The acronym ADSL stands for Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line. ADSL is translated as "Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line". This is one of the high-speed data transmission technologies related to DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) technology, also referred to as xDSL.
The group of DSL technologies also includes:
- High-speed digital subscriber line. HDSL - High data rate Digital Subscriber Line;
- Ultra-high-speed digital subscriber line. VDSL – Very high data rate Digital Subscriber Line;
- ETTH ("Ethernet...");
- GPON;
- FTTH.
What is ADSL technology?
As you already understood, ADSL technology is a technology for connecting to the Internet over wired networks, in particular telephone wires such as twisted pair. The essence of the technology is the ability to carry out high-speed data transmission over twisted pair telephone wires.
To implement this technology, an ADSL line is created that connects two ADSL modems. Twisted-pair telephone cable is used to connect ADSL line modems. Each modem is connected to a telephone cable via an RJ-11 connector.
According to the technology, 3 channels of information transfer are created:
- downstream;
- updraft;
- POTS telephone channel.

At the same time, the channel for the phone is selected by filters and does not depend on the ADSL connection.
Features of ADSL technology
Firstly, ADSL technology is asymmetric. This means that the data transfer rate towards the end user is higher than the data transfer rate from the user to the network. That is, the downstream speed is higher than the upstream speed.
Secondly. Information transmitted over ADSL telephone wires is compressed. For compression, digital signal processing is used using specially created algorithms, advanced analog filters and analog-to-digital converters.
Third. ADSL technology uses a method of dividing the bandwidth of a copper telephone cable into multiple carrier frequency bands. This separation allows several signals to be transmitted simultaneously on one line.
In this case, different carrier bands simultaneously pass different parts of the transmitted data. This process is called Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM), which means frequency multiplexing of the communication line.
FDM allows you to allocate one range for upstream data, and the second range for downstream. In this case, the downstream range is divided into high-speed channels and low-speed data transmission channels. The upstream is also divided into low speed data links.
It is possible to overlap the upstream and downstream ranges with Echo Cancellation technology (echo cancellation).
Fourth. ADSL technology allows you to reserve a narrow bandwidth for the transmission of POTS signals. POTS stands for Plain Old Telephone Service. When using ADSL, telephone communication will not be interrupted, even if the power is turned off.
Advantage of ADSL
Despite all the shortcomings, ADSL technology allows you to use already laid telephone wires to connect to the Internet. This globally expands the possibilities of Internet connection. This does not require expensive upgrades of switching equipment, as for ISDN technology.
Flaws
The main disadvantage of ADSL is the weakening of the signal on long telephone lines. For example, at a standard speed of 1 MHz, signal loss can be up to 90 dB.
ADSL speed
The first letter in the ADSL name means asymmetric. That is, the transfer of data from the network to the computer (downstream) and the transfer of data from the computer to the network (upstream) will go at different speeds.
The transmission speed depends on the state of the line, the cable section, and the presence of taps. In fact, the limit for an ADSL subscriber line is 3500 - 5500 meters in length with a cable cross section of 0.5 mm 2 .
In practice, ADSL will provide a speed to the computer of 1.5 - 8 Mbps, and a speed from the computer from 640 to 1.5 Mbps.
ADSL and Internet
If you want to connect to the Internet via ADSL, you need to understand that you do not need to dial telephone numbers for communication. ADSL technology immediately creates a broadband channel for data transmission over an existing telephone line.
Immediately after installing the ADSL modem, you will receive a permanent high-speed Internet connection. At the same time, only 1% of the bandwidth of the band remains for telephone communication (low frequency up to 4 kHz). 99% go to provide high-speed data transfer. In this case, different frequency bands are used for different functions.
The article discusses in detail the influence of various parameters on the speed and other characteristics of the operation of ADSL equipment.
Abbreviation ADSL(Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) stands for "Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line", which emphasizes the difference in exchange rates in the directions to the subscriber and back, which was originally incorporated in this technology.
asymmetry ADSL, in its essence, implies the transfer of large amounts of information to the subscriber (video, data arrays, programs) and small amounts from the subscriber (mainly commands and requests).
Equipment ADSL located on the PBX, and subscriber ADSL modem connected to both ends telephone line, form three channels:
- high-speed data transmission channel from the network to the computer (speed - from 32Kbit/s to 8Mb/s);
- a high-speed data transfer channel from a computer to a network (speed - from 32Kbps to 1.5Mbps);
- a simple telephone communication channel over which ordinary telephone conversations are transmitted.
The value of the data transfer rate in this case depends on the length and quality telephone line. The asymmetric nature of the data transfer rate is introduced on purpose, since a remote Internet user usually downloads data from the network to his computer, and either commands or a data flow of a significantly lower speed go in the opposite direction. To obtain rate asymmetry, the subscriber termination bandwidth is also divided asymmetrically between channels.
On the PBX side, a so-called access multiplexer should be located on the user's line ADSL - DSLAM. This multiplexer allocates subchannels from the common channel and sends the voice subchannel to the PBX, and directs high-speed data channels to the router connected to DSLAM.
One of the main advantages of technology ADSL compared to analog modems and protocols ISDN And HDSL- the fact that voice support does not affect the parallel data transmission over two fast channels. The reason for this effect is that ADSL is based on the principles of frequency separation, due to which the voice channel is reliably separated from the other two data transmission channels.
Influence of cable parameters on the operation of ADSL equipment
Primary line parameters:(real)
Note:
it is impossible to measure the insulation resistance and capacitance on a damaged cable with a digital multimeter! this is the first a sign of a wet cable, "brokenness", asymmetry ...
Secondary line parameters:(main)
Signal attenuation.
from 5dB to 20dB - the line is excellent.
from 20dB to 30dB - the line is good.
from 30dB to 40dB - the line is bad.
from 50dB and above the line sucks.
(on Upstream and Downstream attenuation is different)
Noise level: RMS Noise Energy
from -65dBm to -50dBm - the line is excellent.
from -50dBm to -35dBm - the line is good.
from -35dBm to -20dBm - the line is bad. (high probability of line damage)
from -20dBm and above, the operation of the equipment is impossible.
Line frequency response.(examples below)
Note:
With line noise levels between -65dBm and -55dBm, normal equipment can operate at exorbitant distances. (up to 6 km or more with a core diameter of 0.5 mm) despite the high signal attenuation (up to 50dB), even at the minimum parameters.
Measuring equipment:
Reflectometer “CableSHARK” manufactured by “Consultronics”. Reflectometer “990DSL CopperPro” from “FLUKE Networks”. Multimeters APPA 101 and UNI-T UT70D
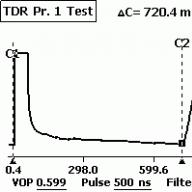
First, let's see how it looks from the point of view ADSL modem ideal line.
twisted pair. 5Cat. 720m. (assembled on rolls from pieces)
Loop resistance 160 Ohm. (24AWG)
Average noise level in the range 4kHz-2000kHz:
RMS noise -65 dBm (or less)
Loop capacitance 0.040uF

Fig.1. Distance check
Figure 2 shows the results of testing the received line.
Blue indicates the frequency response.
Green - noise level in the line.
red denotes DMT.
Note:
DMT (Discrete Multi-Tone), the information stream is divided into several channels, each of which is transmitted on its own carrier frequency using QAM. Typically, DMT splits the 4 kHz to 1.1 MHz band into 256 channels, each 4 kHz wide. This method, by definition, solves the problem of dividing the bandwidth between voice and data (it simply does not use the voice part), but is more difficult to implement than CAP. DMT is approved in ANSI T1.413 and is also recommended as the basis for the specification Universal ADSL.
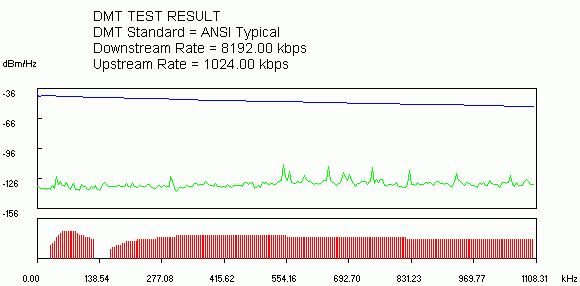
Fig.2. Line Test Results
Note:
The greater the distance, the more line resistance, worse frequency response and higher signal attenuation. This mainly affects the Downstream (middle and end of the chart), i.e. connection speed ADSL modem towards the subscriber.
Real Line:
Loop resistance 420 Ohm
Distance approximately 2.5 km.
The working capacitance of the line is 0.12 uF.
Average noise level in the range 4kHz-2000kHz: RMS Noise -38dBm
DSLAM and SIEMENS modem.
Theoretical speed:
7Mbps Downstream
800kbps Upstream
Real connection speed:
1Mbps Downstream
512kbps Upstream
The connection is stable.
There is some damage on the line:
cable tangle, one of the conductors has a short to ground. As a result - low-frequency noise in the line when the ADSL equipment. plus when turned on ADSL equipment, because of the asymmetry line parameters, audible HF noise appears. splitter replacement is useless.
With a reflectometer, you can "see" the damage. (presumably at a distance of 42.9 m wetting.) A little closer, the upward ejection is most likely an oxidized twist.
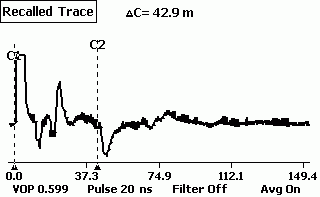
Fig.3. Line with damage

Fig.4. Noise in the line, mainly from the Mayak radio station (549 kHz), etc.

Fig.5. Noise in the line, (Fig. 4 details)
straight wire:
(copper pair without telephony, they like to call it a dedicated line. :)
Loop resistance 1067 Ohm
The working capacitance of the line is 0.18 uF.
Average Noise Level 4kHz-2000kHz: RMS Noise -55.71dBm
DSLAM and SIEMENS modem.
Real connection speed:
64Kbps Downstream
32kbps Upstream
(sometimes loss of sync)
Factory cross, noodles, twists ... a very long distance to the ATS.
Stable operation of ADSL equipment on such a line is impossible.

External factors affecting the operation of ADSL equipment
All sorts of AVU lines, HF seals, UVO signaling, other DSL, passing in the same cable, in adjacent pairs, greatly interfere with the work. Especially if there are all kinds of cable defects, "spread/broken" , cable getting wet, taps. All these devices create a lot of noise in the frequency range from 0 Hz to 100-200 kHz. (Mostly) This reduces the signal of the outgoing stream ADSL (upstream) up to its complete absence and, as a consequence, the loss ADSL modem synchronization.
When DSL and RF seals work together in the same cable on different pairs, crosstalk can occur that interferes with the operation of analog telephony. (noise in the range of 1KHz and above)
In factory and industrial areas, all kinds of power equipment are very much affected. Direct proximity to the railway.
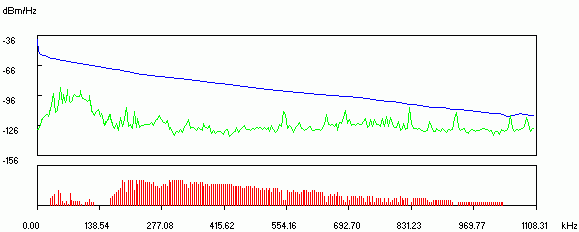
Fig.7. Interference from AVU lines, Peterstar HF seals, UVO alarms
As you can see on the graph, almost all the main noise falls on the Upstream range. (beginning of the graph) does not depend on the time of day. The alarm is usually turned on from 19:00 to 09:00 and on weekends around the clock. Accordingly, at this time ADSL works intermittently or does not work at all.

Fig.8. Operation of power electrical equipment
Very bad cable frequency response. High noise level, clogging almost the entire signal. station part. DSLAM
Damage connecting multi-pair cable from DSLAM to cross plinths:
Cable damage, plinths, poor quality "cable termination". On old crosses: cold soldering or unsoldered wrapping. The result is contact bounce. The result is an unsystematic loss of sync by the modem.
"Broken pairs" - can only be tracked by a tone generator + a test tube with a high-impedance input. Incorrect cutting/installation of the cable. Poor quality/incorrect soldering of connectors. (The most difficult to trace glitches. They are usually solved at the editing stage)
Violation of installation technology crossover cable.
For example:
when another pair of wires is passed through the cross eye, in which there are already many other crosses. And they do it with such an effort that the dragged pair rips off / burns the insulation on adjacent crossings. As a result: the short circuit of the conductors of various pairs between themselves or to the ground.
Incorrect connection of splitter/modem card in DSLAM. Incorrect connection of the splitter port to the line/station. Connection subscriber line to another DSLAM port. Sometimes they just forget to make crossovers. :) Equipment overheating.
Software/firmware buggy, failure of DSLAM operation with some type of subscriber equipment with some line parameters.
conclusions
Line resistance directly dependent on distance. Therefore, knowing the resistance, it is possible to accurately calculate the distance between the subscriber and the PBX. Knowing the reference data ADSL modem, you can estimate at what speed the modem will connect. Unfortunately, that's all. to know secondary line parameters complex expensive equipment is required. It is also possible to view the average signal attenuation on the Upstream and Downstream streams in some ADSL modems: ZyXEL 650, Cisco 800 series, USB ADSL modems and others.
For example:
at cable cross section 0.5 mm2 (0.085 Ohm/m) and line loop resistance 1000 ohm line length L = (1000 / 0.085) / 2 = 5882 m. It should also be borne in mind that in some areas cable section can be 0.4mm.kv (0.133 ohm/m) for the ZyXEL 645R modem, the theoretical speed is 64 kbps
Another example:
Distance 5.5km
Core diameter trunk cable from ATS: 0.7mm
[to the nearest ten-pair branch from trunk cable going to the building of the subscriber] Ie. most of the cable from the PBX to the subscriber has a copper core diameter of 0.7mm
Loop resistance: 570 Ohm!!!
Loop capacitance: 0.3uF
Maximum possible speed: 5M/640Kbps
Real operating speed: 640Kbps / 360Kbps (if set more - sync failure)
Equipment: Cisco 800 series. there are two VoIP lines and Internet access.
At line loop resistance 800 - 1000 ohms the chance of failures/instabilities is very high. (In any case, it is impossible to guarantee 100% reliability) At this point, how lucky you are with the main cable. There are cases when the ZyXEL 645R works with minor interruptions on the line with a resistance of 1200 - 1400 ohms.
You can easily ruin the link even if the resistance is much less than 800 ohms. As a rule, this is the "noodles for cloves" so beloved by everyone on the subscriber's side. The maximum operating frequency is 180kHz and, if desired, 10BaseT can be stirred up through bleach (two pairs) ... but at what distance?
Old soviet telephone sockets. A sort of shYt with a capacitor 1uF x 160V inside. New ones, by the way, also do not shine with quality. The RJ11 plug made in China just falls out of the "Zrobleno in Belarus" sockets. I have not seen RJ11 plugs made in Belarus, so such sockets are immediately thrown into the trash.
In apartments and offices with high humidity (old fund), the resistance of oxidized contacts can reach several hundred ohms.
Sometimes narrow-minded "telephonists" can make telephone input to the office / apartment through a forgotten radio input. The junction box left from the radio. (300 ohm resistor soldered to each wire)
You can also look for diode blockers on the landing in the shield (if once upon a time the line was paired) We get a funny effect: the ADSL modem only works when the phone is off-hook. Or a forgotten high-frequency filter from a private security alarm.
If the line passes through the cross of the old plant / enterprise, then you get additional bonuses in the form of:
- Four thermals per line. each has a resistance of 25-50 ohms + inductance.
- Parallel branches of the line to other workshops, intermediate crosses, couplings, etc.
- System "Granite", against listening. Through it, the work of Dial-UP equipment is difficult, and you can forget about ADSL altogether.
Special clinical cases:
Insulation damage trunk cable :(
Soaked couplings, "broken", etc.
A broken pair is when the wires for the line are taken from different pairs of the cable.
Well, the simplest:
Incorrect connection of the splitter or microfilters.
In the summer... Overheating of the modem.
Or after another thunderstorm - a burned-out modem. :)
At line loop resistance more than 1000 Ohm, the operation of an ADSL modem is almost impossible.
DC line parameters for connecting ADSL equipment
ADSL is an asymmetric Internet access technology. It is an asymmetric system in its structure and allows you to work with connections at speeds up to 8 Mbps. ADSL-technology, the transmission speed of which is calculated up to 1 Mbps, operates on average at a distance of more than 5 km. Today we will look at what this type of connection is and how it works.
History of appearance
Before answering the question: "ADSL - what is it?", we bring to your attention some historical data. For the first time, they started talking about the creation in the late 80s, when even the Internet in its modern form was only its main task in 1989 was to improve and modernize the technology of data transmission over copper telephone wires. Analog-to-digital conversion was created mainly for the rapid transfer of information between various interactive services, video games, video files, as well as for instant remote access to the LAN and other network systems.
Modern ADSL technology: how it works
The operation of the network is based on the subscriber's digital line, which provides access to the Internet through telephone communication channels. But telephone lines use an analog signal to carry voice messages. An ADSL connection is designed to convert an analog signal into a digital one and transfer it directly to a computer. At the same time, unlike already outdated Dial-up modems, ADSL-based devices do not block the telephone line and allow you to use digital and analog signals simultaneously.
The essence of the technology (asymmetry) lies in the fact that the subscriber receives a huge amount of data - incoming traffic, and transmits a minimum of information from himself - downstream traffic. As an input, various kinds of content are meant: video and media files, applications, objects. Downstream sends only important technical information - various commands and requests, emails and other minor elements. The asymmetry is that the speed from the network to the subscriber is several times higher than the speed from the user.

The most important advantage that ADSL technology has is its budget and economy. The fact is that the same copper ones are used for the operation of the system. The number in them, of course, significantly exceeds the number of similar elements in cable modems. But at the same time, no modernization of switching equipment and complex reconstruction is necessary. ADSL connects quickly, and modern types of modems are intuitive to manage and configure.
What equipment is used for this connection?
In order for the technology to work, special types of modems are used, which differ in their structure, design, connection type:
- PCI modems (internal computer devices).
- External modems with USB connection type.
- Devices with Ethernet type interface.
- with Ethernet scheme.
- Profile types of modems (for security companies, private telephone lines).
- Router with internal Wi-Fi hotspots.
Additional equipment: splitters and microfilters
We must not forget that to connect such a gadget as an ADSL modem, you will need splitters and microfilters. Devices are selected in accordance with the design of the telephone cable. In a situation where a cable outlet is made (or can be done) to separate the modem and telephone channel, a splitter is used. In another case, you need to purchase a microfilter, which is installed on each telephone present in the room.

The main task of the splitter is to separate frequencies - voice (0.3-3.4 kHz) and those used directly by the modem itself (25 kHz-1.5 MHz). It is in this way that the simultaneous operation of the modem and the telephone is ensured, which do not interfere with each other and do not interfere. Splitters are compact and will not cause unnecessary inconvenience. The miniature box is equipped with three connectors and is light in weight.
ADSL - what is it? Stages of connecting high-speed Internet

- Provider choice. To date, each provider offers to use this technology. Different types and rates depend on the region, as well as on the technical capabilities of the company, the coverage area of \u200b\u200bwhich may be limited.
- Purchase of equipment. Currently, it is not necessary to buy a modem, splitters and microfilters. When drawing up a connection agreement, the provider offers to rent the necessary equipment, including an ADSL modem. In the future, upon termination of the document, the equipment is returned back. The client pays exclusively for the Internet connection. Modern Internet ADSL - what is it? This is a fast, cheap and high-quality connection method.
- Account activation. For each client, the provider reserves an account, the activation of which can take up to 12 days. However, in most cases, with normal network coverage, the procedure does not require more than a few hours. First, the provider checks the phone number for the possibility of connecting ADSL. If the technology access zone is not enough, then high-speed Internet will not work.
- Equipment setup. At this stage, devices are connected to the telephone line, splitters and microfilters are installed, modem drivers are installed on the computer, and the modem's network parameters are set in the Internet browser.
pros

What are the advantages of ADSL technology? Here are a few of them:
- High ADSL allows you to easily transfer files of any size without a long wait. The technology is constantly being improved, and the speeds are growing, significantly expanding the capabilities of the subscriber.
- Wireless connection. To use an ADSL system, you do not need to stretch the cable to the subscriber and install a large amount of equipment. The reliability, quality and functionality of the network is improved.
- No interference on the telephone line. The ADSL router operates in independent mode and does not create any problems for the phone to work. You can call and surf the virtual space completely freely.
- Permanent Internet access ADSL. What it is? This means that the network will not fail during operation. The technology does not require reconnection. The user gets access to the Internet constantly and can be online around the clock.
- Reliability and stability. Today, ADSL is the most reliable type of Internet connection.
- Profitability. The cost of connecting ADSL and installing a modem with a router is minimal and will not hit the family budget.
Flaws
- Lack of crosstalk protection. If several dozen clients are connected to one channel, you won’t have to rely on high speed. The more subscribers on one ADSL, the lower the quality of data transmission.
- Although ADSL technology has disadvantages, they are not numerous. This also includes the minimum speed from the subscriber. The asymmetry of ADSL has an obvious minus - the transfer of files from the subscriber will be long and inconvenient. But the technology is intended, first of all, for quick access to the Internet, for surfing. In addition, the information transmitted from the subscriber takes up a minimum of space and does not require a large resource.
Speed and factors affecting it
ADSL is a high-speed Internet technology, but there is no universal meaning or formula. For each individual subscriber, the speed is individual and is determined by a whole set of factors. Including some of them can affect the reliability and quality of equipment. Therefore, it is best for professionals to install modems and routers.

The main reason for the low speed of an ADSL connection is the quality of the subscriber line. We are talking about the presence of cable outlets, their condition, wire diameter and length. Signal attenuation is a direct consequence of an increase in the length of the subscriber line, and interference can be reduced by expanding the diameter of the wire. The standard length of an ADSL channel does not exceed 5 km - the optimal range for high-speed data transmission.
Speed characteristics
Compared to other Internet connection technologies, ADSL has a significant speed advantage. An analog modem will give a maximum of up to 56 Kbps, while ADSL at the dawn of its appearance already allowed information to be transmitted at speeds up to 144 Kbps.

ADSL technology, the maximum speed of which is also determined by the characteristics of the modem and can reach 2048 Mbps, optimizes the process of information transfer. Digital lines significantly increase the user's capabilities, taking him beyond the limitations even with several connected computers, mobile phones, tablets and other gadgets.
Technology Perspectives
The possibilities and resources of ADSL technology are far from being exhausted. Even the ADSL2 and ADSL2+ standards, introduced back in the mid-2000s, still retain their relevance and capabilities. This is, in fact, the only technology that can provide wide Internet access without failures and software problems, therefore it is a competitor to many other methods of connecting to the Internet.

The minimum technical equipment is complemented by modern types of modems. Manufacturers annually release new devices designed for continuous operation without the need for maintenance and service. In addition, ADSL speed is constantly growing and is not limited to megabits. The connection becomes relevant both for the home and for the whole office company with several dozen computer clients.
Conclusion
So, we found out what ADSL technology is, what is its essence and principle of operation. As you can see, this is one of those technologies that practically does not fail during operation (even if several dozen users are connected to the network). At the same time, it does not require constant reconnections and speed limits.
ADSL technology
In recent years, the growth in the volume of information transfer has led to the fact that there is a shortage of bandwidth for access channels to existing networks. If at corporate levels this problem is partially solved (by renting high-speed transmission channels), then in the residential sector and in the small business sector these problems exist.
Today, the main way for end users to interact with private and public networks is access using a telephone line and modems, devices that provide digital information transmission over subscriber analog telephone lines. The speed of such a connection is low, the maximum speed can reach 56 Kbps. This is still enough for Internet access, but the saturation of pages with graphics and video, large volumes of e-mail and documents will again raise the question of ways to further increase bandwidth in the near future.
The most promising at present is the ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) technology. This is a new modem technology that turns standard analog subscriber telephone lines into high-speed access lines. ADSL technology allows you to transfer information to the subscriber at a speed of up to 6 Mbps. In the opposite direction, speeds up to 640 Kbps are used. This is due to the fact that the entire modern range of network services involves a very low transmission speed from the subscriber. For example, MPEG-1 video requires 1.5 Mbps of bandwidth. For service information transmitted from the subscriber, 64-128 Kbps is quite enough (Fig. 1).
ADSL service organization principles
An ADSL service (Figure 1) is provided by an ADSL modem and an ADSL modem rack called the DSL Access Module. Almost all DSLAMs are equipped with a 10Base-T Ethernet port. This allows the use of conventional hubs, switches and routers on access nodes.
A number of manufacturers have begun to provide DSLAMs with ATM interfaces, allowing them to be directly connected to WAN ATM switches. Also, a number of manufacturers create custom modems, which are an ADSL modem, but for software they are ATM adapters.
There are three streams in the section between the ADSL modem and the DSLAM: a high-speed stream to the subscriber, a bidirectional service and voice channel in the standard frequency range of the PM channel (0.3-3.4 kHz). Frequency separators ( POTS Splitter) allocate a telephone stream, and direct it to a conventional telephone set. Such a scheme allows you to talk on the phone simultaneously with the transfer of information and use telephone communications in the event of a malfunction of the ADSL equipment. Structurally, the telephone splitter is a frequency filter that can be either integrated into an ADSL modem or be an independent device.
According to the theorem Shannon, it is impossible to achieve speeds above 33.6 Kbps using modems. In ADSL technology, digital information is transmitted outside the frequency range of a standard PM channel. This will lead to the fact that the filters installed at the telephone exchange will cut off the frequency above 4 kHz, so it is necessary to install WAN access equipment (switch or router) at each telephone exchange.
Transmission to the subscriber is carried out at speeds from 1.5 to 6.1 Mbps, the speed of the service channel is from 15 to 640 Kbps. Each channel may be divided into multiple logical low rate channels.
Speeds provided by ADSL modems are multiples of speeds of T1, E1 digital channels. In the minimum configuration, transmission is carried out at a speed of 1.5 or 2.0 Mbps. In principle, today there are devices that transmit data at speeds up to 8 Mbps, but this speed is not defined in the standards.
Speed of ADSL modems depending on the number of channels
| base speed | Number of channels | Speed |
|---|---|---|
| 1.536 Mbps | 1 | 1.536 Mbps |
| 1.536 Mbps | 2 | 3.072 Mbps |
| 1.536 Mbps | 3 | 4.608 Mbps |
| 1.536 Mbps | 4 | 6.144 Mbps |
| 2.048 Mbps | 1 | 2.048 Mbps |
| 2.048 Mbps | 2 | 4.096 Mbps |
| 2.048 Mbps | 3 | 6.144 Mbps |
The maximum possible line speed depends on a number of factors, including the length of the line and the thickness of the telephone cable. The characteristics of the line deteriorate with an increase in its length and a decrease in the cross section of the wire. The table shows several options for the dependence of speed on line parameters.
An ADSL modem is a device based on a digital signal processor (DSP or DSP), similar to that used in conventional modems (Fig. 2). In the general case, the entire bandwidth of the line is divided into two sections. The first section is intended for voice transmission, and is in the range of 0.3-3.4 kHz. The signal range for data transmission is between 4 kHz and 1 MHz. The physical parameters of most lines do not allow data to be transmitted at a frequency above 1 MHz. Unfortunately, not all existing telephone lines (especially long ones) even have such characteristics, so it is necessary to reduce the bandwidth, which entails a decrease in the transmission speed.
Two methods are used to create these streams: the frequency division method and the echo cancellation method.


Rice. 3 Stream separation schemes in the frequency band of a telephone line
The frequency division method consists in the fact that each of the streams is allocated its own frequency bandwidth. The high speed stream may be split into one or more low speed streams. These streams are transmitted using the " "(DMT).
The echo cancellation method is that the ranges of the high-speed and service streams are superimposed on each other. The streams are separated using a differential system built into the modem. This method is used in modern V.32 and V.34 modems. A high-speed stream can be divided into one or more low-speed streams. These streams are transmitted using the " discrete multitone modulation"(DMT).
When transmitting multiple streams, each of them is divided into blocks. Each block is provided with an error correction code (ECC).
Related technologies
There are a number of related technologies, some for end-users, others for high-speed backhaul. The principle of their operation is similar to ADSL. The common name for such technologies is xDSL.
High Data-Rate Digital Subscriber Line (HDSL)
HDSL is a technology that provides transmission at 1.536 or 2.048 Mbps in both directions. The length of the line can reach 3.7 km. Oriented as a cheaper alternative to dedicated channels E1, T1. Requires a 4-wire subscriber line.
Single-Line Digital Subscriber Line (SDSL)
It is similar to HDSL, differs in that a two-wire subscriber line is enough to organize a line. The length of the line can reach 3 km.
Very High Data-Rate Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL)
Similar to HDSL, speed up to 56 Mbps. Distance up to 1.5 km. The technology is very expensive and is not widely used.
Rate Adaptive Digital Subscriber Line (RADSL)
ADSL technology has one significant drawback. It does not allow you to change the speed depending on the quality of the line. In such modems, the choice of speed, a multiple of 1.5 or 2 Mbps, is made using software. Equipment built on the basis of RADSL technology allows you to automatically reduce the speed depending on the quality of the line.
Universal ADSL (UADSL)
ADSL technology has a number of minor drawbacks that prevent the wide implementation of the technology on subscriber access networks. This is the complexity of installing ADSL devices; they require serious tuning to a specific subscriber line (as a rule, with the participation of a technical employee of the company - the network operator), have a relatively high cost.
Not so long ago, there were reports about the creation of a new version of ADSL technology, which is designed to eliminate these shortcomings. It is called Universal ADSL (UADSL), or DSL Lite. True, when using this technology, data is transmitted at lower speeds than in ADSL (with a subscriber line length of up to 3.5 km, the speed is 1.5 Mbps in the direction to the subscriber and 384 kbps in the opposite direction; with a length of subscriber line up to 5.5 km are provided with 640 kbps in the direction of the subscriber and 196 kbps in the opposite direction). However, these devices are easier to install; in addition, they include a frequency separator, so it does not have to be installed separately. Essentially, just plugging a UADSL modem into a telephone jack is as simple as plugging in a regular modem.
The cost of such devices does not exceed the cost of a conventional modem, so it is expected that this particular technology will be widely used in end-user access equipment.
Standards
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) Working Group T1E1.4 recently approved a standard for ADSL up to 6.1 Mbps (ANSI Standard T1.413). ETSI has supplemented this standard with requirements for Europe. T1.413 defines a single terminal interface from the operator side. The second version of this standard, being developed by the T1E1.4 group, expanded the standard in which it defined: a multiplexed interface on the operator side; configuration protocols and network management.
Some numbers
Distances for short range modems depend on the diameter of the copper pair:
1. Telindus Crocus HDSL 2048Kb/s:
| wire diameter (mm) | 2-pair version (km) | 3-pair version (km) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.4 | 3.6 | 4.0 |
| 0.5 | 5.0 | 5.5 |
| 0.6 | 7.1 | 7.8 |
| 0.8 | 8.9 | 9.9 |
| 1.0 | 12.5 | 13.9 |
2. Telindus Crocus SDSL:
| wire diameter | 384 kbit/s | 768 kbit/s | 1152 kbit/s |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.4mm | 5.0 km | 4.3 km | 3.6 km |
| 0.5mm | 6.9 km | 6.0 km | 5.0 km |
| 0.6mm | 9.8 km | 8.4 km | 7.1 km |
| 0.8mm | 12.4 km | 10.6 km | 8.9 km |
| 1.0mm | 17.3 km | 14.9 km | 12.5 km |
| 1.2mm | 19.3 km | 16.6 km | 13.9 km |
3. Telindus Crocus HS (144Kb/s):
| wire diameter (mm) | distance (km) |
|---|---|
| 0.4 | 6.9 |
| 0.5 | 9.5 |
| 0.6 | 13.5 |
| 0.8 | 17.5 |
| 1.0 | 26.0 |
Addition1
The article is well written, everything is correct, however there are some comments regarding the implementation of ADSL in real life. Unfortunately, ADSL can only be used on ordinary Russian communication lines on an experimental basis, so far there is no talk of commercial operation. An ADSL line requires a TWISTED pair (not a noodle) and shielded, and if it is a multi-pair cable, then in compliance with the direction and pitch of the twist.
You can object (S.Zh.), noting that noodles go only in the area from the cross in the house to the apartment, its replacement with a twisted pair does not present both technical and economic difficulties. In the cross-telephone station section, multi-pair cables are used, where each pair is twisted.
It seems to be convincing BUT have you tried to disassemble the telephone cable? Remove the insulation meter from the imported cable and from the domestic one. The imported one will dissolve into twisted pairs that will not fall apart even if they are pulled, and the domestic one almost immediately turns into a broom and a fair amount of skill is required to cut it without additional devices. Replacing noodles also doesn’t seem to be scary, but noodles won’t do here, you will need to replace the KRT (telephone distribution box), especially if it is plastic (remember how LANs are divorced) and it costs in each entrance and often not one at a time. The direction of the lay in domestic multi-pair cables is not respected (disassemble for example our 50-pair cable or 100-pair cable), because no one thought that such cables would be used to transmit wide-spectrum high-frequency signals, and, accordingly, no one also spoke about protection against crosstalk. thought. For the capitalists, perhaps, this benefit also arose by chance, because there is competition and in order for products to be bought, it must meet not even the mandatory, but the parameters recommended by all sorts of commissions (because these commissions do not eat their bread for nothing) and on the territory of one district (or even blocks) there may be two or more telephone service providers. Vooschem, as always, thanks to competition, quality goods and services are obtained.
For E1, a twisted pair is used with as many as two screens isolated from each other along the length of the cable and with a regulated number of cable spans, otherwise there is no need to talk about any mileage and stable communication.
This is true, but in my opinion (S.Zh.) DSL technology is more likely to find its application not in industry, but in the residential sector.
Yeah, that's what I can add (I.Sh.), a couple of years ago this technology was offered to ROSTELECOM for the reconstruction of short trunk lines, and the trunk cable is not your home wiring for such a cable, you can skip 64 Mbps and this upgrade was built according to the station- cable station. Well, ROSTELECOM did not agree to use these technologies, because it is expensive. I doubt that now the equipment has fallen in price so much that it costs like an Ethernet hub? And if I'm wrong, then someone wants to warm their hands a lot on the modernization of cable lines and the introduction of new technology.
Well, now let's imagine that 2-6 Mbit is loaded into the telephone cable, but it (the cable) does not have the appropriate parameters (often the inter-wire insulation is underestimated - well, they wet the poor fellow, they probably heard cod and space conversations in the receiver), as a result, pickups will come out . I think that these pickups will be the result of combinatorial frequencies, and a very wide spectrum, which will interfere with television receivers so much that a real war can begin. So in practice, not everything goes smoothly, unfortunately.
That is why, personally, I think (S.Zh.) that the introduction of UADSL with low speeds (up to 640 Kbps). All these effects in this technology will be expressed to a much lesser extent.
I think (I.Sh.) that anyway, the price of such an implementation will be too high at this stage to seriously think about it. So, there are more problems than it seems at first glance, and in any case, a more serious approach is required.
And here is my information (S.Zh.): providers, in particular Rosnet, do not share your views on technical problems and can provide ADSL equipment. Installing a modem, setting up, connecting, costs about $2,500. At the same time, speeds up to 640 Kbps are provided. The monthly subscription fee is about $300.
ADSL modems now cost around $800-1500. UADSL modems should cost around $250-500, which is more acceptable.
As soon as each telephone node has installed access equipment for data transmission networks, this type of service will become much cheaper, and the introduction of such access equipment is directly related to the introduction of ATM.
Addition2
In the article, Stanislav Zhuravlev expounds the theoretical aspect well, but does not touch upon the specifics of the application of this technology in Russia. In the first addition, some gaps are eliminated, but there are several inaccuracies:
First, xDSL technologies were developed by Bell's research division specifically for use on the existing copper wire infrastructure, which, even in the USA, is old and built on a conventional copper telephone pair, and not on shielded twisted.
Secondly, "noodles" are really not suitable for xDSL lines, but "noodles" are used in the area from the telephone distribution box to the subscriber socket, which is usually about 5-15 meters. In fact, there are two limitations that, with a given line resistance (usually 1-1.5 kOhm), do not allow the use of xDSL devices, these are loading and assembly from wires of various sizes. Line loading is the introduction of an inductive component into the line in order to reduce signal attenuation, but in Russia such lines are almost never used. The second problem is quite common, but if the station part of the equipment is located at the PBX closest to you, then the likelihood of such a problem is small, in any case, this problem can be solved with the local telephone exchange. However, if you need a direct channel, for example, to connect two local networks, then this is not a problem either. In Moscow, there are a fairly large number of direct channels operating on copper at a distance of 5-7 km and a resistance of 1-1.5 kOhm.
The wide distribution of xDSL technologies in Russia is constrained, first of all, not by an insufficient number of telephone pairs with acceptable parameters (while the number of installed lines in Moscow is estimated at tens or hundreds), but by the price of equipment, $ 2000-3000 for a set of station and subscriber parts, the price of connection and the cost of a dedicated channel (for the sake of curiosity, look at any of the providers how much a synchronous channel costs 64K channel, the prices will unpleasantly amaze you). The speed of already installed lines usually ranges from 64-512K. xDSL lines operating at a speed of more than 2Mbit over copper, I have not seen at all and I think their appearance is unlikely in the near future. This is explained by the fact that the cost of a 2Mbit stream is so high that either very large commercial firms or telecommunications companies that are themselves engaged in providing services can afford it, and such a criterion as the probability of an error on the channel is very important for them. The smallest error probability is provided by optical fiber, the stability of which will in any case be several orders of magnitude higher than xDSL lines.
It seems to me that the most promising prospects are for equipment designed for speeds of 64-512K, especially those created in accordance with the UDSL standard, which should be adopted before the end of this year. Manufacturers promise the price of a subscriber UDSL modem not more than $300-400. If large telecommunications companies (ideally MGTS :--)) become interested in providing xDSL services, which will be able to place station equipment sets at a large number of telephone nodes at their own expense, we will expect a sharp increase in the number of xDSL lines used in the near future.
Rostelecom is one of the largest providers in Russia, providing a variety of services: Internet, interactive television, telephone communications, and others.
Most of the devices on the market can work on its network. Some of them are offered by the company to subscribers upon connection.
One of them is D-Link DSL-2640U. Consider what kind of device it is and how to configure it for the correct operation of all services.
Short description
The DSL-2640U router manufactured by D-link is a universal device for accessing the Internet using ADSL technology, that is, through a telephone line. Additionally, the device is equipped with 4 ports for connecting computers, set-top boxes or other equipment and a built-in Wi-Fi interface for wireless Internet access.
Firmware versions
Users may encounter two types of interface of the DSL-2640U router from Rostelecom, which are somewhat different from each other. They depend on the firmware version. It is very easy to distinguish between old and new firmware:
- Old software version. The interface is made in white and blue.
- New firmware version. Interface colors: dark gray and black.

Entering the router settings management interface
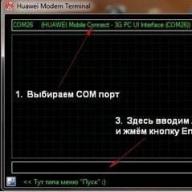
Before you start setting up the DSL-2640U router from Rostelecom, you need to get it out of the box, connect it to a telephone line, a computer and an outlet.
Once the physical installation is complete, you can begin configuring the device. All configurations are performed through the router's web management interface. To access the settings, you must perform the following steps in sequence:
- Launch any browser (Google Chrom, Opera, IE, etc.).
- Type 192.168.1.1 in the address bar.
- Press Enter.
- When prompted for a username and password, enter "admin" without the quotes in both fields. This information is used for authorization.
Internet setup
Rostelecom uses PPPoE in most places to connect to the Internet, so we will consider setting it up based on it. In the old and new versions of the firmware, the settings items are located somewhat differently, so we will give a description for each option separately.
old firmware
In the main menu, select the items "Network", "Connections" in sequence and click on the add button. On the screen that appears, set the following options:
- Connection type. Here you need to select the PPPoE mode. This will allow D-link DSL-2640U to work in router mode.
- VPI and VCI. These options vary by region. You can clarify them in technical support by calling a toll-free number or by finding the corresponding table on the net.
- Enter the username and password for access. You can find out this data from the documents that were received upon connection. Important! The password must be confirmed in the next field.
- Service name. In this paragraph, enter a name for the connection that will allow you to identify it, for example, "Internet".
- Extra options. For normal operation, it is necessary to enable the checkboxes next to the “Keep Alive” and “IGMP” items.
If the line leaves much to be desired and frequent disconnections are possible, then it is better to specify actions in case of an unsuccessful authorization attempt. In the "LCP failures" field, specify the value 2, and in the "LCP interval" - 15. This will allow the device to first try to establish a connection twice, and then pause for 15 seconds.

New firmware
The sequence of actions in the new firmware is somewhat different. After logging into the management interface, the user on the main page sees several buttons and information about the device and the status of the ADSL operation.
The first thing to do to set up the Internet is to switch to advanced management mode. The button for this is located at the very bottom of the screen.

In the "Network" section, select the "WAN" item. A window with available connections will open. If it is not empty, then before setting it is necessary to delete all connections, to do this, click on them in sequence with the mouse and select "Delete" in the lower right corner of the screen.
We press the "Create" button in the WAN interfaces and proceed to the configuration.

In the window that appears, you must specify the standard parameters, namely:
- Connection type - PPPoE. It is he who is used by Rostelecom for all subscribers connected using ADSL technology.
- "Interface" - DSL (new). Otherwise, it will not be possible to specify the VPI and VCI settings.
- VPI and VCI. These two parameters can be found in technical support.
This completes the Internet settings and if you do not need to connect a set-top box for IP TV, then you can save the settings and restart the DSL-2640U. To do this, at the top right of the D-link logo, we find the "System" menu and select the desired action.

Setting up a router to connect an IPTV set-top box
IPTV is actively promoted by Rostelecom under the name "Interactive TV". Often, subscribers can use this service for several months as a gift when connecting to the Internet. To set up the service on a DSL-2640U router from D-link, you will need to perform two steps:
- Create connections. There may be one or two of them for IPTV operation, depending on the region.
- grouping of ports.
old firmware
Again, in the main menu, select the "Connections" sub-item in the "Network" section. Set the "Connection Type" switch to the Bridge position and set the VPI/VCI pair. If two sets of parameters are possible, then repeat the procedure one more time.
After creating a connection, you need to perform port trunking. To do this, go to the "Advanced" section of the main menu and select the "Interface grouping" item. On the page that appears, select the appropriate button at the very bottom to add a group. Fill in the "Name" field with any name, for example "TV".
And we transfer from the left column to the right two bridge connections and ports for the set-top box (usually one, for example, LAN2).
New firmware
The actions that owners of the D-link DSL-2640U router with the new firmware need to perform are similar, but the menu is slightly different, so we will give them in order:
- We go to the "Advanced settings" and go to the "WAN" item in the "Network" section.

- Click "Add".
- Set the “Connection Type” switch to the “Bridge” position, and in the “Interface” drop-down menu, select the “DSL (new)” value.
- Specify VPI and VCI, then save the connection
- If necessary, we create a second connection of the "Bridge" type for the second pair of VPI / VCI.
- On the "Advanced Settings" page, in the "Advanced" section, click on the "Interface Grouping" item.
- Click the "Add Group" button.

- Specify any name for the new group and tick off the necessary ports, for example, LAN 4 and one or two Bridge type connections.
- Click the "Apply" button.
Setting up wireless Internet access
Devices that access the Internet via Wi-Fi today can be found in every home. To provide them with wireless access to the network through the D-link DSL-2640U, some settings must be made.
old firmware
First you need to set the name of the network. This is done on a special page, which can be accessed by successively selecting the “Wi-Fi” and “Basic settings” items in the main menu. The only thing you need to specify on this page is the name of the network. You need to enter it in the appropriate field, which is called "SSID". After entering the data should be saved using the special button below.
It is important not only to create a Wi-Fi network, but also to make it secure enough so that personal data is not at risk. You can do this by setting a key or password for it.
This operation is performed on a dedicated Security Settings page, which can be accessed through the Wi-Fi section of the main menu.
Rostelecom can rightfully be considered one of the largest providers in Russia. This provider provides its subscribers with a variety of services, such as Internet, telephone, and others. Most devices on the market are suitable for connecting to the Rostelecom network. The company offers some devices to its subscribers when connecting services. One such device is the D-Link DSL-2640U. In this article, we suggest that you familiarize yourself with this router and its settings.
Brief characteristics of the router
The DSL-2640U router from D-link is designed to connect to the Internet using ADSL technology, that is, through a thin telephone cable. In addition, this device has built-in Wi-Fi for wireless Internet and 4 ports for connecting computers, set-top boxes or other equipment.
Firmware versions
The DSL-2640U router can be found with two types of interface, which depend on different firmware versions. You can distinguish between old and new firmware by color. The interface of the old version of the firmware is made in white and blue, and in dark gray and black.

Router admin login
To set up the router, first of all, you need to connect it to a computer, a telephone cable and an outlet. When the connection is made, you can start configuring the device. All settings are carried out using the web interface for managing the router. To enter the management system of the DSL-2640U router, follow the instructions:
- Open an internet browser on your computer.
- In the address bar, write the device address - 192.168.1.1.
- Press Enter.
- Next, you need to go through authorization in the system. To do this, enter the value admin in both the username and password fields.
Internet connection setup
Most often, Rostelecom provides the Internet to its subscribers via a PPPoE connection, so this article describes the configuration based on it. The settings items in different firmware versions are also located differently, so we will describe the settings process for each option separately.
Old firmware version
In the main menu of the interface, select "Network", then "Connections" and click "Add". In the window that opens, set the following options:
- In the "Connection type" item, select the PPPoE value.
- Enter the values for the "VPI" and "VCI" parameters. You can find them out in Rostelecom technical support, since this data is individual for each region of the country.
- Enter your username and password to access the Internet. This information, as a rule, is issued by the provider when concluding a contract for the provision of services. The password must be entered in the next field to confirm it.
- In the next paragraph, think up and write the name of your connection.
- In the additional parameters, it is necessary to mark the items "Keep Alive" and "IGMP".
- In the "LCP failures" field, enter the value 2, and in the "LCP interval" field - 15. Thanks to these settings, if the connection is lost, the device will try to connect to the network 2 times, and if the attempts are unsuccessful, it will pause for 15 seconds.

New firmware version
After successful authorization, the main interface page will open on your screen, which contains information about the router and several buttons. To further configure the device, you must switch to the advanced control mode using the corresponding button at the bottom of the screen.

- Next, select the "WAN" item in the "Network" section. In the window that opens, delete all existing connections, to do this, select them and click "Delete".
- In the "WAN" item, click the "Create" button.

A window will open on the screen, in which specify the following parameters:
- Connection type - PPPoE.
- "Interface" - DSL (new).
- The values of the VPI and VCI parameters for your region, which can be found in Rostelecom technical support or searched on the Internet.
After the steps have been completed, the Internet setup can be considered complete. If you do not plan to connect an IPTV set-top box, you can restart the device and use the Internet. To reboot, use the appropriate button in the "System" menu at the top right of the D-link logo.

Setting up IPTV television
Rostelecom is actively offering subscribers an IPTV service called Interactive Television. To configure IPTV on a DSL-2640U router, do the following:
In old firmware
- In the main menu, in the "Network" section, select "Connections".
- In the "Connection type" column, set the value to "Bridge" and enter the VPI / VCI values \u200b\u200b(these values \u200b\u200bwill differ from those that you entered for the Internet connection). Depending on the region, IPTV may need one or two connections to work. If you need two sets of parameters, then repeat the procedure again.
- Now that the connection has been created, we need to perform port trunking. To do this, go to the "Advanced" section and select the "Interface grouping" item.
- Add a group using the appropriate button at the bottom of the page.
- Come up with and enter the name of the group in the "Name" field.
- Move from the left column to the right two bridge connections and ports for the set-top box (usually one, for example, LAN2).
In the new firmware
- Open "Advanced settings", then in the "Network" section, go to the "WAN" item.

- Click Add.
- In the "Connection type" item, select "Bridge", and in the "Interface" drop-down menu, set the value to "DSL (new)".
- Specify the VPI and VCI (these values will be different from those you entered for the Internet connection) and save the created connection. Depending on the region, IPTV may need one or two connections to work. If necessary, we create a second similar connection for another pair of VPI / VCI.
- In the Advanced section of the Advanced Settings page, click Interface Grouping.
- Click the "Add Group" button.

- Specify any name for the group being created and check the necessary ports and bridge connections with checkboxes.
- Click Apply.
Setting up a Wi-Fi network
To use wireless Internet via Wi-Fi, you must perform the following router settings:
For old firmware
- In the main menu, go to the "Wi-Fi" section, then select the "Basic Settings" item.
- On the page that opens, you must specify the name of your network in the "SSID" field and click the "Save" button.
Everyone has long known that a Wi-Fi connection should be as secure as possible so that personal data is not at risk and that other users cannot use your Internet. Therefore, it is recommended to set a password for your Wi-Fi network.
- Through the "Wi-Fi" section in the main menu, enter the "Security Settings" item.
- Select the authentication type "WPA2-PSK", then enter the password in the appropriate field (do not forget to write down the password, because without it you will not be able to connect to the created Wi-Fi network). After that, click the "Edit" button.
For new firmware
- In the "Advanced settings" section, set the Wi-Fi switch to the "On" position.

- In the Wi-Fi section, select "Basic Settings".
- Specify the name of the network to be created in the "SSID" field and click "Apply".

Recall that the Wi-Fi connection must be protected from unauthorized users. Therefore, you need to return to the "Advanced Settings" section and enter the "Security Settings" item. Select "WPA2-PSK" as the authentication type, and enter the password to access the network in the corresponding field.
At the end of the setup, it remains to save all the settings and restart the device. As a rule, configuring routers does not cause difficulties for users. However, if you are unable to connect and configure your router, please contact .
XDSL technology from Rostelecom and a number of other providers has long since replaced analog modems, whose maximum speed was limited to 56K. The ability to transfer data over the same lines as the phone allowed not only to save operators on laying new wires, but also provided a good quality of Internet communication for users.
XDSL from Rostelecom: what is it?
Interested in the question of what is XDSL and how to connect the Internet from Rostelecom using this technology? The abbreviation XDSL stands for Digital Subscriber Line or Digital Subscriber Line in Russian. The maximum speed of incoming traffic when using this technology can reach 8 Mbps. The main role in the development of DSL was played by the low price of equipment, as well as the absence of the need to lay additional communication lines.
Analog modems, which also worked through the phone cord, are long gone for two reasons:
- low communication speed;
- the impossibility of using the Internet simultaneously with the phone.
This option was especially inconvenient at a time when the communication line was divided into two apartments. Thus, if one of the subscribers spoke on the phone or used the Internet, the other did not have any access to telecommunications services.
XDSL technology has completely solved this problem. Thanks to her, the signal no longer needed to be converted from analog to digital on a computer, but was transmitted directly. In addition, the problem with the simultaneous use of the Internet and the phone was taken into account here. Now the user can enjoy two services at the same time.
Of course, when talking about XDSL technology, one cannot fail to mention that there are many branches of its development: ADSL, IDSL, HDSL, SDSL, VDSL.
ADSL technology, which has earned the most positive feedback among all types of XDSL connections from Rostelecom and other providers both among experts and in the user community, has gained the most popularity. This is easily justified by its speed characteristics. The data transfer technology in this case is asynchronous. In practice, this means that the incoming and outgoing speed have different values. The maximum throughput "to the user" is limited to 8Mbps. The speed of the outgoing connection does not exceed 768Kbps. Nevertheless, for use as a home or work network, these characteristics are quite enough. An ADSL connection can provide a comfortable experience not only when surfing the Internet, but also when playing high-definition online content and participating in multiplayer games.

One of the interesting Internet connection technologies is VDSL. This is the fastest way to transfer data over a telephone line. But for the reason that this technology is also asymmetric, it was necessary to sacrifice the data reception speed, which has no more than 2.3 Mbps. But the outgoing throughput here has grown to a huge value for a DSL connection of 52 Mbps.

The rest of the technologies did not gain much popularity, as they could not boast of their high-speed characteristics.
Pros and cons of XDSL connection
Despite the fact that there are faster methods of accessing the Internet on the telecommunications market, the number of Rostelecom customers using XDSL communication lines represents a fairly large audience. This is easily explained by the main advantage of the technology - cost minimization. Unlike a fiber optic connection, which requires additional cabling, XDSL operates over a telephone line, which is present in almost every home.
However, such a connection may not always work correctly. For example, if the provider's substation is located remotely, the Internet speed will noticeably drop. Also, weather conditions that directly affect the telephone line can lead to a deterioration in the quality of communication.
Compared to a fiber optic connection, a telephone line is not capable of providing a stable speed of up to 100 Mbps.

For Rostelecom users who wish to subscribe to the Non-Stop promo package, it is worth noting that the declared speed of 50 Mbps cannot be achieved when using XDSL equipment.
Attention: If you are already using a tariff with a speed of 8 Mbps, you will not be able to increase the line bandwidth to a higher value. Nevertheless, the tariffs for XDSL services from Rostelecom have a lower cost.
XDSL connection from Rostelecom, which made a breakthrough in data transfer speed in the past, is still a good option for accessing the Internet. Download speeds up to 8Mbps and low connection costs without the need for additional cables become decisive factors when choosing a telecommunications service.
The technology of broadband high-speed access via telephone lines - ADSL was originally considered a transition from the ancient Dial-Up to more or less modern FTTB ETTH technology, and no one thought that it would live for so long. Nevertheless, ADSL lives on and is not going to rest in the Bose yet. With its help, the private sector is connected on the outskirts of megacities. And in smaller towns and rural areas, this may be the only high-speed technology at all. And despite this, the quality of services provided through the existing telephone lines is declining every year, less and less money is allocated for the maintenance of LKS, to the point that even a field worker for repairs sometimes does not receive line crews for a month or more. With cable damage, the situation is sometimes even worse. Providers are trying to squeeze the maximum profit at minimal cost and at the same time “make a good face on a bad game”: short deadlines for eliminating damage are set, fitters are chasing from corner to corner, more noise-resistant profiles are set on station equipment.
Subscribers, on the other hand, want to keep up with the times and require the highest possible data transfer rate. Is it possible to somehow influence it and how to get the most out of your line, we'll talk today.
The maximum download speed via ADSL, according to the specifications, is 24 megabits per second. Is it really achievable? Yes, it can be achieved, but only on short lines of very good quality. But is it worth it to bother with it? The fact is that telecom operators are also not fools and make tariff plans that can be pulled by a regular telephone line - often up to a maximum of 8 or even up to 6 Mb / s.

Accordingly, even if there are 20-21 megabits per second on the line, it will still not be possible to accelerate more than the tariff. But if the operator has its own file-sharing network, or there are some interesting internal resources such as game servers and torrent portals, then it makes sense.
ADSL technology has 2 main factors on which the speed depends:
- Setting up access equipment
- Line quality
They are closely interconnected with each other. On an ideal line, cut the speed to a minimum on one side and no matter how optimally the equipment is configured, the “bottleneck” will be a barely live line. Therefore, the approach must be comprehensive.
Setting up ADSL equipment for maximum performance:
What is an ADSL line? These are two modems connected to each other by a telephone line. One stands at the subscriber, the other - on the side of the provider. When you turn on the modem at home, it coordinates the signal parameters and speed with the station counterpart. This procedure is called HandShake (English, handshake). After that, the link rises on the best values from the received ones.
You can view the current ADSL connection speed in the web interface of your modem on the status page. For example, this is how it looks on the D-Link DSL-2640U:

On some modem models, it is possible to view more extended information:

Here the configuration of the device at both ends of the line plays a significant role. Pay attention to the Estimated speed parameter, it is much higher than the connection speed. This means that the line still has a certain resource that can be used. Of course, it is not a fact that you will be able to achieve those values that the modem calculated, but it is quite possible to squeeze out half of this difference.
This can only be done if the hardware is configured correctly. From the side of the subscriber device, there are very few available settings:

In fact, you can only change the modulation used - for example, leave only ADSL2+. If you need a higher upload speed, also check the box annexM. But again, these modulations must also be enabled on the station modem, otherwise the coordination will not pass, the link will not rise, which means there will be no sense from these actions. Therefore, you need to call the technical support of your telecom operator and chat with them. Moreover, you will first have to go through the “filter” of the first line and, by any means, contact the engineers who are directly involved in the station equipment and set speed profiles on the ports.
Here it is worth saying a single word about the relationship with the technical support of the provider. Firstly, people work there and where one person can easily help, another can simply refuse and that's it. Secondly, there are certain regulations that employees must comply with. And here, no matter how you beg, you won’t get more than you can.
If you can find a common language with a specialist, then he can choose the optimal profile for you, or the maximum one. This is what it looks like on the station DSLAM:

Although I would not advise you to squeeze the maximum - you will lose in noise immunity and if interference occurs on the line, you will lose the link. It is better to let the connection be a little slower, but more stable.
Another trick - you can ask support staff to enable Fast Mode on your port. In simple words, this is a profile on a DSLAM with error correction disabled. Due to this, the ping on the last mile becomes a little less and the response speed increases accordingly.
Checking and repairing a telephone (dedicated) line
First of all, remember - Everything that goes to the house (apartment) is the provider's area of \u200b\u200bresponsibility. And now the wiring around the house or apartment - you are already responsible for this. Here, of course, there are also nuances. For example, if the main cable is old, then there is practically no chance of replacing it. In my memory, cable replacement cases can be counted on the fingers. Basically, only repairs, replacement of cable sleeves, etc. are done.
The situation is not easy with the last section from the junction box to you.
If you live in a private house with an overhead cable entry, then, as I said above, it can sometimes be not easy to get a fitter to replace a field worker. And the field worker himself (cable P-274, P-274M and P-279) has recently not been of good quality. Therefore, by all means, seek replacement with a new cable - TCPPt, sometimes also called "digital":

With its help, we were once able to connect a subscriber at a distance of 5 kilometers from the station and at the same time provide him with a speed of about 6 Mb / s. For such a length, this is just the ideal speed.
In a multi-storey building, from the KRT box to the socket in the apartment, the so-called "Noodles" are usually thrown - a TRP cable, a TRV, etc. I don't like it at all - a bad, unreliable and brittle cable. Better buy yourself a two-pair twisted pair cable UTP-2x2xo.5. Firstly, it is a more reliable cable. Secondly, it will have a second, reserve pair. And thirdly, it can be crimped into an RJ11 telephone connector and plugged into an ADSL splitter. This will eliminate another weak link - the telephone socket.
If the socket is already installed, but of the old model with an adapter for the "euro" RJ11 connector, it is better to replace it with a new one:

Adapters are usually of very low quality, often fail. And the sockets themselves, after 10-15 years of work, begin to spoil due to dirty and oxidized contacts.
In the apartment, the wiring must be intact and without twists. The more damage and twisted connections, the worse the quality of the line will be and the lower the data transfer rate of the ADSL line. If the wire is old, and even has a couple of twists on it, it’s better to replace it with a new one. Twisted pair is also great for this.

As an option, you can use a 2-pair KPSV (I don’t advise a single-pair one - it’s flimsy in my opinion).
Remember, only a good line with a good, intact cable can provide excellent ADSL Internet speed and the best high-speed link quality.