How to choose a hard drive. The hard drive must also be chosen correctly so that it is smart, quiet and reliable. Unfortunately, you do not have time to look around, as the disk is already filled to capacity. There are users who, even after several years, have enough disk space to work for another 10 years.
But this is usually the exception. For many, the hard disk space is sorely lacking, and sometimes just somewhere. Now a computer is not just a typewriter. Many users are engaged in serious projects on it and earn good money on it. And the hard drive, as you know, stores a lot of useful information, so you should not buy it anyhow.
How to choose a hard drive
It all depends on what you will do on your computer. It’s best if you have more than one hard drive on your computer, but two or even three. How to install such a drive, read. On the main disk you will have operating system, and the rest is better to store your data.
Usually hard drive space is sorely lacking. Do not think that you are the only one. Now I even wonder how I once had enough of 10 GB. The most annoying thing is that all files are needed and expensive, and I don’t want to delete anything at all.
Any device has its own parameters and resources, and the computer’s hard drive is no exception. If you just come to the store and ask for a disk, then they may not advise you what is needed, but most likely what is more expensive. Why overpay if you can take the same or the remaining money.
WHERE IT IS POSSIBLE TO STORE YOUR DATA EXCEPT THE HARD DISK
Previously, you could write your data onto a “blank” (CD or DVD) and sleep peacefully. Now everyone has so much information on computers that there is no longer any way to copy everything to a CD. At best, you can rewrite something most important.
And still it is not very convenient. You won’t carry around a whole briefcase with CDs or DVDs and insert one by one into the drive to find the information you need.
You can buy small in size, but large in volume external drive and carry it with you. But, again, there is no guarantee that one day he will not be “buggy”. And then “goodbye” valuable information. I recently had it. But now is not about that.
2.5 'external hard drive
Capacity (volume) of the hard drive
A large disk volume is not needed for the operating system. Since the minimum disk capacity of 500 GB is currently on sale, this is enough for your eyes. But another disk, if you constantly download something from the Internet, you need to take as much as possible.
Spindle speed
For an operating system, you need a disk with a good spindle speed. At low speed, your operating system will slow down, no matter what memory it is, or whatever the microprocessor is smart.
Everything should be in a complex. Otherwise, you will throw away “money down the drain”. Saving on the hard drive is impossible!
Modern hard disks (HDD) 2.5 and 3.5 ”have a spindle speed of 5400 or 7200 rpm. The higher the spindle speed, the higher the speed of the disk.
For home computer hard speed the disk on which the operating system, graphics programs and your games will be installed must be at least 7200 rpm.
If you buy a drive for the office, then 5400 rpm is enough. The same speed is suitable for data storage, i.e. second hard driveespecially since it is cheaper.
There are drives with an SAS or SCSI interface, with a speed of 10,000 and 15,000 rpm, but they are used for servers, and are not cheap.

SCSI Hard Drive
But if you have old computer and IDE hard drive, then the choice is not big, and you can forget about the good speed of the spindle drive. And finding such a drive is already problematic.
How to identify an old hard drive or not
If your drive has a wide loop, then this is the IDE interface. They are no longer used in new computers, and the speed of these drives is low.

IDE cable
New computers install hard drives with sATA interface, SATA 2, and SATA 3.

SATA cable
The data transfer speed of a SATA drive is 50% higher than that of an IDE drive.
SATA, SATA 2, and SATA 3 drives are interchangeable. But the data transfer speed of SATA 3 is much better than that of SATA.
Please note that the SATA and SATA2 drive cable are not suitable for SATA3 drive. They have different frequency characteristics, although the connectors are the same and they will work anyway. The cable (cable) for SATA3 is thicker and usually black.
It is also important to know what type of SATA hard drive your motherboard supports, otherwise the drive will not work at full capacity. But this is not critical. But if the motherboard is very old, then sATA drive it may not support at all, i.e. there will be no connector for it.
Buffer size or cache size
The next item to select a drive is memory cache size (buffer memory). There is a cache size of 8, 16, 32, 64 and 128 MB. The higher the number, the better the data processing speed.
For storage, 16 MB is suitable, but it is better to buy from 32 MB for the system. If you are engaged in graphics, then for programs such as Photoshop and AutoCAD, it is better to take a hard drive with cache memory - 64 or 128 MB, especially since the price difference between them is not significant.
Medium linear read speed
Linear read speed means the speed of continuous reading of data from the surface of the plates (HDD) and is main characteristicreflecting the actual performance of the disk. It is measured in megabytes per second (Mb / s).
Modern HDD drives with SATA interface have an average linear read speed from 100 to 140 Mb / s.
The linear read speed of HDD disks depends on the density of data recording on the magnetic surface of the plates and the quality of disk mechanics.
Access time
This is the speed with which the disk finds the desired file after accessing the operating system or any program. Measured in milliseconds (ms). This parameter has a big impact on the performance of the disk when working with small files and not large - when working with large files.
Hard drives have an access time of 12 to 18 ms. A good indicator is an access time of 13-14 ms (depends on the quality (accuracy) of the disk mechanics).
Now there are new hard drives for sale - SSDs consisting of only microchips, but they are very expensive and therefore not intended for data storage. They are only good for running programs. SSD drives do not have a spindle, therefore completely silent, do not heat up, and are very fast.
And the most important! Try not to install hard drives right next to each other. It is better if there will be more space around them, because during operation, they become very hot and can fail due to overheating.
And even better, especially in the summer - to cool them by opening the computer cover and directing a fan on them. Overheating for a hard drive is just as fatal as it is for a video card and microprocessor.
Any company manufacturer of disks has discs more expensive and cheaper. But this does not mean that companies are juggling. Just one product for state employees, and the second for the more affluent. Both discs are made in good faith, but the parts are made of different materials that have different wear periods.
Hard drive manufacturers
Major manufacturers hard drives (HDD) are:
Fujitsu - The Japanese company, previously famous for the high quality of its products, is currently represented by a small number of models and is not very popular.
Hitachi - The Japanese company, both earlier and now, is characterized by stable quality of hard drives. By purchasing a Hitachi hard drive you will not lose, getting good quality at an affordable price.
Samsung - This is a Korean company. Today, Samsung produces the fastest and highest quality HDD drives. The price of them may be slightly higher than that of competitors, but it is worth it.
Seagate - An American company, a pioneer in technology. Now the quality of the hard drives of this company, unfortunately, leaves much to be desired.
Toshiba - Japanese company. Now represented by a small number of models in our market. In this regard, there may be problems in servicing such manufacturers.
Western Digital (WD) - An American company specializing in the production of hard drives. IN lately, the discs of this company are not distinguished by outstanding characteristics, and are very noisy.
It is better to choose between Samsung or Hitachi, as the most high-quality, fast and stable.
So, the main characteristics of hard drives:
- Spindle speed
- HDD capacity
- Cache size
- Average Linear Read Speed
- Noise level
- Manufacturer
Now you know which hard drive to choose. Unfortunately, there is not always a choice in stores, so I prefer to order online. In big cities there is more choice. Therefore, do not be lazy and study their main characteristics.
Initially, a computer was invented to calculate data and solve various problems. But an important function of the computer was the storage of various data. The amount of information stored depends on the capacity of the drive. In this article we will discuss a simple, but for many ambiguous problem in choosing the right characteristics of the hard disk capacity. So what is the amount of hard drive you need to choose for your personal computer?
The capacity (volume) of the hard drive is an indicator of the maximum amount of information that your hard drive can save. Hard disks are now common with volumes ranging from 100 GB to 5000 GB (5 TB).
So, let’s take a look at the optimal and maximum hard drive capacity of average personal computers presented in stores today.
After browsing several online computer equipment stores, we analyzed the hard drives presented there and pretty clearly saw that the maximum volume of drives is in the region of 4-5Tb, and the cost varies around 300-500 US dollars.
We can’t say that the presented drives will appeal to a wide circle of customers, because the prices are not very friendly. Yes ordinary user and you don’t need such a volume drive.
How much data to choose
This leads us to the conclusion that such a volume of the drive will be redundant, and it is suitable only for specific requirements. But one should not exclude the fact that there are fans of collecting films or games that just lie and “gather dust” on the hard drive, but there are very few such strange people, since almost everyone has the Internet. Or there are people who really need to keep the source of uncompressed video files after installation. Such files really take up a lot of space, so you may need several 5TB drives. If you are such a fan of shooting videos or storing a lot of films, then this option is just for you.
But returning to the review of online stores of computer equipment, we see that drives from 500 to 1000 GB are the most popular. For a regular personal computer, 500 GB is enough for our opinion. Let’s explain why: the volume of installed software (operating system, different programs) will not exceed the size of 50-60 GB, music will occupy (if you are not a music lover) about 10-60 GB, films, games will take up space in the region of 100-150 GB, it will take all the rest about 20-50GB. As a result, after several years of accumulating information, about 250GB will be occupied, and another 250GB will simply be empty. If you follow such calculations, then for especially economical users, a hard disk of 250-320 GB is enough.
Note that everything presented in this article is purely individual, but the above calculations will completely cover the average user’s request with a personal computer. So before choosing a hard drive for your personal computer, you should first of all think about what exactly you will store on your hard drive. Even if the calculations are incorrect, you can always buy another drive. If you have a laptop, you can always buy external hard disk. Of course, with choosing hard A disk needs to consider many factors, such as price or volume, data transfer speed, but more on that later.
Such are the arguments on the volume of hard drives on personal Computer. Ultimately, the choice of drive volume is yours.
- the amount of data that can be placed on disk. The volume of modern, which can be found on sale, can reach 2 TB or 2000 GB. Manufacturers designate the volume of the hard drive as a multiple of 1000, and not 1024, as it should be. And in the end, the physical volume declared as “2000 GB” is 1863 GB.
The volume of the hard drive needs to be calculated depending on the tasks that it will face.
. How much do you need?
For office PCs 120-200 GB will be enough.
For multimedia computers Already need at least 500 GB, unless of course you are going to clog his video files with high resolution.
One film, depending on the resolution (720p or 1080i), takes on the hard disk from 4 to 10 GB;
Blu-ray movie takes up to 25 GB of space;
Season 1 of the popular series, depending on the quality, will take from 6 to 120 GB on your disk. Moreover, we are talking about one season and all seasons can weigh quite a lot;
With music a little easier. One album in lossless quality format (FLAC, Ape) rarely weighs more than 600 MB, however, the full discography of one group can even take up 20 GB, but this is rather the exception, mainly the discography of 12 albums takes 5 GB.
For gaming computers The volume should be at least 400 GB. Of course, nothing prevents you from choosing a larger hard drive, but you should not turn the hard drive into a storage of images and installed gamesthat you don’t play.
It should be borne in mind that modern games already require up to 20 GB free space on disk for installation.
For myself, I see no reason to buy too voluminous hard drives. Yes, the quality of digital content is growing quite quickly, and with it the size of this content is growing. But along with this, the speed of access to the Internet also increases. And options are already being created when all the content will be stored on special Internet servers, and the user will be able to view them without downloading. And for this you will need special systems in which the hard drive will be replaced with a more efficient flash memory.
Technology Comparison Chart
| Ibm ramac | Maxtor 7040A | WD 20EARS | |
| Year of issue | 1956 | 1991 | 2010 |
| Volume | 5 MB | 40 MB | 2 TB |
| Number of plates | 50 | 3 | 4 |
| Plate diameter | 24 inches | 3.5 inch | 3.5 inch |
| Recording density | 2 kbps 2 | 10 Mbps 2 | 347 Gbps 2 |
| Rotational speed | 1200 rpm | 3500 rpm | 7200 rpm |
| Average access time | 1 s | 30 ms | 5.6 ms |
| Maximum interface speed | 9 kb / s | 800 kb / s | 300 MB / s |
| Unit cost | $ 10,000 / MB | $ 6 / MB | $ 0.08 / GB |
Today, of course, interesting, but at the same time difficult times for the drive industry. The transition to high-resolution multimedia formats has significantly improved the visual component, but also affected the requirements for data storage subsystems accordingly. The volumes of digital sound, video and photos are constantly increasing, which requires more and more storage capacity. Therefore, today 3.5 "hard drives have already reached 750 GB. Unfortunately, performance cannot grow at the same speed.
The industry has come a series of takeovers. Maxtor bought Quantum several years ago, after which the company merged with Seagate. Hitachi, Samsung and Western Digital are still on the desktop hard drive market.
Seagate is the leader in capacity today, providing 750 GB for the 3.5 "Barracuda 7200.10 drive, Samsung is renowned for its quiet operation and good capacity / price ratio. Western Digital Raptor hard drives at 10,000 rpm have been leading in performance for several years, although initially they They were positioned on the entry-level professional market, and Samsung, finally, can significantly advance due to the release of hybrid hard drives.This is the only company in the four engaged in the production of not only hard drives, but also flash memory.
All modern 3.5 "drives have a maximum read speed of at least 55 MB / s, and access time is 15 ms or less. The fastest models at maximum speed exceed 70 MB / s, and access time, on average, is 13 ms. Western Digital Raptor hard drives deliver over 85 MB / s with a very low access time of 8 ms. Ideal if you want to get quick start applications or just more fast boot Windows Although for this you will have to pay a higher price and lower capacity compared to traditional models. If you are interested in the performance of modern hard drives, check out the reviews in our section.
Of course, many will have a question: what do all these numbers mean in practice? How to compare hDD with other components in the pc? How much is the performance of modern hard drives different from the old ones? Can a modern hard drive easily get around old models?
This time we decided to add old hard drives to our testing. Yes, we tried to find really ancient models. Interestingly, they still work great, despite the fact that they were born in the era of MS DOS 5.0 and Windows 3.1.
Hard drives: from 40 MB to 750 GB, from 3,500 to 10,000 rpm
We decided to go back about 15 years ago, when IDE hard drives were just beginning to appear with very decent by the standards of 40 MB. Then we took the model of the mid-90s (3.2 GB), then increased the capacity to a double-digit number (10 GB) and, finally, upgraded the hard drive to 60 GB. The latest models are represented by the market leaders in hard drives: Seagate Barracuda 7200.10 for 750 GB and Western Digital Raptor RD1500 for 150 GB and 10 000 rpm.
| Manufacturer | Maxtor | Quantum | Ibm | Seagate | Seagate | Western digital |
| Product | 7000 Series IDE 3524 | Fireball st | Deskstar 16GP | Barracuda iv | Barracuda | Wd raptor |
| Model number | 7040A | ST3.2A | DTTA-351010 | ST360021A | 7200.10 | WD1500ADFD |
| Capacity | 40 MB | 3.2 GB | 10.1 GB | 60 GB | 750 GB | 150 GB |
| Spindle speed | 3524 rpm | 5400 rpm | 5400 rpm | 7200 rpm | 7200 rpm | 10,000 rpm |
| Other capacity options | 60 - 130 MB | 1.6, 2.1, 3.2, 4.3, 6.4 GB | 3.2, 4.3, 6.4, 8.4, 10.1, 12.9, 16.8 GB | 20, 40, 60, 80 GB | 500, 400, 320, 300, 250, 200 GB | 74, 36 GB |
| Number of plates | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 to 4 | 1 to 4 |
| Number of heads | 5 | 4 | 6 | 3 | 8 | 8 |
| Capacity per plate | 26 MB | 1.6 GB | 5.6 GB | 40 GB | 200 GB | 37.5 GB |
| Cache | 32 - 64 kb | 128 kB | 512 kB | 2 MB | 16 MB | 16 MB |
| Interface | IDE | UltraATA / 33 | UltraATA / 33 | UltraATA / 100 | SATA / 300 | SATA / 150 |
| date of manufacture | 1991 | 1996 | Jul-98 | 2003 | 2006 | 2006 |

Before us is a hard disk of 40 MB (yes, megabytes) with three plates rotating at a speed of 3500 rpm. The interface is a regular IDE. The hard drive was made in 1991, and at that time it was a very average model. The top-end Maxtor 7000 Series hard drive had a capacity of 130 MB, distributed across eight plates. 32 or 64 KB of cache memory was integrated into the hard disk, depending on the model. Specifications still available on the Maxtor website if you search well.
The capacity of 130 MB for the top model was then the limit, although quite quickly the volume increased to 170 and 240 MB. Curiously, all the hard drives at that time cost several hundred dollars. Today you get a thousand times more capacity, moreover, cheaper!
The hard drive is too old, so PCMark05 refused to run tests on it. But we were able to run the test c "t magazine h2benchw 3.6. The average access time of the 7040A was 27 ms, which seems like an eternity compared to 8-15 ms with modern 3.5" hard drives. The bandwidth of the interface is 800 kB / s (0.8 MB / s) against the current 80-200 MB / s. Actual read performance is also close to this value: h2benchw showed 600-700 kB / s, which can be compared with the four-speed CD-ROM. Any modern drive, quite naturally, overtakes the 1991 hard drive.



Quantum Fireball appeared five years after the 40 MB Maxtor hard drive discussed above. Capacity ranged from 1.6 to 6.4 GB. As you might guess, the new generation has some improvements. Fireball ST 3.2A got a double cache (128 kb) and got a higher spindle speed - 5,400 rpm. The drive turned out to be one of the first equipped with an UltraATA interface at 33 MB / s, in addition, it first began to use magnetoresistive read / write heads.
The throughput of the interface was 31.3 MB / s, which is very close to the theoretical maximum, and the internal data transfer rate was declared at 132 Mb / s (about 16 MB / s). In reality, we got almost 10 MB / s. If you count, this hard drive offers 80 times more capacity than the Maxtor model. Or 50 times larger when comparing the 6.4 GB Fireball with the top 130 MB Maxtor model. The speed increased by about 13 times.
Around the same time, users began to say goodbye to the old 16-bit FAT file system in favor of FAT 32 on Windows 95, NTFS on Windows NT, HPFS on OS / 2 or ext2 on Linux. FAT16 is built on 16-bit cluster addressing. A cluster is the smallest disk element that the controller understands. One FAT 16 cluster contained a maximum of 32 kbytes, which, with 65,536 possible addresses (2 16), gave a maximum amount of 2 097 152 bytes or 2 GB.
Of course, this limitation could be circumvented by creating several partitions, but the new FAT 32 file system, in which the cluster addressing was increased from 16 to 28 bits, was the best solution. This made it possible to address millions of clusters ranging in size from 4 to 32 KB, depending on the size of the partition. FAT 32 theoretically supports partitions up to 2 TB (terabytes, thousand gigabytes), but since the high capacity of the partition increases the size of the FAT 32 table (256 MB in the case of a 2048 GB partition), it’s better to use a more modern one due to other limitations file system. For example, nTFS systems under Windows XP or ext3 under Linux.


With the launch of the DeskStar 16GP line, IBM, while still engaged in the production of hard drives, introduced giant magnetoresistive heads (Giant Magneto-Resistive, GMR), an important step to overcome the capacity of 10 GB per hard drive. Indeed, the announcement of more sensitive GMR-heads allowed to increase the maximum capacity of the hard disk in the IBM lines from almost 9 GB to 16.8 GB.
This line of hard drives came with different capacities: 3.2, 4.3, 6.4, 8.4, 10.1, 12.9 and 16.8 GB and used up to three plates. The hard drives were equipped with 512 KB of cache and an UltraATA / 33 interface. DTTA-351010 showed a maximum data transfer rate of 12.4 MB / s, while the throughput of the interface was 31.4 MB / s.



Seagate Barracuda hard drives with capacities ranging from 6.8 to 26 GB were the first desktop models with speeds of 7,200 rpm. But the first generation was quite noisy, and the hard drives warmed up significantly. The second and third generations have improved significantly in these respects, and the capacity has increased to 40 GB. But only the fourth generation of 7,200 rpm desktop hard drives turned out to be really fast and quiet.
The Barracuda ATA IV line was characterized by a higher data recording density, which allowed Seagate to reach a capacity of up to 80 GB with just two plates. In addition, a distinctive feature of this line was the metal plate below, which protected the electronics of the disk. Seagate named it Seashield, very similar to the name of the plastic packaging Seashell. However, later, Seashield had to be abandoned for price reasons.
The fourth "barracuda" was among one of the latest generations of drives produced only for the parallel ATA interface, since at the end of 2003 the fifth generation of Barracuda ATA V was announced with support for the Serial ATA interface and up to 120GB capacity. All fifth-generation Barracuda drives use the Serial ATA or UltraATA / 100 interface (like this model).


750 GB Seagate Barracuda 7200.10 and WD Raptor WD1500, 150 GB (2006)
Before us are two relatively new hard drives. In order not to repeat and not to tell again their characteristics, we will provide links to relevant reviews.
- Seagate Barracuda 7200.10 750 GB: Superior Capacity and Performance
- WD1500AD Raptor-X Hard Drive: Desktop Performance Leader
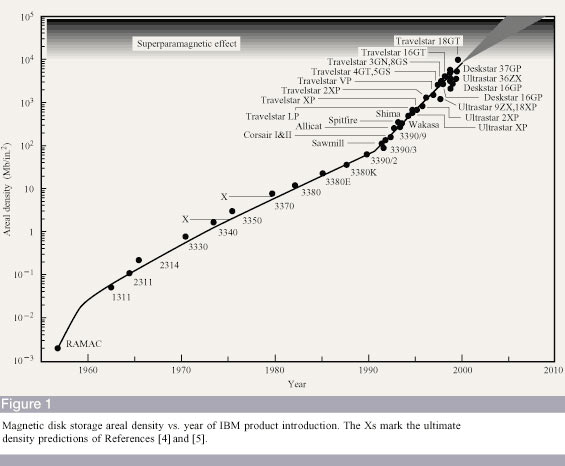
The increase in recording density is impressive: over the past 15 years, it has increased 10,000 times!
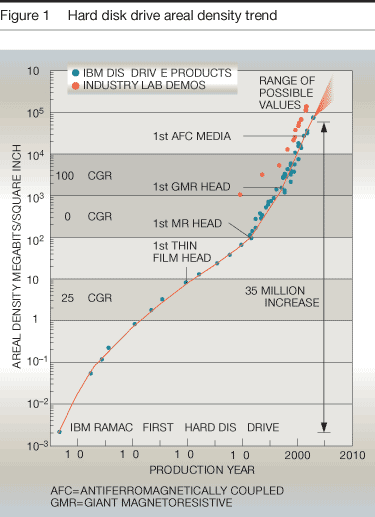
The hard drive industry is still looking for ways to increase recording density. The latest technology of perpendicular recording (Perpendicular Magnetic Recording, PMR) is built on the vertical orientation of magnetic domains instead of horizontal, which allows you to store more bits in the same area.
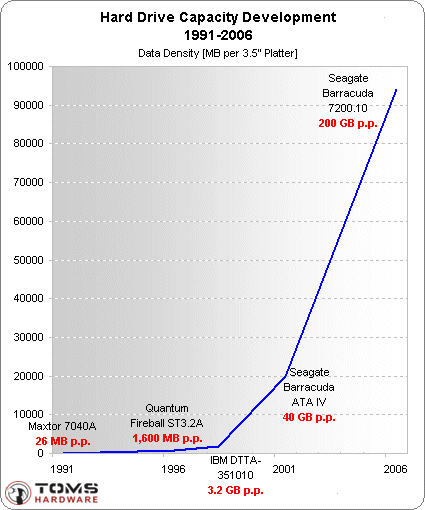
If we take the maximum capacity of 130 MB for 1991 and compare it with modern hard drives of 750 GB, then we can calculate: over the past 15 years, the capacity has increased 5,700 times. If we compare the capacity of the plates, the difference will be even greater.
As you can see, the progress in recording density has been very significant. Unfortunately, the performance of hard drives has grown far from the same pace.

If we compare the performance of the 1991 Maxtor hard drive (0.7 MB / s) with the modern Barracuda 7200.10 hard drive at 750 GB (64 MB / s), we get an increase of 91x. If we compare it with 85 MB / s on the WD Raptor hard drive at 10,000 rpm, then we will get an improvement of 121 times.
That doesn't sound too good. Now let's take into account the average size of files and programs. If executable microsoft file Word used to occupy no more than a few megabytes and even less space in RAM, then modern applications easily master dozens of megabytes. And they call additional code in the form of plugins, libraries and extensions. For example, Adobe Photoshop CS2 consumes more than 60 MB of RAM, moreover, most of this information needs to be read from the hard drive. Or think about photographs: about ten years ago we worked with JPEG files of size 640x480 and a volume of several tens of kilobytes. Today we are no longer surprised at photos of several megabytes with a resolution of 3872x2592.
Recording density and performance
If we compare the increase in recording density with the increase in productivity, then immediately the discrepancy becomes noticeable: almost 6,000 times more capacity and only 100 times increased productivity. In other words, capacity grew 60 times faster than performance! What do the results of our testing say?
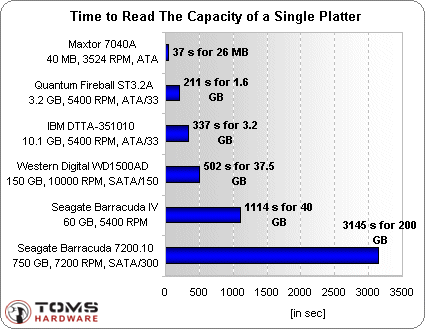
Look at the results. They clearly show that although the performance of the hard drive in absolute values \u200b\u200bhas increased, the performance relative to the capacity of the hard drive decreased significantly! From this point of view, modern hard drives are no faster than old models. Judge for yourself.
In 1991, a 40 MB hard drive took 37 seconds to read the capacity of one plate (26 MB).
In 1998, a 3.2-GB hard drive took 3 minutes and 31 seconds to read the capacity of one plate (1.6 GB).
In 1999, a 10 GB hard drive took 5 minutes and 37 seconds to read the capacity of a single plate (3.2 GB).
In 2004, a 60 GB hard drive took 18 minutes and 34 seconds to read the capacity of one plate (40 GB).
In 2006, a 750-GB hard drive took 52 minutes to read the capacity of one plate (200 GB).
Of course, this comparison is greatly simplified and does not take into account other factors, for example, the number and diameter of plates, rotation speed and average file size. The results will also turn out to be different if we take other hard drives and other capacities for comparison. But the trend will be the same: the time it takes to fill or read a full hard drive has significantly increased over the past 15 years.

Over the same 15 years, a series of purchases and mergers has taken place in the hard drive market. Maxtor bought Quantum several years ago, and by the end of 2006, Seagate will complete the merger with Maxtor.
Why is hard drive performance so important?
Any user can easily answer this question: just turn on your PC or laptop, after which you will notice that most of the delays and expectations are associated with reading data from the hard disk. At windows startup reads information and fills the RAM. Although the OS boot time has decreased in recent years (partly due to BIOS optimization), and some PCs start in 15-20 seconds, hard drives are the same bottleneck that significantly limits PC performance.
Who likes to wait 30 seconds or more while the computer boots up? And wait 20 seconds until the game or program starts? And the few seconds that are required to close the application is also not the best option.
Another important issue is redundancy. It takes almost an eternity to read the entire hard drive. How long does it take to reserve? In recent years, along with an increase in the volume of user data, the backup time is also increasing. If documents can be copied quickly enough, then what about custom databases of photos, videos, and music?
Test configuration
| System hardware | |
| Processors | 2x Intel Xeon (Nocona Core), 3.6 GHz, FSB800, 1 MB L2 Cache |
| Platform | Asus NCL-DS (Socket 604), Intel E7520 chipset, BIOS 1005 |
| Memory | Corsair CM72DD512AR-400 (DDR2-400 ECC, reg.), 2x 512 MB, delay CL3-3-3-10 |
| System hard drive | Western Digital Caviar WD1200JB, 120 GB, 7200 rpm, 8 MB cache, UltraATA / 100 |
| Drive controllers | Intel 82801EB UltraATA / 100 (ICH5) Silicon Image Sil3124, PCI-X |
| Network | Integrated Broadcom BCM5721 Gigabit Ethernet Controller |
| Video card | Built-in ATi RageXL, 8 MB |
| Tests and Settings | |
| Performance tests | c "t h2benchw 3.6 |
| Input / output tests | IOMeter 2003.05.10 Fileserver-benchmark Webserver-benchmark Database benchmark Workstation benchmark |
| System software | |
| OS | Microsoft Windows server 2003 Enterprise Edition, Service Pack 1 |
| Platform driver | Intel Chipset Installation Utility 7.0.0.1025 |
| Graphics driver | Default Windows Graphics Driver |
Any modern hard drive is quite capable of coping with your daily data. And most of them give good enough speed for everyday tasks. But if you don’t like to wait, your budget is not limited to a student scholarship, or your requirements are simply high, then you can’t do without a Western Digital Raptor hard drive at 10,000 rpm. Everyone else can recommend a decent model at 7,200 rpm, it costs less, and the capacity gives a good one.
Over the past fifteen years, the capacity of hard drives has increased faster than performance by more than an order of magnitude! That is why hard drives are the most bottleneck of your PC today. Whether you boot or shut down your computer, launch applications and games, write or read files, transfer large amounts of data, you will immediately notice how performance rests on the hard drive. Fast hard drives and interfaces reduce the tedious wait, but even high-performance RAID-arrays on several hard drives do not allow to get rid of it.
In any case, there is no one to blame. On the contrary, we must evaluate all the work and the genius of engineers and scientists in hard drive manufacturing companies that are trying to squeeze out the capacity, and with it the performance of the technology, which in essence has not changed over the past 50 years. (The IBM 305 RAMAC drive was announced in 1956.)
Prospects
The performance situation is unlikely to change unless there is a revolution in technology. While hard drives are built on rotating plates, we are unlikely to circumvent the limitations of this physical mechanism. Fortunately, the new generation of hard drives is built on perpendicular recording technology, which allows you to create hard drives with a capacity of several terabytes and squeeze even more performance out of them.
Windows Vista will improve the situation programmatically. The new OS has smart prediction and caching technologies, for example, SuperFetch, which allow you to load your favorite applications into the RAM cache, as a result of which startup time is noticeably reduced. Other technologies, such as flash-based hard drives, reduce access times to a minimum, but only at the cost of a high price per gigabyte. In addition, flash drives are not yet able to bypass hard drives in terms of data transfer speed.
32GB Flash Drive Samsung Flash SSD: Goodbye Legacy Hard Drive Products
Deskstar - ATA / IDE Desktop Hard Disk Drives
Why is a hard drive called a hard drive?
Hard drives began to be called Winchesters in the USA in the 70s of the XX century. Then IBM released the first analogue of modern hard drives: a device consisting of two cabinets, inside of which there were magnetic disks with a capacity of 30 MB each.
It was marked with the inscription "30x30" - exactly the same inscription was present on the rifle of the well-known company "Winchester". At first, hard drives were called "winchesters" for fun, but soon the name was firmly entrenched in them and became almost official.
Not everyone knows that there are several hard drives on the computer. For example, opening the My Computer program, we see the drive icons C, D, E, F. But this does not mean that you have one hard drive - in most cases, these are several logical disks on which the only physical disk is installed on the computer.
But it also happens that several physical drives are installed on the computer, if you are not afraid to open your system unit and find them, if again you know how they look.
Each of the hard drives can be marked with one Latin letter, or in turn can be divided into several logical drives. This is convenient, for example, for storing separately movies, games, documents, photos. And also in case of disk defragmentation by programs, which will take less time.
So how do you determine the number of hard drives on a computer without opening it?
Everything is very simple. Click "Start" and right-click on the item "Computer". You can also click on the My Computer icon on the desktop, unless this icon is without an arrow at the bottom, that is, it is not a shortcut. In the context menu that appears, select the "Manage" item.
This window will open:

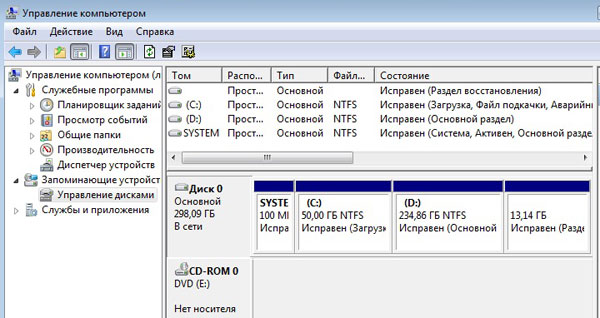
Here you need to select the "Disk Management" section. The display will show information about the physical drives and the logical volumes to which they are mapped. The following illustration shows an example of a single hard disk partitioned into two logical drives. There are also two hidden partitions designed for the system needs of the computer - they do not interest us.
And here we see two at once hard drive - Disk0 and Disk1:

Disk 0 is divided into logical - C, D, E, F. We do not see all the letters here. If you have Windows installed on Disk0, then even after removing Disk1, the operating system will quietly boot.
Disk 1 - whole and not divided into logical partitions, marked with the letter G.
How to find out the actual hard drive capacity
For a better understanding, manufacturers and sellers indicate the traditional volume of disks: 40, 60, 120, 160, 320, 500, 640 GB and so on. However, in reality it is always less than stated, because:
1 GB \u003d 1024 MB
1 Mb \u003d 1024 Kb
1 Kb \u003d 1024 bytes
ANDso we see that logical drive C has a capacity of 400.76GB, and the physical drive G - 931.51GB. The total size of drive C can be found by adding up the volumes of its logical drives.
First things first, you need to learn that there are 2 types of “screws” (hard drives) for desktop computers, mostly differing in the type of connection:
- IDE (he ATA he PATA ) — obsolete but still used type of hard drives. Visually, it can be distinguished by a wide cable slot (40 pins in 2 rows) at the end of the HDD itself (hard disk) and four thick contacts on the right to connect the power cable. You can read more about the ATA standard on Wikipedia

- SATA (SATA2) - next, more advanced level in the development of the previous standard. It has much better performance in terms of data exchange. And this means recording, copying, deleting your favorite movies, music, movies, your computer will be faster.

The main characteristics of the hard drive:interface, capacity, buffer volume, physical size (form factor), random access time, data transfer rate, number of I / O operations per second, spindle speed, noise level.
The first thing you should pay attention to when choosing a hard drive is interface - a device that converts and transmits signals between the HDD and the computer. The most common interfaces now are: SCSI, SAS, ATA (IDE, PATA), Serial ATA (SATA), eSATA and USB.

SCSI interface has a speed of 640MB / s, it is used mainly on servers; SAS - its higher-speed counterpart (12 Gb / s), backward compatible with the interface SATA.
ATA (IDE, PATA) - predecessor SATA, now it is no longer relevant due to its low speed of 150MB / s.
eSATA and USB - interfaces for external hard drives.
Serial ATA (SATA)- this is the most common hard interface drives. It is he who should be guided when choosing a hard drive. There are several variations at the moment. SATA. From a physical point of view, they do not differ (interfaces are compatible), the differences are only in speed: (SATA-I - 150 MB / s, SATA-II - 300 MB / s, SATA-III - 600 MB / s.).
As for capacity: everything is simple. The larger it is, the better, since more information can be recorded. This feature does not affect the performance of the hard drive. Defined by the user based on the need for a place to store files. The table below shows the average size of the main file types that you should pay attention to when choosing HDD.
| Name | Unit Volume | Name | Unit Volume |
| OC Windows | up to 20 GB | HD movie | 5 - 50 GB |
| Linux OS | up to 20 GB | Music files | 3-10 Mb |
| Mac OS | up to 20 GB | Images | 1-20 Mb |
| Virtual machine | from 10 GB | Modern games | 10 - 20 GB |
| DVD movie | 1 - 5 GB | Programs and Utilities | 10 Mb - 5 GB |
Buffer (cache) size. Buffer (cache) - volatile memory built into the hard drive (similar random access memory), designed to smooth out differences in read / write speeds, as well as storing data that is accessed most often. The larger the cache, the better. The indicator varies from 8 to 64 MB. The most optimal value is 32 MB.
There are two main form factor for hard drives: 3.5 inches and 2.5 inches. The first is mainly used on desktop computers, the second - on laptops.
Random access time. This characteristic shows the average time for which the hard drive performs the operation of positioning the read / write head to an arbitrary area magnetic disk. The parameter ranges from 2.5 to 16 milliseconds. Naturally, the lower the value, the better.
Data transfer rate.Modern hard drives have a speed of 50-75 Mb / s (for the internal zone of the HDD) and 65-115 Mb / s (for the external zone).
The number of I / O operations per second.This characteristic ranges from 50 to 100 operations per second, depending on the placement of information on the disk.
The last three parameters should be considered in a hierarchical sequence, depending on the purpose of the hard drive. If you often use bulky applications, games, often watch movies in HD quality, they should be selected in the following sequence: data transfer rate\u003e number of input / output operations per second\u003e random access time. If your arsenal has a lot of small, often launched applications, then the hierarchy will look like this: random access time\u003e number of I / O operations per second\u003e data transfer rate.
Spindle speed - the number of spindle revolutions per minute. Access time and average data transfer rate are largely dependent on this parameter. The most common are rotation speeds: 5400, 5900, 7200, 10000 and 15000 rpm. Optimal for a PC is a speed of 7200 rpm.
Noise level The hard disk consists of spindle rotation noise and positioning noise. Measured in decibels. This characteristic should be drawn from the conviction of comfort.

Manufacturer of hard drives.
At the moment, the main manufacturers of hard drives are - Western digital, Hitachi, Samsung, Seagate technology, Toshiba. You can up to us.achki :) argue which company is better ... But let's turn to the facts. We type in an intelligent search engine Nigma.ru "a problem with hard drive....." (instead of dots - we write a company):
hard drive problemHitachi -requests 5 400 000.
hard drive problem Seagate - requests 5 500 000.
hard drive problemWestern Digital -requests 7,400,000 .
hard drive problemSamsung -requests 17 000 000.
As you can see, the first place in reliability is Hitachisecond y Seagate Although I would, based on my own experience, put in second placeWestern Digital (WD).
Wdcome with stickers in different colors - Black (the black), Blue (blue), Green (green). Considered the most reliable Black, In second place Blue and at the last Green.
So, when choosing a hard drive:
1. Important! You need to find out - which plug at your old hard drive. If IDE, then I advise you to look at the connectors on motherboard. In the presence of SATA-connectionsbetter to buy SATA hard drive. With absence SATA buy IDE.
2. Important! Find out if your old power supply will pull with a power of, as a rule, 300 watts - a new one (perhaps more voluminous and faster) hDD.
For normal disk operation, they must be periodically, once a month, defragmented.
So what is fragmentation ...
In the process, the files written to the drive are often not located in successive clusters, but are distributed in several pieces in different parts of the plate. This happens when the file size increases during the operation of the computer and when writing large files to the filled hard drive, when it simply does not have enough consecutive free clusters. The more often files are modified, the more their fragmentation grows (i.e., the file is split into large quantity "Pieces"). This leads to the fact that reading the file will take more and more time, because the hard disk will have to intensively move its heads, collecting disparate pieces of the file over the entire area of \u200b\u200bthe plates. The more fragments in the file, the slower our computer runs. Probably, each of us at least once got angry at how slowly the game level is being loaded or if a “heavy” application like Adobe Photoshop starts up.
So file fragmentation is evil. And evil must be ruthlessly fought, moreover, better on its territory. :)
The main weapon in the fight against file fragmentation are defragmenters. There are a lot of them, but the essence of their work is one. In the process of analyzing the hard disk, a file allocation map for clusters is created, after which fragmented files are moved to free space so that the entire file is in successive clusters. Consider a defragmentation program.
Defraggler 1.01
Developer: Piriform ltd
Distribution Size: 445 kB
Work under control: Windows 2K / XP / 2003 / Vista
Distribution Method: freeware (http://www.defraggler.com/download)
Price: is free
Defraggler is a very simple and convenient tool for defragmentation, characterized by high speed and offered for free. The program is extremely easy to manage, does not require any settings and is very compact - to run it, you need only one file that can be copied to a USB flash drive and subsequently used on any computer without installation. The principle of operation of Defraggler is somewhat different from similar solutions.

First, the program analyzes the specified disk and issues full list having fragmentation of files, and indicating the full path to each of them. And then, also at the request of the user, she can defragment the selected folders and files, or immediately the entire drive as a whole. When defragmenting, the program processes even very large filesbut skips files locked by the system and the MFT area.