Storage devices and storage media.
Information Store - a device that reads and / or writes information.
Information storage devices are:
· internal and external:
· with removable and non-removable media;
· stationary and portable.
Internal drives are located in the PC system unit and are connected to special connectors on the motherboard.
External and portable drives are located in their own case and connects to the computer through standard input / output ports. External storage devices are used to reserve copy and storage of information, as well as for transporting data from one computer to another.
Storage medium - a device on which information is directly recorded (stored), for example, a disk, a magnetic tape cassette, etc.
The drive and the storage medium can be made in one housing, i.e. make up a whole, for example, a hard diskHDD (Fig. 13).
Fig. 13. Hard disk drive HDD
The drive may have removable media, eg:
· FDD drive removable storage medium - diskette (Floppy drive);
DVD drive - RW (Fig. 14) removable storage medium -DVD drive.

Fig. 14. DVD-RW drive
In some cases, the division into a drive and a carrier is arbitrary. For example, an internal storage device of RAM (RAM ) and portable storageFlash The card is both a storage device and a storage medium.
Major drives and storage media
|
Storage device |
Russian designation |
International designation |
Type of drive |
Carrier |
Media view |
|
RAM |
RAM |
interior |
she is |
– |
|
|
Persistent memory |
ROM BIOS |
interior |
she is |
– |
|
|
HDD (hard disk drive) |
HDD |
interior |
hDD |
fixed built-in |
|
|
FDD Drive (floppy disk drive) |
Fdd |
interior |
floppy disk (floppy disk) |
removable portable |
|
|
CD-ROM, CD -RW - a drive for reading and writing CD-disks |
CD-ROM Cd-rw |
interior |
CD-ROM (CD) |
removable portable |
|
|
DVD -RW - a drive for reading and writing CDs and DVDs |
– |
DVD-R |
interior |
DVD drive |
removable portable |
|
Flash card |
Flash |
external portable |
she is |
The main characteristic of a carrier (drive) is its capacity, i.e. the maximum amount of information that can be recorded on this device. Drive capacity is measured in the following units:
|
designation |
International designation |
|
|
kilobytes |
Kb |
|
|
megabyte |
Mb |
|
|
gigabyte |
Gb |
Latelyfloppy discs and CDs -disks are outdated, in the near future will cease to be used and are actively replaced by more capacious mediaFlash -cards (Fig. 15) andDVDs.

Fig. 15 .. FLASH card
The capacity of the main carriers (drives).
become obsolete
Cd
650 Mb, 700 Mb
become obsolete
DVD disc
4.7 Gb, 9 Gb
DVDs can be single-sided and double-sided, single-layer and double-layer
Flash card
256 Mb, 512 Mb,
1 Gb, 2 Gb
Internal storage media
RAM RAM
512 Mb
1 gb
standard for Windows XP
standard for Windows Vista
HDD
120 - 300 Gb
Typical HDD capacity of a modern PC
A data storage device is an abstract device for storing information, which can be placed at any time in a storage device and after some time removed, moreover, the storage and extraction methods can be any.
The data storage device can be implemented physically in the form of a microfiche, a drawer in a file cabinet, a table in random access memory, magnetic media file, etc. The data storage device on the data flow diagram is depicted as shown in Figure 2.16.
Fig. 2.16. Data storage
The data storage device is identified by the letter "D" and an arbitrary number. The name of the drive is selected for reasons of greatest information for the designer.
The data storage device in the general case is a prototype of the future database and the description of the data stored in it should be linked to the information model.
2.3.5. Data streams
The data stream determines the information transmitted through some connection from the source to the receiver. A real data stream can be information transmitted over a cable between two devices, mailed by letters, magnetic tapes or floppy disks transferred from one computer to another, etc.
The data flow in the diagram is represented by a line ending with an arrow that shows the direction of the flow (Figure 2.17). Each data stream has a name that reflects its content.

Fig. 2.17. Data stream
2.3.6. Building a hierarchy of data flow diagrams
The first step in building a hierarchy of DPDs is to build contextual diagrams. Usually, when designing relatively simple ICs, a single contextual diagram with a star topology is built, in the center of which is the so-called main process connected to receivers and information sources through which users and other external systems interact with the system.
If for a complex system it is limited to a single contextual diagram, then it will contain too many sources and receivers of information that are difficult to place on a sheet of paper of a normal format, and in addition, the only main process does not reveal the structure of a distributed system. Signs of complexity (in terms of context) may include:
availability a large number external entities (ten or more);
the distributed nature of the system;
multifunctionality of a system with an already established or identified grouping of functions into separate subsystems.
For complex IP, a hierarchy of context diagrams is built. Moreover, the top-level context diagram does not contain the only main process, but a set of subsystems connected by data streams. Next-level context diagrams detail the context and structure of subsystems.
The hierarchy of contextual diagrams determines the interaction of the main functional subsystems of the designed IP, both among themselves and with external input and output data streams and external objects (sources and receivers of information) with which the IP interacts.
The development of contextual diagrams solves the problem of rigorously determining the functional structure of IP at the very early stage of its design, which is especially important for complex multifunctional systems in the development of which various organizations and development teams participate.
After constructing contextual diagrams, the resulting model should be checked for completeness of the initial data on system objects and the isolation of objects (lack of information links with other objects).
For each subsystem present in the context diagrams, it is detailed using the DPS. Each process on the DPD, in turn, can be detailed using the DPD or minispecification. When detailing, the following rules must be followed:
balancing rule - means that when detailing a subsystem or a process, a detailed diagram as external data sources / receivers can have only those components (subsystems, processes, external entities, data storage devices) with which the detailed subsystem or process on the parent diagram has informational connection;
numbering rule - means that when detailing processes, their hierarchical numbering should be supported. For example, processes detailing a process with number 12 get numbers 12.1, 12.2, 12.3, etc.
The mini-specification (description of the process logic) should formulate its main functions in such a way that in the future the specialist performing the project could fulfill them or develop an appropriate program.
Minispecification is the ultimate peak of the DPD hierarchy. The decision to complete the process details and use the mini-specification is made by the analyst based on the following criteria:
the process has a relatively small number of input and output data streams (2-3 streams);
the ability to describe the conversion of data by a process in the form of a sequential algorithm;
performing a process of a single logical function of converting input information into output;
the ability to describe the logic of the process using mini-specification of a small volume (no more than 20-30 lines).
When building the hierarchy of DPD, one should proceed to the process detailing only after determining the content of all streams and data stores, which is described using data structures. Data structures are constructed from data elements and may contain alternatives, conditional occurrences, and iterations. Conditional occurrence means that this component may be absent in the structure. An alternative means that the structure may include one of the listed elements. Iteration means the occurrence of any number of elements in the specified range. For each data item, its type (continuous or discrete data) can be indicated. For continuous data, a unit of measure (kg, cm, etc.), a range of values, the accuracy of the presentation and the form of physical encoding can be indicated. For discrete data, a table of permissible values \u200b\u200bmay be indicated.
After building a complete model of the system, it must be verified (checked for completeness and consistency). In the full model, all its objects (subsystems, processes, data streams) must be described in detail and detailed. Identified non-detailed objects should be detailed, returning to the previous development steps. In a consistent model, for all data streams and data storage devices, the rule of preserving information must be fulfilled: all data arriving somewhere must be read, and all read data must be written.
Any electronic computers include memory drives. Without them, the operator would not be able to save the result of his work or copy to another medium.
Punch cards
At the dawn of the appearance, punch cards were used - ordinary cardboard cards with digital markings.
On one punch card 80 columns were located, in each column it was possible to save 1 bit of information. The holes in these columns corresponded to one. Data reading occurred sequentially. It was impossible to record anything on a punch card again, so a huge number of them were required. To store a 1 GB data array would require 22 tons of paper.
A similar principle was used in punched tapes. They wound on a bobbin, took up less space, but often torn and did not allow adding and editing data.
Floppy disks
The appearance of floppy disks was a real breakthrough in information technology. Compact, capacious, they allowed to store from 300 Kb on the earliest samples to 1.44 Mb on latest versions. Reading and writing was carried out on magnetic diskenclosed in a plastic case.
The main disadvantage of floppy disks was the fragility of the information stored on them. They were vulnerable to action and could be demagnetized even in public transport - a trolley bus or tram, so for long-term storage They tried not to use their data. Floppy disks were read in drives. At first there were 5-inch floppy disks, then they were replaced by more convenient 3-inch disks.

The main competitor to floppy disks is flash drives. Their only drawback was the price, but as microelectronics developed, the cost of flash drives dropped dramatically and floppy disks went down in history. Finally, their release ceased in 2011.
Streamers
Streamers were previously used to store archive data. They looked like videotapes in appearance and in principle. Magnetic tape and two reels made it possible to read and write information sequentially. The capacity of these devices was up to 100 MB. Such drives did not receive mass distribution. Ordinary users preferred to store their data on hard drives, and it was more convenient to keep music, films, programs on CD- and later DVD-disks.
CD and DVD
These storage devices are still in use. An active, reflective and protective layer is applied to the plastic substrate. Information from the disc is read by a laser beam. A standard disk has a capacity of 700 MB. This is enough, for example, to record a 2-hour movie in average quality. There are also double-sided discs when the active layer is sprayed onto both sides of the disc. To save a small amount of information used mini-CD. Drivers, instructions for computer products are now written specifically on them.

DVDs replaced CDs in 1996. They allowed to store information already 4.7 GB. Their advantage was also that the DVD drive could read both CD- and DVD-disks. At the moment, this is the most massive memory drive.
Flash drives
The CD and DVD drives discussed above have a number of advantages - low cost, reliability, the ability to store large amounts of information, but they are designed for one-time recording. You cannot make changes to the recorded disc, add or remove unnecessary ones. And here a fundamentally different drive comes to the rescue - flash memory.

For some time he competed with floppy disks, but quickly won this race. The main limiting factor was the price, but now it has been reduced to an acceptable level. Modern computers are no longer equipped with drives, so the flash drive has become an indispensable companion for everyone dealing with computer equipment. The maximum amount of information that fits on a USB flash drive reaches 1 Tb.
Memory cards
Phones, cameras, e-books, photo frames and much more that memory drives require for work. Because of its relatively large size, USB drives are not suitable for this purpose. Memory cards are specially designed for such cases. In fact, this is the same flash drive, but adapted for small-sized products. Most of the time, the memory card is in the electronic device and is removed only to transfer the accumulated data to a permanent medium.

There are many standards for memory cards, the smallest of them have a size of 14 by 12 mm. On modern computers, instead of a drive, a card reader is usually installed, which allows you to read most types of memory cards.
Hard disks (HDD)
The memory drives for the computer are inside it are metal plates, coated on two sides with a magnetic composition. The engine rotates them at a speed of 5400 for older models or 7200 rpm for modern devices. The magnetic head moves from the center of the disk to its edge and allows you to read and write information. The volume of the hard drive depends on the number of disks in it. Modern models allow storing up to 8 Tb of information.
There are practically no drawbacks to this type of memory drives - these are very reliable and durable products. The cost of a unit of memory in hard drives is the cheapest among all types of drives.
Solid State Drives (SSD)
No matter how good hard disksbut they have almost reached their ceiling. Their speed depends on the speed of rotation of the disks, and its further increase leads to physical deformation. Flash technology, which is used in the manufacture of solid-state memory drives, is devoid of these disadvantages. They do not contain moving parts, therefore they are not subject to physical wear and tear, are not afraid of shock effects and are not noisy.
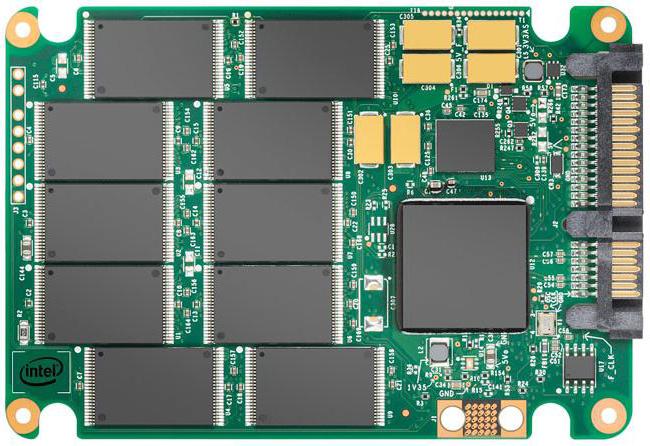
But while there are serious flaws. First of all, the price. The cost of a solid state drive is 5 times higher hard drive similar volume. Another significant drawback is the short life. SSDs are usually chosen for installation operating system, and for data storage is used hDD. Cost solid state drives steadily declining, there is progress in increasing their resource. In the near future, they should supplant traditional hard drives, as in due time flash drives supplanted floppy disks.
External drives
Internal storage and inner memory everyone is good, but often you need to transfer information from one computer to another. Back in 1995, a USB interface was developed that allows you to connect a wide variety of devices to your PC, and memory drives are no exception. At first, these were flash drives, later DVD players with a USB connector appeared and, finally, hDD drives and SSD.
The attractiveness of the USB interface is its simplicity - just stick a USB flash drive or other drive and you can work, you do not need to install a driver or other additional steps. The development of the interface and the emergence of USB 2.0 at first, and then USB 3.0 dramatically increased the speed of data exchange on this channel. Performance now differs little from the internal, and their size can not but rejoice. An external memory drive easily fits in the palm of your hand, while it allows you to store hundreds of gigabytes of information.
Information storages were invented so that the source data can be recorded, and the results of the work - saved. But today they have firmly taken their place in our daily lives, when we have to pass through ourselves a sea of \u200b\u200bworking and personal information. The most common at present are: hard drives, magnetic storage devices in plastic cards, SDRAM chips, flash memory (memory cards in modern devices, USB drives), optical discs (CD, DVD, Blu-Ray).
Hard disk or "Winchester"
Today it is impossible to imagine a computer without such an important storage device as a storage device hard magnetic data in abbreviated form - HDD. Its unofficial but widely used synonym is Winchester. They are intended for permanent storage of information that is used when working with a computer: document editors, operating system programs, translators from programming languages, frequently used software packages, and much more. Hard choice The drive is now huge for every taste and color. To do this, you need to study the full range hard drives.
Magnetic storage devices in plastic cards
A floppy disk or floppy disk is a compact low-speed, low-capacity tool that allows you to store information and transfer it from one computer to another. There are disks of the following sizes: 3.5, 5.25, 8 inches (the last two types are now rarely seen). An interesting fact is that the size of 3.5 inches corresponds exactly to the size of the shirt pocket.
Microchips sdram
Translated from English means "synchronous dynamic memory with random access." This type of information storage device is used in the computer as random access memory.
Flash memory
Flash memory - A special type of non-volatile (energy is needed only for recording) rewritable semiconductor memory. It got its name due to the way that this type of memory is recorded and erased. Today, the phrase "flash memory" refers to a wide class of solid-state storage devices. They are distinguished by low cost, compactness, mechanical strength, as well as large volume, speed and low power consumption.
The most popular type of information storage device is USB flash drives. It is very easy and convenient to work with them, the main thing is not to lose the flash drive itself.
Various modern devices (digital cameras, cordless phones, voice recorders) have flash memory - memory cards. Today you can find their various formats: Compact Flash, SD (Secure Digital Card), XD - Picture Card, Memory Stick, MMC (Multimedia Card) / SD (Secure Digital Card), MMC (Multimedia Card), Smart Media Card.
Optical Information Storage
CD discs not only allow you to record, but also reliably store data in all formats (audio, video, photos) on a cheap and simple laser CD-ROM drive.
DVD discs are visually not much different from ordinary CD-ROMs, but they have much more features: record and rewrite a large amount of information, play it on a DVD set-top box. There are two main formats: DVD R (W) and DVD + R (W), which are created by various organizations. The plus and minus formats are not compatible between each other, so when choosing media you need to familiarize yourself with the list of discs that your recorder supports.
Blu-ray discs are the latest generation optical discs that allow you to store high-definition video and high-density data.
Information needs to be stored, but with the development of modern technologies, the information storage devices themselves are changing very quickly. And it’s better to rewrite the video cassette with a wedding recording to a more modern storage medium.