot-repair
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y boot-repair
After installing the utility, you can run it directly from the terminal by entering the name boot repair, or through the main menu - the Administration section.
After starting the utility, it will scan the hard drive, and then the program window will open. Click on the Recommended Repair button to proceed with the recovery.
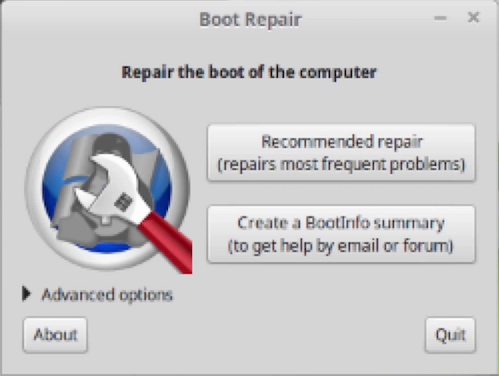
After the recovery is complete, restart the computer. Everything should work as before.
Well, in conclusion, I will say a few words about uninstalling Linux.
The Linux removal process is as simple as the installation process. All you need to do is delete its sections and add them to windows partitions. This can be done, for example, using the standard computer management console in Windows (disk management) or free program EaseUS Partition Master.
The problem can only occur with the bootloader Grubsince his instructions will still be in MBR. Therefore, to solve the problem, it will be necessary to restore MBR.
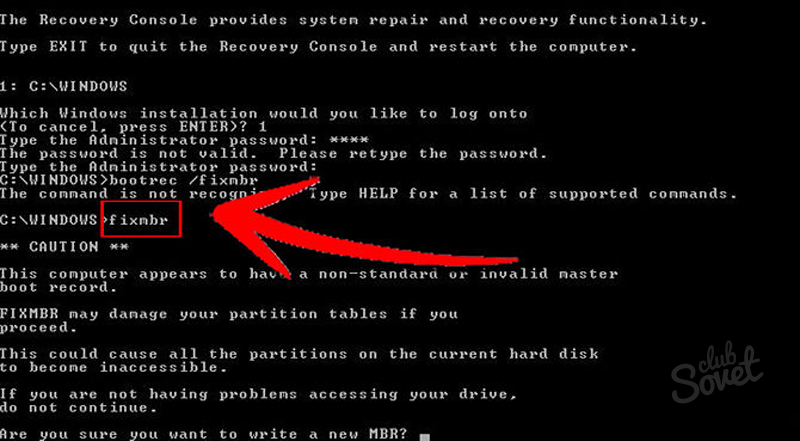
This is done very simply, but we will need boot disk with your windows version. If you have a laptop with Windows preinstalled, then look in the documentation for how to get into recovery mode (usually it is called by pressing one of the function keys when the computer boots). There is no general algorithm, since laptop manufacturers usually do what is most convenient for them. In general, we will need command line mode, so look for how you can run it in your situation.
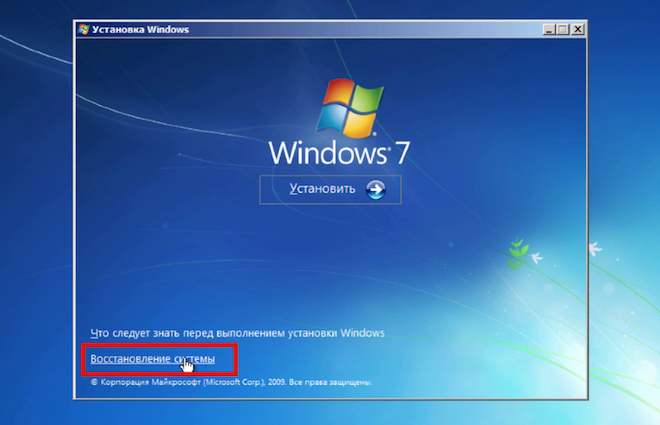
I will demonstrate the process using the example of Windows 7. I boot from a disk or flash drive and at the beginning of the installation I select "System Restore"
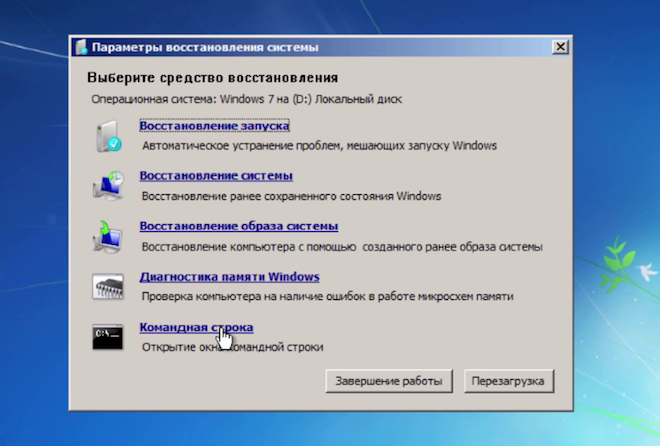
At the command prompt, I enter two commands in order:
bootrec / fixmbr
bootrec / fixboot
After that, I reboot the computer and everything should work.
Well, on this note, it is logical to complete this overview video course on the Linux operating system.
I hope that I was able to open the curtain into the Linux world and contribute to the popularization of this family of operating systems.
If you were interested in this course and you are already using Linux, then I am sure that you now have a lot of questions, the answers to which you did not find in my course.
The computer world is so arranged that there will always be questions and in the overwhelming majority of situations an answer or a solution to a problem has to be found independently.
I believe that it’s worth learning to work with Google or Yandex, since using search engines You can access the knowledge of hundreds of thousands and millions of other users around the world.
Just know that if you have a problem, it is very likely that someone already had it and he decided it, as he spoke about on his blog, any topic forum or video on Yotube. Well, you can find this information by asking Google or Yandex.
The site has a forum on which a lot of answers to frequently asked questions are already concentrated, but if you don’t find a solution to your problem there, you can always create a new topic and ask a question. More experienced users will help you solve it.
If you installed Linux, and then realized that you are not yet ready to work in an unknown environment, then you will definitely have a question how to get rid of the new system. Let's see how to remove Linux if it was installed next to Windows or was the only installed system on the computer.
Linux removal
The easiest way to get rid of Linuska is to install on top of Windows by applying disk formatting. Consider the procedure for installing Windows 7 (for details, see the article on how to install Windows 7 from a USB flash drive). After choosing the type of installation and accepting the license agreement, the wizard will offer you to specify the section on which the system will be installed.
You can split the disk again or use existing partitions. In any case, after installing Windows, there will be no Linux traces on the computer. Instead of Windows, you can put another version of Linux. The principle is the same: during installation, you must re-partition the disk, deleting all old data.
Uninstall in Windows
If you have installed Windows, then to uninstall Linux you need to remove the corresponding hard sections drive. It is done like this:
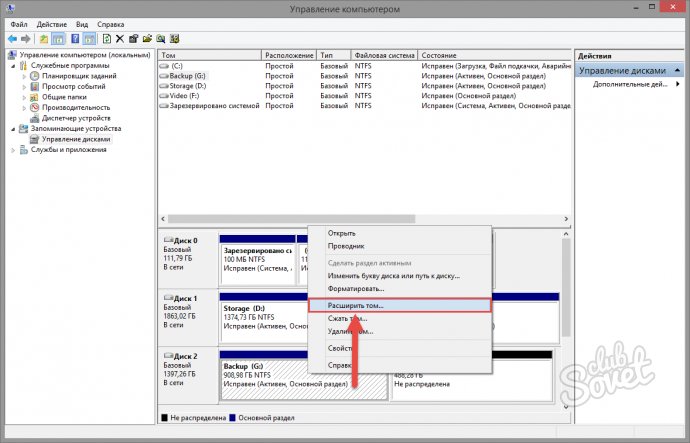
When you delete a partition, all the information that was stored on it will be destroyed. Therefore, if you had any important files on Linux, discard them on a USB flash drive or transfer them to the partitions that are used by the Windows system. After deleting partitions, unallocated space will appear. To start using Windows, you need to expand one of the remaining sections by adding free space to it.
- Right-click on the section you want to expand.
- Select the “Expand” option.
- Indicate the volume to be added to the existing section.
It is not necessary to expand an existing volume - you can simply create a new partition by assigning it a different letter. In any case, the main difficulty awaits you ahead - after a reboot computer windows will not start. The reason is described above: the bootloader was deleted along with Linux. You can fix this error using the Windows installation disc.
We have already examined in detail how to restore windows launch 7. Let's try to apply the acquired knowledge to solve a specific problem - after uninstalling Linux, Windows does not boot.
- Connect the installation flash drive (disk) with the distribution kit of installed Windows.
- Go to the "System Restore" section.
- Select the Command Prompt tool.
To restore the bootloader, you must enter two commands. After entering each command, do not forget to press Enter:
- bootrec / fixmbr - a boot record is created.
- bootrec / fixboot - recording a new one boot sector to the system partition.
The Windows bootloader has been restored, there should not be any more problems when trying to start the system. If you decide to install another version of Linux, then the whole story will repeat: options launch windows will be registered in the common bootloader of the two systems. 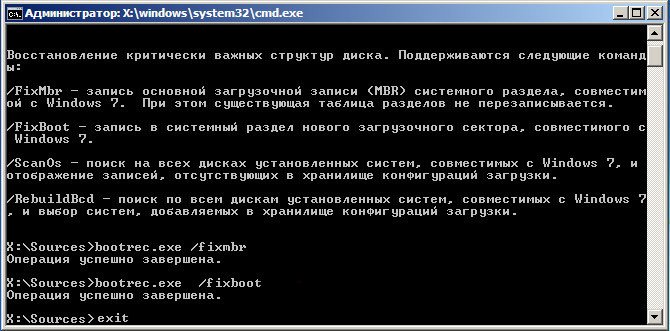
Lastly, a bit of theory.
Deleting a boot record is not an error. This is a consequence of installing Linux next to Windows.
Linux during installation sees that there is a second system and puts it on the list so that users can choose which environment to boot into when they turn on the computer. Removing Linux, you also erase the bootloader program, which contained the Windows boot record. Therefore, then you have to use installation disk to restore the download.
You bought a computer, and it has the Linux operating system on it. The platform, of course, is good, but a simple user with it can decently suffer. Therefore, if you are not an avid computer scientist, then either immediately or later, when you spend a little time trying to master an alternative OS, you will want to get rid of the unfamiliar software and switch to a more traditional one. But Linux is so fundamentally different from Windows that you won’t even be able to remove it using your usual methods. How exactly then to do it - read on.
A feature of Linux that causes difficulties when it is removed is that it uses a different file system than Windows. Therefore, to completely remove the traces of Linux from the computer, you need to physically format the sectors where the folders and files of this operating system are located. If there are no other operating systems on the disk from which you want to remove the unwanted platform, then this is not difficult. Turn on the computer and boot from your live-cd. If such a cd is not observed, find it from friends or create it yourself. Typically, the boot menu from a CD can be accessed by pressing F8, F10, F11, F12, depending on the type of BIOS. From the live-cd that opens, run the hard drive program. The most famous of them are Partition Magic and Acronis. Using these programs, format the entire disk space on your computer. File system at the same time choose only NTFS.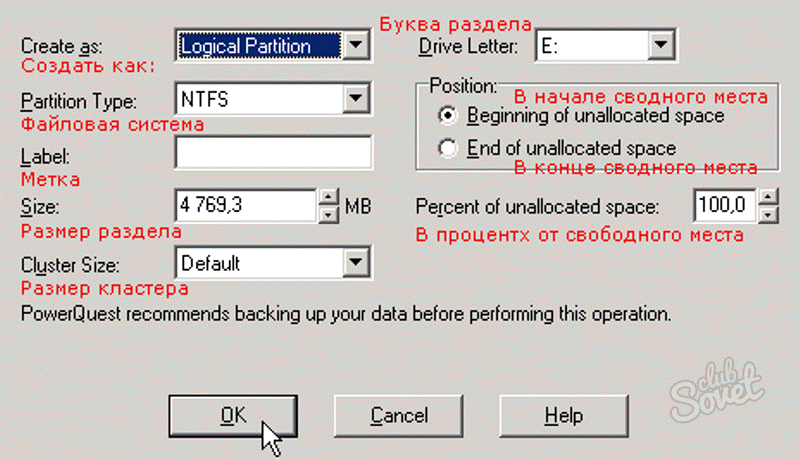

To work in Linux, you really need to make more mental effort than using the operating room. windows systems. But still, do not delete the ruffled OSes right away. First, try to work on the two systems alternately, because each development has its own advantages and disadvantages. After all, destroying something is easy, and you can always do it. And restoration is labor-intensive work.