Introduction
When you work on a computer, there is often a need to move data from one computer to another, located in a remote place. This requires an external storage medium on which you can write data, and then transfer the recorded data to another computer system
Ability to exercise backup data is relevant for everyone whose work is connected with a computer. Backing up data is important not only in connection with the problem of the safety of documents, the loss of even work files can be a very unpleasant event.
To back up data, you must deal with a reliable, voluminous device. And, besides this, the storage medium used should be convenient, and backing up data should not turn into a separate complex process.
Currently, several types of devices using magnetic or magneto-optical media are used for external data storage.
The need for external storage devices arises in two cases:
- when more data is processed on a computer system than can be placed on a basic hard drive;
when the data is of high value and it is necessary to carry out regular backups to an external device (copying data to the hard disk is not a backup and only creates the illusion of security).
Main part.
1. Streamers
Streamers are tape drives. They are distinguished by a relatively low price. The disadvantages of streamers include low productivity (it is associated primarily with the fact that magnetic tape is a sequential access device) and insufficient reliability (except for electromagnetic interference, streamer tapes experience increased mechanical stress and may physically fail. Streamer device: tape drive, reading head , housing. The capacity of magnetic cassettes (cartridges) for streamers is up to several hundred MB. Further increase in capacity by increasing the recording density with reduces the reliability of storage, and the increase in capacity by increasing the length of the tape is constrained by the low access time to the data.
2. ZIP drives.
ZIP drives are manufactured by Iomega, a company specializing in creating external storage devices. The device works with disk media that are slightly larger than standard floppy disks and have a capacity of 100/250 MB. ZIP drives are available in both internal and external versions. In the first case, they are connected to the controller hard drives motherboard, and in the second - to the standard parallel port, which negatively affects the speed of data exchange.
Benefits of Zip Drives:
- low unit cost of information storage (cost / volume);
- high performance (almost 100 times higher compared to a floppy disk);
- ease of use (the small size of the ZIP allows you to carry it in your pocket);
- ease of installation (one small program and driver are required to work);
- A wide selection of options and interfaces.
3. HiFD devices
The main drawback of ZIP drives is their lack of compatibility with standard 3.5-inch floppy disks. Devices have this compatibility.Hifd Sony company. They allow you to use both special media with a capacity of 200 MB, and conventional floppy disks. Currently, the proliferation of these devices is constrained by the increased price.
A servo signal is prerecorded on the media, allowing you to position the read / write head. The drive is compatible with standard 3.5-inch floppy disks of 1.44 MB, and for reading / writing 1.44 and 200 MB of disks uses a different gap between the surface of the disk and the head. There are devices with ATAPI and LPT.
Dimensions of the Sony HiFD drive 143x42x214 mm, weight about a kilogram. The drive enclosure is equipped with legs for horizontal or vertical positioning on a table. HiFD diskette looks like a standard floppy disk. It is distinguished by a T-shaped metal curtain and a recording lock slider, which is located not on the right, but on the left. Extra slots in the plastic case of the HiFD diskette do not allow you to mistakenly install it in a regular floppy drive.
3. JAZ drives
.
This type of drive, like ZIP drives, is manufactured by Iomega. According to its characteristics, the JAZ carrier approaches hard drivesbut unlike them is replaceable. Depending on the model of the drive, 1 or 2 GB of data can be placed on one drive.
Allows you to store on one disk up to 1 GB of data, which is enough to record a movie in MPEG format. But, since the drive uses a non-standard media format, both partners must have Jaz drives for file sharing.
Interesting statistics are the use of Bernoulli drives. It turned out that 28% of users use Bernoulli drives for backup, 22% as a replacement hard drive, 21% for data transportation, 13% for secrecy, and 8% for archiving.
Modern Bernoulli drives have a capacity of 90,100,150,230 Mb and 1 GB per cartridge and are compatible from the bottom up (with the exception of Jaz). Please note that if an ordinary hard drive can “fall” after 2-4 years after purchase, “burying” all the programs with it, then such “funeral” with Bernoulli is practically impossible.
5. Storage on magnetic disks.
Magnetic disks are used as storage devices that allow you to store information for a long time, with the power off. To work with Magnetic Disks, a device called a magnetic disk drive (NMD) is used.
The main types of drives:
· Drives on flexible magnetic disks (HMD);
· Drives on hard magnetic disks (HDD);
· Tape drives (NML);
· Drives CD-ROM, CD-RW, DVD.
They correspond to the main types of media:
Floppy Disk (3.5 '' diameter and 1.44 MB capacity; 5.25 '' diameter and 1.2 MB capacity (currently outdated and almost never used; release drives designed for disks) 5.25 '' diameter, also discontinued)), disks for removable media;
· Hard magnetic disks (Hard Disk);
· Cartridges for streamers and other NML;
· CD-ROM, CD-R, CD-RW, DVD.
Storage devices are usually divided into types and categories in connection with their principles of operation, operational and technical, physical, software and other characteristics. So, for example, according to the operating principles, the following types of devices are distinguished: electronic, magnetic, optical and mixed - magneto-optical. Each type of device is organized on the basis of the corresponding technology for storing / reproducing / recording digital information. Therefore, in connection with the type and technical design of the storage medium, there are: electronic, disk and tape devices.
The main characteristics of drives and media:
· Information capacity;
· Speed \u200b\u200bof information exchange;
· Reliability of information storage;
· Cost.
6. Flash Cards
The latest storage technology, flash memory, has been the primary or secondary storage medium for several years. laptop computers. However, the booming market for digital cameras and MP3 players using this memory has led to the widespread adoption of these devices.
How does flash memory work?
Flash memory refers to long-term storage devices. The data in it is stored in the form of blocks, not bytes, as in conventional memory modules. Flash memory is also used on most modern computers for BIOS chips that are rewritable using the Fowler – Nordheim tunneling process. Flash memory must be erased before writing new data.
High performance, low reprogramming requirements and the small size of the latest flash memory devices make this type of memory a great addition when used in laptop computers and digital cameras. Flash is often referred to as “digital film” in this area. Unlike a real film, a digital one can be erased and reused. Types of flash memory devices Several types of flash memory devices are popular today and it is important to know which one is used in your digital camera.
In addition to the above basic devices for storing and storing information, there are some others, for various reasons, less popular. Such devices include:
- magneto-optical disks;
- Bernoulli discs;
- data backup devices;
- some other devices.
All these devices have different capacities, speeds of access to information, their minuses and pluses, as well as different prices. They have their own limitations, but there are undoubted advantages. One thing they all have in common - these devices were created to store, accumulate and backup data.
7. Removable USB - drives.
A USB drive is a small device that is used to transfer data from computer to computer using a USB port.
USB - HDD removable external drive - removable external hDD which can perform all the functions of a regular hard disk drive (HDD) and, besides, it has a number of advantages, for example, the “removability” function is indispensable when transferring large amounts of information, miniature size is no more than a “standard” cigarette case. Moreover, USB - HDD removable external drive , a very stylish accessory, and usually has a convenient carrying case.
USB - HDD removable external drive clad in a steel case, reliably protecting it from mechanical damage. Some models USB - HDD removable external drives equipped with LCD-displays, which provide additional convenience when using them.
8. Iomega Clik
Floppy disk Iomega Clik! (compact mylar media with a diameter of about 5 cm in a hard steel casing), in my opinion, now remain the only real alternative to expensive flash cards. A media with a 40 MB rounded capacity should cost about $ 9, which in a good sense is not comparable with the cost of a flash card of a similar size (the difference is almost ten times). Released over a year ago, the Clik standalone drive! (less than $ 200) was designed as a faithful companion to a digital camera. The battery-powered drive included a card reader with slots for CompactFlash and SmartMedia, and data was transferred from the card to a diskette by pressing a single button.
Compared to it, released much laterclik drive
! in size PC Card Type II (about $ 200) looks like a real work of art. No installation problems, no drivers, 600 KB / s performance, the ability to quickly connect to a desktop PC via a proprietary USB docking station ($ 50) - what else does a laptop user need? By the way, the disk rotation speed in the Clik drive! is 2941 rpm., which is slightly less than that of Zip, and is approximately two to three times lower than the speed of modern hard drives.
9. Castlewood ORB - a 2.2 GB hard drive removable drive
Castlewood ORB is a rare example of longevity among non-mass storage devices. He became a sensation Comdex’97 and was awarded a prestigious award. Since then, close relatives of ORB (for example, SyQuest drives) have already left this market, andoRB standard drives now produced by several companies and, in principle, normally sold. By the way, the intrigue is that Castlewood was opened by the former founder of SyQuest.So what is an ORB? This is a hard disk drive for removable drives. A three-inch disk (cartridge) ORB has a capacity of 2.2 GB (2.16 GB in FAT16) at a cost of about $ 30 per carrier. The USB ORB drive itself can cost $ 250-280, and models for connecting to the FireWire bus will be available in the near future. However, the internal ORB model with the IDE interface (ATAPI) can still be considered the optimal price.
The ORB drive develops a disk rotation speed of 5400 rpm, which corresponds to the performance of real modern hard drives in the average price range. In addition, reading / writing is performed by the subsystem of magneto-resistive heads. At the same time, the declared search time for ORB drives is 10 and 12 ms for reading and writing, respectively, which is again comparable with the speed characteristics of modern hard drives. According to the specification, the potential data transfer speed of the ORB drive is 12.2 MB / s (you can definitely count on 8 MB), but it is often limited by interface performance. So, for example, when connected to a printer port, the actual drive performance becomes six times less than the maximum.
etc.................
In this section I will talk about external storage media. Let me remind you that they are the last in the hierarchy of memory. They can record most of the data. Such drives are not so convenient (for example, often the user is too lazy to change the CD), but they are very cheap.
External media - This is not only disks or floppy disks. These also include external hard disks, optical drivesUSB flash cards, etc.
External hard drive
External hard drives exist for a long time. In structure, they almost do not differ from internal ones. We can say that these are the most common hard drives, but they are not supplied with a computer (in particular, with a laptop), but in a special plastic case.
In addition to the hard drive, there is a special chip that converts signals for transmission through one of the connectors displayed on a laptop or desktop PC). You connect a small box using a cable to the computer, and after a few seconds the operating system determines new hard disk (Fig. 4.11). She does not even have to reboot.
Fig. 4.11. External hard 2.5 ”format disc
Today, there are two ways to connect a hard drive: via USB and FireWire. The first type has been discussed more than once. Its purpose is universal, so not only a mouse, keyboard, printer, scanner, but also some external media are compatible with it.
Some time ago, FireWire (also known as IEEE 1394 and i.Link) was available only to owners of professional and expensive computers, but now it is in almost every laptop. Formally, FireWire is preferred for connection external hard drive. Due to better security, it will be able to provide greater reliability and data transfer speed. However, there are very few external hard drives that support the IEEE 1394 format on the market. Most often, they are compatible with USB 2.0.
There is a way to turn ordinary internal hard drive to external. In computer stores there is a good selection of external cases for hard drives. You need to purchase a case and a hard drive for it. Then, according to the instructions, insert the hard drive inside - and you're done.
It is important to observe a few rules. In the previous chapter, I said that there are several sizes of hard drives, the most common - 3.5 and 2.5 ”. The former are used on desktop computers, the latter on mobile. Remember that a case can only be compatible with one of them.
Pay attention to the connection interface. It can be Serial ATA (or SATA) and IDE (or UDMA, Ultra ATA). Both the hard drive and the case must support the same connection method. Otherwise, nothing will work.
External optical drive
Today, laptop manufacturers are trying to equip each model with an optical drive for working with CDs. In the case of miniature subnotebooks, this cannot be done for obvious reasons. However, if you need to work with disks, the way out of the situation is to purchase an external optical drive.
As is the case with hard drives, external drives are most often internal versions enclosed in a case. They come in different sizes. The largest and heaviest are analogs of drives installed in desktop computers. Probably, they should not be purchased. Firstly, these drives are rather bulky, and secondly, an additional outlet may be needed for operation, which does not speak in favor of mobility.
If desired, you can find a "laptop" external drive. It will be much more compact and, of course, more expensive. If you need a special version for transportation, then this option will be one of the best. “One of” because there are models designed specifically for transfer with a laptop (Fig. 4.12).

Fig. 4.12. A special drive designed to carry with a laptop
Such optical drives are not based on internal counterparts, which negatively affects their cost. But the convenience of transportation at altitude.
The disks on which the information is stored on the computer have their own names - each disk is called a letter of the Latin alphabet, and then a colon is placed. So, for floppy disks the letters A: and B: are always assigned. Winchester logical drives are named starting with the letter C :. All logical drive names are followed by the names of the CD-ROM drives. For example, installed: a diskette drive, a hard drive, divided into 3 logical disks and a CD-ROM drive. Identify the letters of all storage media. A: - diskette drive;
C :, D :, E: - logical drives Winchester
F: - CD-ROM drive.
Full file name
The uniqueness of the file name is ensured by the fact that the full file name is considered to be the file’s own name along with the path to it. It is clear that in this case on one medium there cannot be two files with identical full names.
An example of writing the full file name:
<имя носителя>\<имя каталога-1>\…\<имя каталога-М>\<собственное имя файла>
Here is an example of recording two files that have the same proper name and are located on the same medium, but differ by access, that is, their full name. For clarity, the names of directories (folders) are printed in capital letters.
D: \\ Documents \\ Information about students \\ 2004-05 academic year \\ Certification results. doc
D: \\ Dean \\ Certification of students \\ Certification results. doc
2.4. File systems
All modern disk operating systems provide the creation of a file system designed to store data on disks and provide access to them. The principle of file system organization is tabular. The surface of the hard disk is considered as a three-dimensional matrix, the measurements of which are the numbers of the surface, cylinder and sector. A cylinder is a set of all tracks belonging to different surfaces and located at an equal distance from the axis of rotation. The physical structure of data storage is presented in figure 2.2.

Figure 2.2. Physical structure of information storage
Data on where a particular file is recorded in the disk is stored in the system area of \u200b\u200bthe disk in special file allocation tables (FAT tables). Since violation of the FAT table leads to the inability to use the data recorded on the disk, special reliability requirements are imposed on it and it exists in two copies, whose identity is regularly monitored operating system.
The smallest physical unit of information storage is a sector. The sector size is 512 bytes. Since the size of the FAT table is limited, it is not possible to provide addressing to each individual sector for disks whose size exceeds 32 MB. In this regard, groups of sectors are conditionally grouped into clusters. A cluster is the smallest unit of addressing information. Cluster size, unlike sector size, is not fixed and depends on disk capacity.
As mentioned earlier, information on disks is recorded in sectors of a fixed length, and each sector and the location of each physical record (sector) on a disk is uniquely determined by three numbers: the surface numbers of the disk, cylinder and sector on the track. And the disk controller works with the disk in these terms. And the user does not want to use sectors, cylinders and surfaces, but files and directories. Therefore, somehow it is required during operations with files and directories on disks to translate this into actions that the controller understands: reading and writing certain sectors of the disk. And for this it is necessary to establish the rules by which this translation is performed, that is, first of all, determine how the information on the disks should be stored and organized. The set of these rules is called the file system.
A file system is a set of conventions that define how data is organized on storage media. The presence of these agreements allows the operating system, other programs and users to work with files and directories, and not just disk sections (sectors). The file system determines:
How files and directories are stored on disk;
What information about files and directories is stored;
How can I find out which parts of the disk are free and which are not;
The format of directories and other service information on disk.
To use discs recorded (tagged) using some file systemoperating system or special program must support this file system.
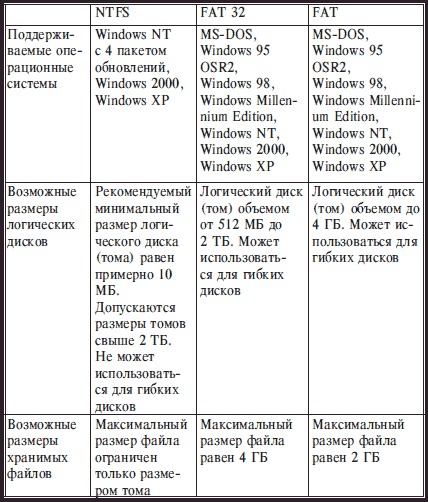
The file system, the most common on IBM PC-compatible computers, was introduced back in the early 80s in the operating systems MS DOS 1.0 and 2.0. This file system is quite primitive, as it was created to store data on floppy disks. Usually this file system is called FAT, since the most important data structure in it is the file allocation table on disk, in English - file allocation table, in short - FAT. This table contains information about which sections (clusters) of the disk are free, and about the chains of clusters that make up files and directories.
In the FAT file system, file and directory names must be no more than 8 characters plus three characters in the name extension. It leads to significant losses (up to 20%) disk space due to the large cluster sizes on high capacity drives. This is due to the fact that at the end of the last cluster of the file remains free place, on average equal to half the cluster. And on large disks, the size of FAT clusters can reach 32 Kbytes. Thus, on a disk with a capacity of 2 GB with 20,000 files, the loss will be 320 MB, that is, about 16%. Finally, the FAT file system is inefficient, especially for large disks, not adapted for multitasking (all operations require access to the file allocation table, and therefore, you cannot start another before completing one operation).
When developing Windows 95, Microsoft decided not to introduce a new file system, but to patch up the existing FAT file system, allowing it to give files and directories long names. This file system became known as FAT 32. The approach adopted in Windows 95 is good because it allows you to use old disks with the FAT file system - they just start to write long names. But still this solution is very artificial, and many programs - for fixing the file system of disks, "compressing" disks, backup, etc. - can lead to the loss of long names on the disk. FAT 32 supports smaller cluster sizes, which allows more efficient use of disk space.
When developing the Windows NT operating system, a new file system was created - NTFS. It was focused on large disks containing many files, they took significant measures to ensure the efficiency of data storage and access control to them. This file system supports long file names. On logical disks with a capacity of 1-2 GB file nTFS system allows you to store on average 10-15% more information than FAT. And access to files in it is much faster, especially in a multitasking environment.
NTFS developers, not forgetting about the effectiveness, also tried to ensure the reliability of the file system and data recovery during failures. For this, in particular, NTFS duplicates all critical information and ensures that all changes are recorded on disks in a special registration file, and for each change, the method of canceling it is also remembered. As a result, in almost any failure, NTFS is automatically restored. NTFS also (unlike FAT) can work with logical drives and files larger than 2 GB - the maximum size of logical drives and files there is 4x1018 bytes.
If the file system on the disk is not supported by this operating system, then all information on this disk will be inaccessible (when working in this operating system, of course). For such logical drives, either a letter may not be assigned at all (that is, it will not be possible to access the drive), or an error message will be displayed for any access to the drive.
Table 1. Comparative characteristics of file systems
A special file system is designed for compact discs (CD-ROM). This turned out to be necessary, since the physical device of compact disks is not the same as that of hard disks or floppy disks: information is recorded in them not in ring tracks, but in a single spiral-shaped track (like in audio CDs). This file system is called CDFS.
It is difficult to be a good specialist in any field, having no idea about the tools that are used in the work. To work in the field information technologies such tools are a computer and its many external devices. Of course, these are complex tools, and their thorough study is a separate professional field. But to have general information, to represent the purpose, the principle of work, the most important characteristics, possible reasons The most likely failures are essential for any competent specialist. This will allow the task to be set for professionals, to understand their recommendations, and to use all the capabilities of technical devices correctly and fully.
The English word computer, like the Russian abbreviation for computers, means the same thing - a machine for computing. That is, initially the computer was created for mathematical calculations, for working with numbers. However, any kind of information existing in the surrounding world can be encoded with numbers: text, image, sound ... And by performing mathematical operations with these numbers, the computer is able to receive, convert, save, transmit the most diverse information.
Therefore, at present, a computer is a device for processing information: reception, digitalization, analysis, storage, delivery in a given form, transmission to the right place ...
The main blocks of a standard computer, its minimum configuration, can be considered
- keyboard mouse - devices for entering information,
- system unit, where information is mainly processed and stored,
- monitor - device for outputting information
Of course, these blocks do not always exist separately. IN laptops, and especially in PDA, all of them are already combined in one device. But let's look at the contents of the system unit of a conventional computer.
- I Consider your computer, identify its main blocks. If you already have a used system unit at your disposal, try to remove one of the walls of its case, or the entire case cover. First make sure that it is really idle, and disconnected from the network!
Motherboard, purpose, device
The main electronic board of the system unit is called motherboard (motherboard). The motherboard is a multi-layer circuit board with microcircuits, connectors, slots for connecting other boards and elements of the system unit located on it. It serves as a "bridge" that connects all the devices of a computer. The main features of the motherboard determines chipset (Chip Set) - a chipset. The type of set basically determines functionality boards: types of supported processors, possible combinations of types and volumes of memory modules, support for energy-saving modes, the ability software setting parameters, etc.
On the motherboard There is also a special connector for installing the main computer chip - the processor. On motherboards designed to install Pentium, Pentium MMX, and Cyrix M2 processors, processor socket - square shape (Socket 7).
There are also special connectors on the motherboard ( slots) to install additional boards and RAM chips. A set of conductors (lines) connecting various components of the motherboard and other elements of the computer for supplying power to them and exchanging data is called the tire. The bus specifications also determine the capabilities of the motherboard and the computer as a whole.
There are connectors on the motherboard for connecting external devices - ports. Usually they go to the back of the computer.
- I If you have revealed the system unit, try to make out the motherboard and its details in its contents. Perhaps this will interfere with the wires and elements installed on the board. With some skill, you can try to remove everything that is in the way and remove the motherboard. Preliminarily think: do you need it? If not, limit yourself to a drawing. If yes - more boldly, the system unit was non-working anyway ..
Processor, purpose, characteristics

The most important microcircuit in a computer, its “brain” is a processor - a small, but containing millions of transistors microcircuit that performs all calculations at a speed of hundreds and thousands of millions of operations per second.
Microprocessors differ in type and clock frequency. A type characterized in the name: Intel-8088 (3500 transistors), 80286, 80386, 80486, Pentium, Pentium Pro, Intel Core 2 (151 million transistors). Each next model contains more transistors, has great capabilities and great speed.
Clock frequency shows how many elementary operations are performed by the processor per second. Processors of the same type can operate at different clock speeds, for example, the Pentium 60 MHz and Pentium 200 MHz processors differ in speed by three times. The maximum frequency of modern Core 2 Duo processors is 2.66 GHz, while in Core 2 Extreme this value increases to 2.93 GHz. (1 GHz \u003d 10 12 operations per second) By changing the parameters of the processor (applying more voltage to it), the processor can be overclock, make it work with a frequency greater than that specified in the characteristics. However, this can lead to processor failure. 
Another way to improve computer performance is to multi core processors. They contain several processor cores in one housing (on one or several crystals). At the moment, processors with two cores are massively available, in particular Intel Core 2 Duo. The core of the Duo contains 151 million transistors,
Along with Intell, there are other processors manufacturing companies (Celeron, AMD).
Since the high power of the processors is associated with large heat dissipation in order to keep the temperature within the limits acceptable for semiconductors, a heat sink metal radiator with a fan is fixed on top of the processor - cooler (cooler).
- I Having found the cooler on the motherboard, deal with its fastening and remove it from the processor. After that, you can carefully remove the processor itself. Try to decompose the removed parts in a certain order, which will facilitate subsequent assembly ...
RAM, purpose, characteristics
In addition to the processor, microcircuits are located on the motherboard that provide the RAM (RAM) of the computer. It is from it that the processor takes indications of the order of calculations (program) and the initial data for processing, and the intermediate and final results of the calculations are also entered there. Otherwise, the processor speed would depend on the speed of mechanical devices that read information from other sources and write it.
RAM is characterized by type and capacity. More than rAM computer, the more complex programs it can use, large amounts of information and process it with greater speed, the less often it uses disk I / O, which greatly slows down the work. First personal computers could use up to 640 kB of OP, in modern computers the amount of memory reaches several gigabytes.
The type of memory characterizes its speed, the speed of information transfer to the processor and other computer devices.
It should be borne in mind that information in RAM is stored only when the computer is turned on, and may be lost when it is suddenly turned off.
Additional boards of the system unit
Special connectors (“slots”) are also installed on the motherboard, into which electronic boards that control other computer devices (drives, a monitor, etc.) are inserted. These boards are called "controllers", "cards." This makes it possible to upgrade the computer, put, for example, a new hard drive by installing its controller in the corresponding connector on the motherboard. Many cards have a special connector - "port"overlooking the back wall of the system unit.Ports are used to connect the system unit with external computer devices. There are parallel and serial ports, which differ in the number of wires and, accordingly, the speed of information transfer. To protect "from the fool", all the connectors have a different configuration, so you can not be afraid that something will stick in the wrong place. The most modern port is the USB port.
- I Determine the position of the described parts on the motherboard of your computer, the nature of their fastening. Try removing and reinserting them in the same connectors.
Hard drive, device, purpose
An important element of a modern computer is the hard drive - "Winchester", HDD. Outwardly, this is a relatively small box, inside of which are placed not one, but a whole stack of disks coated with a magnetic layer. To read and write information, a magnetic head is supplied to each disk in this stack. Rotation of disks and movement of magnetic heads is provided by electric motors and control electronic circuits.
The main characteristics of the hard drive are capacity and speed.  Computers with 8088 (\\ and XT) and 80286 (\\ and AT) processors used 10, 20, and 40 MB hard drives. Such disks allowed working in a DOS environment with programs that did not use a large amount of data. To use the operating room wINDOWS systems, databases, image files, disks with a capacity of 120-520 MB were required (a file with one high-quality color image can occupy about 10 MB). Digital video files and high-quality audio files require even more disk space. The complexity and size of the programs used when working on a computer are also constantly increasing. Therefore, the capacity of modern hard drives is usually several tens and hundreds of GB, and copies have appeared with a capacity measured in Terabytes (2 10 GB).
Computers with 8088 (\\ and XT) and 80286 (\\ and AT) processors used 10, 20, and 40 MB hard drives. Such disks allowed working in a DOS environment with programs that did not use a large amount of data. To use the operating room wINDOWS systems, databases, image files, disks with a capacity of 120-520 MB were required (a file with one high-quality color image can occupy about 10 MB). Digital video files and high-quality audio files require even more disk space. The complexity and size of the programs used when working on a computer are also constantly increasing. Therefore, the capacity of modern hard drives is usually several tens and hundreds of GB, and copies have appeared with a capacity measured in Terabytes (2 10 GB).
It is clear that for working with large volumes of information, the speed of reading and writing to disk is also important. Therefore, the second important characteristic of a hard disk is its speed.
- I Locate the hard drive on your computer
The principle of the computer
How does a transformer work? - Oooo! The computer makes approximately the same sounds.
- I Knowing the purpose of the individual devices of the system unit and other computer units, try to independently describe the principle of its operation.
External storage media. Floppy disks, laser disks, ...
Drives - devices for writing and reading to floppy disks. Floppy disks allow you to transfer information from one computer to another, create archives. Currently, 3.5-inch floppy disks, which have a capacity of 1.44 MB, are used. A floppy disk is a plastic case, inside of which is a plastic disk coated with a magnetic layer. When a diskette is inserted, the metal shutter shifts and the magnetic head of the drive may approach the disk.
CD-ROM devices. Due to growth with volumes and complexity software, the introduction of multimedia (color + sound + movement) required inexpensive and capacious storage media. Such media are compact disks, which allow storing up to 650 MB of information with great reliability, replacing dozens of floppy disks. It is a disc made of transparent plastic, into which metal (aluminum) foil is pressed. A laser beam on a metal surface can burn out areas that are not able to reflect light. When reading information, a less powerful laser beam is also sent to the disk, its reflection from the surface is received by a special detector and converted into electrical signals. Therefore, modern computers are equipped along with conventional CD-ROM drives. CDs are used to supply large software packages (WINDOWS), encyclopedias, databases, training and gaming programs. The disadvantage of CDs is the difficulty of writing to them, as well as significantly lower read speeds than from floppy disks. DVD discs have an even higher recording density and hold several GB of information.
Flash drives - A relatively new external storage medium, with capacities from hundreds of MB to several GB, in the absence of mechanical parts. Based on the property of field-effect transistors to store electric charge for many years. Modern flash memory, on average, can withstand about 100,000 erase / write cycles, but the erase and write processes wear out the chip. Therefore, it is not recommended to edit documents, databases directly on the "flash drive", because at the same time, processes of writing / erasing and updating the file system table constantly occur. The flash drive may also fail due to overheating. Less impact on the chip have the processes of reading information.
- I Determine what external storage media your half-disassembled computer could use, other computers that you have to work with. Learn how to use these devices.
Monitors, types, basic characteristics.
A monitor is a very important device that is part of a computer. Not only the ability to use certain programs depends on it, but also the convenience and safety at work. CGA-EGA-VGA-SuperVGA are consistently developed types of monitors that are characterized by increasing video memory (up to 1 MB) and speed, smaller grain (up to 0.25 mm) and higher resolution (up to 1024 * 768 pixels). Only monitors with good resolution allow you to clearly see the texts that accompany wINDOWS work. The screen size of the monitor should be large enough, otherwise the inscriptions will be small, which also bores the eyesight. Good monitors cost up to $ 1,000. Different CRT and LCD monitors.
The main characteristics of the monitor:
- Screen size (in inches, diagonally, 17 - 19 - 21 inches ...)
- Resolution - the number of pixels horizontally and diagonally (1024 * 768 or more)
- I Determine the type and characteristics of your computer monitor.
Printers, scanners, modems ...
Printers - matrix, inkjet, laser - the name reflects the method of applying the image to a sheet of paper (with a needle matrix through an ink ribbon, droplets of liquid ink or a laser beam and a special ink powder). The latter method gives the most durable and high-quality image. Inkjet printers are significantly cheaper, especially for printing color images. Printers for printing large format images are called plotters.
Scanners - devices for entering information from a solid medium (paper), converting it into a digital code, which can subsequently be saved as an image file or recognized and converted into a text document.
Modems - devices for exchanging information through the telephone network. In a special way, they convert (modulate) the electrical signals of a computer for transmission to an external network, and demodulate signals from the outside for processing by the system unit. Distinguish between internal (network cards) and external modems.
- I What additional input / output devices does your computer use?
Projectors, interactive whiteboards
 Relatively new devices for outputting information and entering it into a computer. Projectors display the contents of the monitor screen on a large screen, ensuring its perception immediately large group of users.
Relatively new devices for outputting information and entering it into a computer. Projectors display the contents of the monitor screen on a large screen, ensuring its perception immediately large group of users.
If we use a special touch surface as a screen that can convert it into electrical signals by pressing it, we get interactive whiteboard, information with which it enters the computer and can be used to control its operation. These devices are promising for the use of IT in training.

Floppy disks (floppy disks). A floppy drive is fundamentally similar to a hard drives. Rotational speed floppy disk about 10 times slower, and the heads touch the surface of the disc. Basically, the information structure on a floppy disk, both physical and logical, is the same as on a hard disk. From point of view logical structure there is no disk partition table on the diskette.

The principle of operation of a floppy disk. The floppy disk drive (floppy disk, or just a diskette) has two motors: one provides a stable speed of rotation of the diskette inserted into the drive, and the second moves the read / write heads. The speed of rotation of the first engine depends on the type of diskette and ranges from 300 to 360 rpm. The motor for moving the heads in these drives is always stepping. With its help, the heads move along the radius from the edge of the disk to its center at discrete intervals. Unlike the drive of the hard drive, the heads in this device do not “hover” above the surface of the floppy disk, but touch it.

Optical (laser) disc. The first optical laser discs appeared in 1972 and demonstrated great opportunities for storing information. The volumes of information stored on them made it possible to use them to store huge amounts of data (such as databases, encyclopedias, collections of video and audio data). Easy replacement of these discs made it possible to "carry" all the materials required for work, in any volume. Optical disks had very high reliability and durability, which allowed them to be used for archival storage of information.

The principle of operation of the disk. The principle of operation of the drive resembles that of conventional floppy drives. The surface of the optical disc (CD-ROM) moves relative to the laser head at a constant linear speed, and the angular velocity varies depending on the radial position of the head. The laser beam is directed onto the track, while focusing using a coil. The beam penetrates through the protective layer of plastic and enters the reflective layer of aluminum on the surface of the disk. When it hits the protrusion, it is reflected on the detector and passes through a prism deflecting it to the photosensitive diode. If the beam enters the pit, it is scattered and only a small part of the radiation is reflected back and reaches the photosensitive diode. On a diode, light pulses are converted into electrical ones, bright radiation is converted to weak zeros - to units. Thus, the holes are perceived by the drive as logical zeros, and a smooth surface as logical units

Hard disk drive (hard drive). A hard disk drive or a Winchester drive is the most massive mass storage device in which information carriers are round aluminum plates of the plotter, both surfaces of which are coated with a layer of magnetic material. It is used for permanent storage of program information and data.

The principle of operation of the hard drive. The surface of the plotter has a magnetic coating with a thickness of only 1.1 microns, as well as a lubricant layer to protect the head from damage when lowering and raising on the go. When the plotter rotates above it, an air layer forms, which provides an air cushion for the head to hang at a height of 0.5 μm above the surface of the disk. Winchester drives have a very large capacity: from hundreds of megabytes to tens of GB. In modern models, the spindle speed reaches 7200 rpm, the average data search time is 10 ms, and the maximum data transfer rate is up to 40 MB / s. Unlike a floppy disk, a Winchester disk rotates continuously. The Winchester drive is connected to the processor through the hard disk controller. All modern drives are equipped with a built-in cache (64 KB or more), which significantly improves their performance.

Advantages and disadvantages. Carriers. Advantages. Disadvantages. Diskette Compact, low price. Low speed of information exchange, small amount of memory, Disk Durable, convenient to use. Information is not secure enough, fragile. Winchester Memory capacity is significantly higher than flexible; the speed of information exchange is much greater. Immobile.