Do you have a chest of drawers? And how many drawers are there? Three four five? Each will give its own number, because chests of drawers are different.
I think you do not quite understand what I'm getting at, but it does not matter. With such a simple example, I want to explain to you what a hard drive (hard drive) is and what its structure is. And by the way, do not confuse two related concepts - a hard disk and a local disk.
Any hard drive (physical media that can be touched) can be divided into several sections, they are called local disks ( virtual disk, which exists in the “imagination” of a computer, which is necessary for its operation). And only in a single case both a local disk and a hard disk are one and the same thing (when one hard disk corresponds to one part - the local disk), but these concepts are not identical!It may be that several hard drives are one virtual. And vice versa - several local ones correspond to one hard one.
HDD - a physical storage medium that you can touch, see, buy.
Local disk - a virtual disk that does not really exist; it is created by a computer for convenience.
I hope you now understand what a local disk is and how it differs from a hard disk.
Why is this needed? After all, you can safely use the entire hard drive by simply creating folders and distributing all the information on them. Alas, this is not so. Breakdown hard drive into separate sections, called local disks, is necessarily a procedure that carries several useful functions at once.
The division itself can be carried out as during installation operating systemso after it. In the first case, this is necessary. In the second, the operation is carried out at the request of the user and requires the installation of special programs that serve to delete, create or change the volume of local disks. This is still difficult material, so we will not focus on it. You have a general concept and okay.
Each local disk is marked with a Latin letter, starting with “C” and then alphabetically. And now let's talk about what is the local C drive, which is available on each computer. Why is it so unique?
Local diskC
The most important part of the entire hard drive called the system drive is local drive C. The fact is that it is here (by default) that the operating system is installed. All its files and programs installed on the computer are stored there (again, by default). The user can use any other disk as he wishes, just specify the path during application installation.
what NOT do with local drive C:
- save important information on it - when changing the operating system it will be impossible to recover;
- try to delete files stored on it - you can delete files of the operating system;
- try to format it (although the system will not allow you to do this, anything happens) - the operating system will disappear;
- open it without urgent need - the likelihood that you will delete something increases.
In my opinion, the “Windows” OS has one major drawback. Important folders and files, such as “My Documents”, “My Music”, etc., are based on drive C. I don’t quite understand why, but what we have, we have. Just create similar folders on other drives.
By the way, if you try to download a file from the Internet, remember, a priori it will be recorded somewhere on this local disk (possibly in the “Downloads” folder). Just change the directory at boot.
So why all these precautions? Nothing is eternal. Including OS “Windows”. A situation may arise when you need to reinstall it. Nothing, it seems, is terrible. For an experienced user, this is not a problem at all, but!
When reinstalling the OS, FORMAT the local disk on which it was previously located. In this case, all information from this disk will be deleted. Of course, such a moment often does not happen. But the cause of the reinstallation may also be an accident, such as a sudden power outage, for example. No one is safe from this, and losing any important document or photograph will be very unpleasant. By the way when formatting one local disk, the information on the other remains unchanged. This is another reason why you need to split the hard drive (hard drive) into partitions (local drives).
Modern operating systems require a very large margin free space on the local drive. This should be taken into account when breaking down the hard drive into departments. I recommend that you allocate up to 20 gigabytes of memory for the local C drive. This will be enough for any version of “Windows”.
By the way, all temporary files that, without your knowledge, enter the computer from the Internet, are also based on the system drive (local drive C). This cannot be changed, therefore, if there is not enough space (the strip of memory under the local drive will be red, not green), you should clean it. The system itself will tell you how to do this (right-click on the desired drive \u003d\u003d\u003e line "properties" \u003d\u003d\u003e "erase disk").
Other local drives (D, E, F)
If it suddenly happened that your computer has only one local disk, then I strongly advise you to contact knowledgeable people who will help you break it into several parts.
Most often you will have several disks on your computer. Local drives D, E, F and so on - all of them serve exactly the same purpose. It is to store information. For your convenience, you should distribute files across disks, taking into account their contents. For example, if your computer is stored a large number of documentation, rename any local disk and store all the documents on it (Right-click on the disk \u003d\u003d\u003e “rename” line \u003d\u003d\u003e enter the name \u003d\u003d\u003e save). Arrange files into folders carefully and you will never get lost in your computer. If you take this without due attention, you run the risk of getting just such a local drive, more like a Vietnamese jungle.
So how many exactly local drives D, E, F should be on the computer? The answer to this question you must give yourself. For example, I use as many as six pieces! You can do even two (this is usually a minimum). The operating system will be stored on one (local drive C), and your information on the other (local drive D). World experience shows that even an office computer must have 3-4 local disks: a system one, for documentation, for entertainment (music, games, etc.) and for programs. You want to say that you work at work, and you don’t need any trash like mini-games and music tracks? Well, for now. I am 100% sure that in the future, having learned to use a computer at least a little, you will change your opinion. Therefore, let us now worry about the presence of several specialized local drives.
In my advice, I have repeatedly asked you to use the context menu. Do not remember what it is? Select any local disk and right-click on it.
There you will find a lot of useful functions that I suggest you explore on your own. Pay attention to the line "properties". Open this menu. There are several particularly useful features designed to speed up your system. This is a search for errors and defragmentation. From time to time, do both. This takes some time, but will help optimize the system.
Remember any dictionary. All terms go there alphabetically, right? And if they were going into a disagreement? Exactly. Defragmentation just allows you to build data “in alphabetical order”, that is, systematize them.
So, from this article you learned what a local disk is, and how the system (local disk C) differs from non-system (local disks D, E, F and others) disks. I hope this knowledge will help you master the computer.
How to create a disk D? Windows 7 is installed, there is one disk (C :) of 465 GB in size, in Disk Management, right-click on it and select Compress Volume. Further, as usual, the volume is polled for available space for compression, and what you think is that it does not compress more than 4 GB at a time. So I’ll divide it into two years, they say use Acronis on the forum, but I'm afraid he is dear, and I have never used it. Without a signature.
How to create drive D?
Let's carry out this operation using the tools of Windows 7 itself, maybe the person who wrote to us does something wrong, and at the end of the article we will create a disk (D :) using the Acronis Disk Director program, we also have an article on how to do this operation using a free manager hard drives.
- Note: If you try to compress the C: drive, only 40 or 50 GB are compressed, that is, the C: drive is not divided in half, respectively, the D: drive will be small, but you want it to be larger, then read our article " "
- Also drive D: You can create with free program (and in Russian)
We return to our article. As you can see, I have one system partition (C :) on my computer with a capacity of 464 GB and of course he will be sad without a friend.
The first thing we will do is to pluck the space from it for the future disk (D :), unfortunately this letter is occupied by the drive, so we will assign another letter. Also, my friends, if you had a drive (D :) for some reason, some problems disappeared, you can try to return it using this one of ours.
so create a disk (D :).Start -\u003e Computer, right-click on it and open Management, then Drive management, right-click on the drive (C :) and select Compress Volume in the drop-down menu.

Choose 300 GB to store your files and documents.
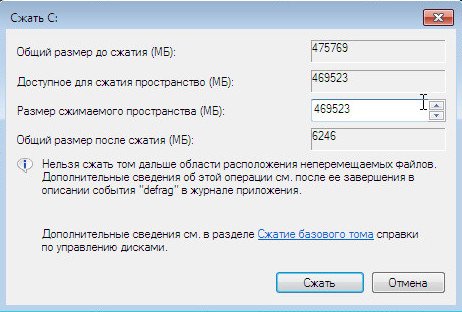
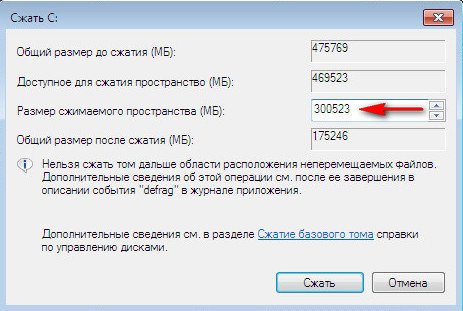
Unallocated space appears for the future drive (D :).
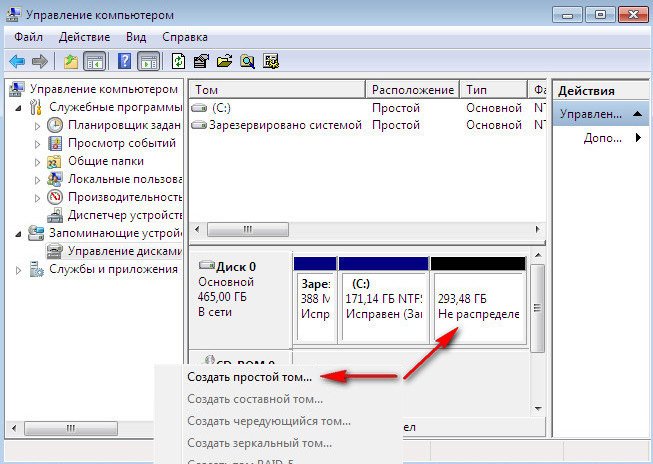
We right-click on it and select Create a simple volume from the Create menu or in other words create a disk (D :), we do not change the size, then.

Let the letter (E :), as I already noticed the letter (D :) is occupied by the drive.
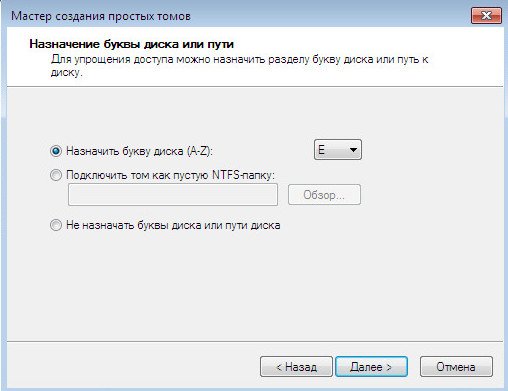
We don’t change anything in this window either, file system NTFS. Further. Done.

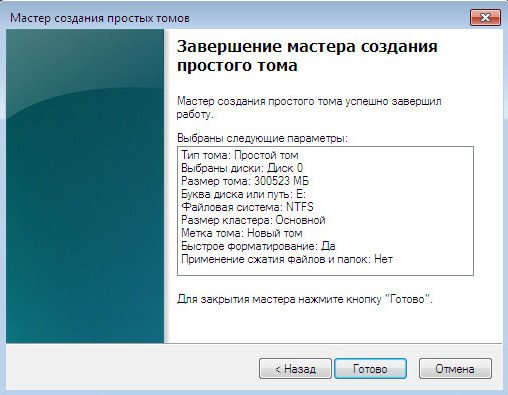
We look in Disk management what we did. Here you are, appeared new disc, only under the letter (E :), to store our files.
And now we will talk about how to create a disk (D :) using Acronis Disk Director. Personally, I always use boot diskhow to create it in the program itself, you can read from
Local disks in a computer perform the same function as pantries. Only in the pantries are stored a variety of things, from the right ones to all kinds of junk, and on local disks - information. There you can put anything you want - photos, music, movies and much more.
As a rule, there is at least one, at most several local disks on the computer. You can see their designations by going to the "computer" section. If you have two drives, you can see that one is called “local drive C”, and the second, respectively, “local drive D”. What is the difference?
It is better not to overload C drive with unnecessary information, since it stores all the main data of the operating system.
It’s not worth touching anything on it - this can lead to a freeze of the computer and incorrect operation . All the data stored on it is needed for the smooth operation of the computer.
The user can “add” all other information to the second local disk - “D”. It is specifically designed to store user information. Folders are created on it and data is placed. If this is not done, during a failure that is always possible, important information may be lost. In addition to the local disk “D”, you can also store data on other disks, if any. However, there are situations when there is only one local disk on a computer. How to be in this case?
Partitioning a Hard Disk
The answer is simple: you need to create an additional local disk yourself. This happens. This is very convenient, since in case of any malfunction of the operating system, you can reinstall it again, having one more local disk in stock. Creating new discs is as follows.
First you need to find the section in the "start" menu - "control panel". There, select the item "security", in it - "computer management". Find the item "disk management" there. Among them choose desired drive, place the cursor on unused memory, and press the right mouse button. Select "create ...", then name the new disk and specify the size of its memory. The disk is almost ready. It remains to format it, and can be used.
Disk compression to increase free space
It also happens that the local disk that needs to be divided does not have free space, but buy hard drive no opportunity. Then you need to resort to the compression process of the source disk. To carry out this action, you need to find the heading "extension ...." in the menu, click on it and specify a size that will be smaller than in the original disk. Then you need to do the same thing that you need to create a new local disk.
If something went wrong during the execution of all these actions, or the user can’t cope on his own, then it’s better not to take risks, but to use the services of professionals. Or ask someone from acquaintances who is well versed in this. The main thing is to do everything correctly and then work on the computer will go without problems, and with almost inevitable failures, valuable data will not be lost.
- Winchester, which is physical carrier information. The hard disk, in turn, can be divided into so-called local drives. Those. Winchester is a physically quite tangible object that you can touch with your hands. But local disks are partitions on the hard drive, which the operating system perceives as several virtual media. For ease of understanding, imagine an apartment with rooms. In this example, the total area of \u200b\u200bthe apartment is divided into several rooms. Rooms can be one, two or more. Those. we can say that rooms are local disks on one physical medium.
HDD Is a physical item designed to store information. You can look at it and touch it. Located in the system unit.
Local disk - This is a virtual storage medium that does not exist in a physical state and located in the form of a partition on a hard disk.
Why do I need local drives?
Why do we need local drives, because you can use the entire hard drive, "scattering" all the information in folders? Of course, you can do this as well, in which case you will have one logical drive, which occupies the entire volume of the hard drive. Let's go back to the apartment analogy. Suppose you have a sufficient size of the total area in which there is no division into rooms. Living room, bedroom (s), kitchen and bathroom are located in one room without partitions and doors. It is unlikely that you will be comfortable living in such an apartment. Also in the computer, the partition of the hard drive into logical drives serves for convenient storage of information and ensuring the normal functioning of the operating system. For example, on one disk you have the operating system and the programs you need installed, on the other you store music files sorted by folders, on the third video files and (or) photos, also arranged in folders.
You can see what disks you have in the system and their volume can be done by left-clicking on the button "Start"select menu item "A computer".
Creating local disks and storing information on them.
Local disks are created during the installation of the operating system using the prompts of the installation program, the so-called installation wizard. It is possible to create, delete, split and merge local disks even after the installation of the system. There are special programs. The operating system always assigns a Latin letter to all local disks: C, D, E, etc. In addition to the letter designation, you yourself can also give a name to the disk or rename it. For example, call drive “System,” and drive D, “Documents.”
On the example of Windows 7, to give a name to a disk or rename it, left-click on the button "Start" c, on the right side of the menu, select "A computer". A window opens with the available local drives. Select the desired drive, and right-click to bring up the context menu where select "Properties". In the window that opens, enter the name of the disk and click "Apply". In the properties window, you can also see the total size of the local disk, how much space is used for files and folders and how much is free.
Depending on the hard You can create several local drives. They can be the same size or different, depending on your needs. Let's say you store a lot of movies and photos on your hard drive. In this case, it would be reasonable to allocate a larger volume for the video collection than for the disk under the photo, because Video files are large.
No matter how many local partitions you have on the system, the most important is C drive, which is called the system drive. Here, by default, the vast majority of programs are installed. Under the system partition, it is recommended to allocate 50-60 GB of space. It is not recommended to store your documents on drive C, as if you need to reinstall the operating system, then you risk losing all your data. During system installation, all data in this section is erased. Therefore, make yourself a rule not to store your documents on section C, despite the fact that by default in Windows, data for saving is sent to the My Documents pack on this section. To do this, any available local drive is suitable.
Share.If you have one hDD, for the convenience of using a computer, it can be divided into two parts - the operating system will be placed in one, and the files will be stored in the second. This will allow you, for example, to reinstall the operating system without affecting the files, and will make it possible to organize the data on your computer.
Ideally, of course, you should split the disk even at the stage of installing the operating system, which we discussed in detail in. But you can do this already after installation. To create a local disk D in addition to the existing system disk C, read below. But keep in mind: before proceeding with disk operations, be sure to create backup operating system and important files in case something goes wrong.
Disk compression
You can create new discs using the Disk Management utility. To start it, open the Start menu, select “Run” and in the window that appears, enter “diskmgmt.msc” (without quotation marks), and then click the “OK” button. If you have Windows 8, just type on the start screen keyword “Partition” (without quotes) and select “Create and format hard disk partitions” in the results.
In any case, the "Disk Management" window will open. To make drive D from drive C, first you need to free up space for it. Select drive C, right-click on it and select the "Compress Volume" option. The system analyzes the distribution of data on the disk and displays a dialog box with a message about how much space can be freed up in this way and what will be the size of the disk after compression. Click OK.
Create a new disc
And now it’s possible to create disk D. To do this, right-click on the unallocated space and select the option “Create a simple volume” in the menu that appears. The Create Wizard window appears. simple volumes. The first page is just a greeting, so click Next immediately.
In the next window, you can change the size of the future disk, but, in principle, the maximum possible value is set by default, and if you are not going to create two new disks from unallocated space, then you do not need to change anything. Click "Next".
At the next step, you can select the drive letter - most likely, option D will be specified by default, but if not, you can specify the drive yourself. Other settings do not need to be changed. Click "Next".
Now you should format the disk so that you can use it right away. The default settings for you have already been selected and most likely you do not need to change them, but if you wish, you can enter some understandable name in the “Volume Label” field, for example, “Files” or “Multimedia” so that when viewing a disc in The conductor immediately understood what was stored on it. Then click the “Next” button.
On the final page, you will have the opportunity to once again check the selected settings. After making sure that everything is in order, click the Finish button. After that, the system will start creating and formatting. Depending on the size of the disk, this can take quite a while. But after the procedure is complete, you will already have two disks - C and D.
Third Party Utilities
You can create drive D from drive C not only using the operating system itself, but also using third-party programs. Among the most famous developers of this kind software - Acronis, EaseUS, and Paragon, although not all of them offer free versions their products. In addition, there is a free Linux-based GParted utility that allows you to perform operations with hard disks by booting a computer from a USB flash drive or CD. However, the optimal solution for creating partitions in Windows is still the built-in “Disk Management” tool, especially when manipulations are planned with system drive C. So the risk of disabling the system is minimal.