The article examines in detail the influence of various parameters on the speed and other characteristics of the operation of ADSL equipment.
Abbreviation ADSL(Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) stands for "Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line", which emphasizes the difference in exchange rates in the directions to the subscriber and back, which was originally incorporated in this technology.
asymmetry ADSL, in its essence, implies the transfer of large amounts of information to the subscriber (video, data arrays, programs) and small amounts from the subscriber (mainly commands and requests).
Equipment ADSL located on the PBX, and subscriber ADSL modem connected to both ends telephone line, form three channels:
- high-speed data transmission channel from the network to the computer (speed - from 32Kbit/s to 8Mb/s);
- a high-speed data transfer channel from a computer to a network (speed - from 32Kbps to 1.5Mbps);
- a simple telephone communication channel over which ordinary telephone conversations are transmitted.
The value of the data transfer rate in this case depends on the length and quality telephone line. The asymmetric nature of the data transfer rate is introduced on purpose, since a remote Internet user usually downloads data from the network to his computer, and either commands or a data flow of a significantly lower speed go in the opposite direction. To obtain rate asymmetry, the subscriber termination bandwidth is also divided asymmetrically between channels.
On the PBX side, a so-called access multiplexer should be located on the user's line ADSL - DSLAM. This multiplexer allocates subchannels from the common channel and sends the voice subchannel to the PBX, and directs high-speed data channels to the router connected to DSLAM.
One of the main advantages of technology ADSL compared to analog modems and protocols ISDN And HDSL- the fact that voice support does not affect the parallel data transmission over two fast channels. The reason for this effect is that ADSL is based on the principles of frequency separation, due to which the voice channel is reliably separated from the other two data transmission channels.
Influence of cable parameters on the operation of ADSL equipment
Primary line parameters:(real)
Note:
it is impossible to measure the insulation resistance and capacitance on a damaged cable with a digital multimeter! this is the first a sign of a wet cable, "brokenness", asymmetry ...
Secondary line parameters:(main)
Signal attenuation.
from 5dB to 20dB - the line is excellent.
from 20dB to 30dB - the line is good.
from 30dB to 40dB - the line is bad.
from 50dB and above the line sucks.
(on Upstream and Downstream attenuation is different)
Noise level: RMS Noise Energy
from -65dBm to -50dBm - the line is excellent.
from -50dBm to -35dBm - the line is good.
from -35dBm to -20dBm - the line is bad. (high probability of line damage)
from -20dBm and above, the operation of the equipment is impossible.
Line frequency response.(examples below)
Note:
With line noise levels between -65dBm and -55dBm, normal equipment can operate at exorbitant distances. (up to 6 km or more with a core diameter of 0.5 mm) despite the high signal attenuation (up to 50dB), even at the minimum parameters.
Measuring equipment:
Reflectometer “CableSHARK” manufactured by “Consultronics”. Reflectometer “990DSL CopperPro” from “FLUKE Networks”. Multimeters APPA 101 and UNI-T UT70D
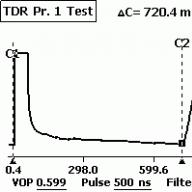
First, let's see how it looks from the point of view ADSL modem ideal line.
twisted pair. 5Cat. 720m. (assembled on rolls from pieces)
Loop resistance 160 Ohm. (24AWG)
Average noise level in the range 4kHz-2000kHz:
RMS noise -65 dBm (or less)
Loop capacitance 0.040uF

Fig.1. Distance check
Figure 2 shows the results of testing the received line.
Blue indicates the frequency response.
Green - noise level in the line.
red denotes DMT.
Note:
DMT (Discrete Multi-Tone), the information stream is divided into several channels, each of which is transmitted on its own carrier frequency using QAM. Typically, DMT splits the 4 kHz to 1.1 MHz band into 256 channels, each 4 kHz wide. This method, by definition, solves the problem of dividing the bandwidth between voice and data (it simply does not use the voice part), but is more difficult to implement than CAP. DMT is approved in ANSI T1.413 and is also recommended as the basis for the specification Universal ADSL.
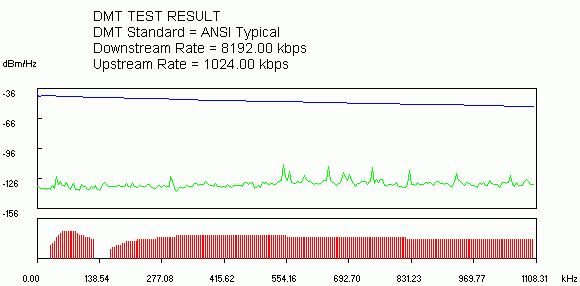
Fig.2. Line Test Results
Note:
The greater the distance, the more line resistance, worse frequency response and higher signal attenuation. This mainly affects the Downstream (middle and end of the chart), i.e. connection speed ADSL modem towards the subscriber.
Real Line:
Loop resistance 420 Ohm
Distance approximately 2.5 km.
The working capacitance of the line is 0.12 uF.
Average noise level in the range 4kHz-2000kHz: RMS Noise -38dBm
DSLAM and SIEMENS modem.
Theoretical speed:
7Mbps Downstream
800kbps Upstream
Real connection speed:
1Mbps Downstream
512kbps Upstream
The connection is stable.
There is some damage on the line:
cable tangle, one of the conductors has a short to ground. As a result - low-frequency noise in the line when the ADSL equipment. plus when turned on ADSL equipment, because of the asymmetry line parameters, audible HF noise appears. splitter replacement is useless.
With a reflectometer, you can "see" the damage. (presumably at a distance of 42.9 m wetting.) A little closer, the upward ejection is most likely an oxidized twist.

Fig.3. Line with damage

Fig.4. Noise in the line, mainly from the Mayak radio station (549 kHz), etc.
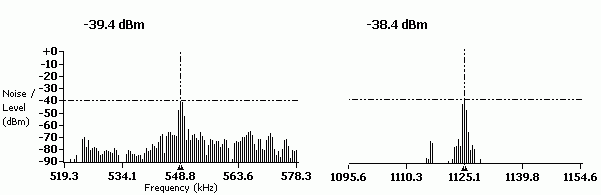
Fig.5. Noise in the line, (Fig. 4 details)
straight wire:
(copper pair without telephony, they like to call it a dedicated line. :)
Loop resistance 1067 Ohm
The working capacitance of the line is 0.18 uF.
Average Noise Level 4kHz-2000kHz: RMS Noise -55.71dBm
DSLAM and SIEMENS modem.
Real connection speed:
64Kbps Downstream
32kbps Upstream
(sometimes loss of sync)
Factory cross, noodles, twists ... a very long distance to the ATS.
Stable operation of ADSL equipment on such a line is impossible.

External factors affecting the operation of ADSL equipment
All sorts of AVU lines, HF seals, UVO signaling, other DSL, passing in the same cable, in adjacent pairs, greatly interfere with the work. Especially if there are all kinds of cable defects, "spread/broken" , cable getting wet, taps. All these devices create a lot of noise in the frequency range from 0 Hz to 100-200 kHz. (Mostly) This reduces the signal of the outgoing stream ADSL (upstream) up to its complete absence and, as a consequence, the loss ADSL modem synchronization.
When DSL and RF seals work together in the same cable on different pairs, crosstalk can occur that interferes with the operation of analog telephony. (noise in the range of 1KHz and above)
In factory and industrial areas, all kinds of power equipment are very much affected. Direct proximity to the railway.
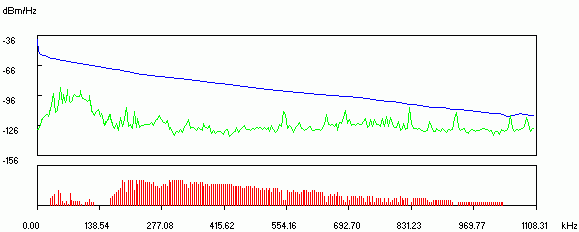
Fig.7. Interference from AVU lines, Peterstar HF seals, UVO alarms
As you can see on the graph, almost all the main noise falls on the Upstream range. (beginning of the graph) does not depend on the time of day. The alarm is usually turned on from 19:00 to 09:00 and on weekends around the clock. Accordingly, at this time ADSL works intermittently or does not work at all.

Fig.8. Operation of power electrical equipment
Very bad cable frequency response. High noise level, clogging almost the entire signal. station part. DSLAM
Damage connecting multi-pair cable from DSLAM to cross plinths:
Cable damage, plinths, poor quality "cable termination". On old crosses: cold soldering or unsoldered wrapping. The result is contact bounce. The result is an unsystematic loss of sync by the modem.
"Broken pairs" - can only be tracked by a tone generator + a test tube with a high-impedance input. Incorrect cutting/installation of the cable. Poor quality/incorrect soldering of connectors. (The most difficult to trace glitches. They are usually solved at the editing stage)
Violation of installation technology crossover cable.
For example:
when the next pair of wires is passed through the cross eye, in which there are already many other crosses. And they do it with such an effort that the dragged pair rips off / burns the insulation on adjacent crossings. As a result: the short circuit of the conductors of various pairs between themselves or to the ground.
Incorrect connection of splitter/modem card in DSLAM. Incorrect connection of the splitter port to the line/station. Connection subscriber line to another DSLAM port. Sometimes they just forget to make crossovers. :) Equipment overheating.
Software/firmware buggy, failure of DSLAM operation with some type of subscriber equipment with some line parameters.
conclusions
Line resistance directly dependent on distance. Therefore, knowing the resistance, it is possible to accurately calculate the distance between the subscriber and the PBX. Knowing the reference data ADSL modem, you can estimate at what speed the modem will connect. Unfortunately, that's all. to know secondary line parameters complex expensive equipment is required. It is also possible to view the average signal attenuation on the Upstream and Downstream streams in some ADSL modems: ZyXEL 650, Cisco 800 series, USB ADSL modems and others.
For example:
at cable cross section 0.5 mm2 (0.085 Ohm/m) and line loop resistance 1000 ohm line length L = (1000 / 0.085) / 2 = 5882 m. It should also be borne in mind that in some areas cable section can be 0.4mm.kv (0.133 ohm/m) for the ZyXEL 645R modem, the theoretical speed is 64 kbps
Another example:
Distance 5.5km
Core diameter trunk cable from ATS: 0.7mm
[to the nearest ten-pair branch from trunk cable going to the building of the subscriber] Ie. most of the cable from the PBX to the subscriber has a copper core diameter of 0.7mm
Loop resistance: 570 Ohm!!!
Loop capacitance: 0.3uF
Maximum possible speed: 5M/640Kbps
Real operating speed: 640Kbps / 360Kbps (if set more - sync failure)
Equipment: Cisco 800 series. there are two VoIP lines and Internet access.
At line loop resistance 800 - 1000 ohms the chance of failures/instabilities is very high. (In any case, it is impossible to guarantee 100% reliability) At this point, how lucky you are with the main cable. There are cases when the ZyXEL 645R works with minor interruptions on the line with a resistance of 1200 - 1400 ohms.
You can easily ruin the link even if the resistance is much less than 800 ohms. As a rule, this is the "noodles for cloves" so beloved by everyone on the subscriber's side. The maximum operating frequency is 180kHz and, if desired, 10BaseT can be stirred up through bleach (two pairs) ... but at what distance?
Old soviet telephone sockets. A sort of shYt with a capacitor 1uF x 160V inside. New ones, by the way, also do not shine with quality. The RJ11 plug made in China just falls out of the "Zrobleno in Belarus" sockets. I have not seen RJ11 plugs made in Belarus, so such sockets are immediately thrown into the trash.
In apartments and offices with high humidity (old fund), the resistance of oxidized contacts can reach several hundred ohms.
Sometimes narrow-minded "telephonists" can make telephone input to the office / apartment through a forgotten radio input. The junction box left from the radio. (300 ohm resistor soldered to each wire)
You can also look for diode blockers on the landing in the shield (if once upon a time the line was paired) We get a funny effect: the ADSL modem only works when the phone is off-hook. Or a forgotten high-frequency filter from a private security alarm.
If the line passes through the cross of the old plant / enterprise, then you get additional bonuses in the form of:
- Four thermals per line. each has a resistance of 25-50 ohms + inductance.
- Parallel branches of the line to other workshops, intermediate crosses, couplings, etc.
- System "Granite", against listening. Through it, the work of Dial-UP equipment is difficult, and you can forget about ADSL altogether.
Special clinical cases:
Insulation damage trunk cable :(
Soaked couplings, "broken", etc.
A broken pair is when the wires for the line are taken from different pairs of the cable.
Well, the simplest:
Incorrect connection of the splitter or microfilters.
In the summer... Overheating of the modem.
Or after another thunderstorm - a burned-out modem. :)
At line loop resistance more than 1000 Ohm, the operation of an ADSL modem is almost impossible.
DC line parameters for connecting ADSL equipment
ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line), less often - an asymmetric digital subscriber line - a technology that provides access to the Internet with asymmetric bandwidth distribution and data transmission priority. Initially, the technology was created to provide access to interactive television, but was not widely used.
The widespread use of the ADSL standard occurred in the middle and late 90s of the last century, when providers looking for an opportunity to reduce the cost of building networks discovered the potential of ADSL modems as subscriber Internet access points. Compared to all other technologies that provided access to the network at that time, the cost of a modem connection was the lowest, and the potential for development of the technology led to its ubiquitous distribution.
Since the beginning of the 2000s, ADSL technology has been supplanted by faster types of subscriber connections, primarily Ethernet, which provides a throughput of up to 1 Gbps, against a ceiling of 24 Mbps for ADSL technology. At the same time, this type of connection is widely used in a number of European countries as a basic one: most Finnish users receive an ADSL connection as a constitutionally guaranteed access to the Internet. According to British analysts, 99% of residential buildings in the country are connected using this technology. Naturally, its use is much lower and accounts for a small percentage of subscribers.
Advantages and features of using ADSL technology

The key advantage of the Internet with an ADSL connection is its implementation through a regular telephone line. Analog telephony is connected to a subscriber ADSL modem. To receive services, special equipment must be installed at the PBX to provide all subscribers with broadband access to the network.
The use of technology makes it possible to use a telephone line in parallel and gain access to the Internet via ADSL. To do this, frequency separation of channels is used.
The main disadvantages of the technology:
- low communication speed. Even with the most modern circuitry, the 25Mbps ceiling remains insurmountable;
- many extraneous factors affect the connection speed - starting from the quality and cross-section of the twisted pair connecting the subscriber and the PBX, and ending with the distance between them.
FAQ
Is the connection via ADSL justified in today's realities?
In most cases, such a connection can be considered obsolete. Even in remote areas where for a long time the only communication channel was a telephone line, there is an alternative in obtaining faster network access through LTE technologies or laying fiber optic communications.
For what use cases will ADSL data rates be sufficient?
Restriction in reception at the level of 25 Mbit / s can actually be much lower - a lot of factors depend on the state of the telephone line and the distance of the subscriber from the PBX. Thus, the use of ADSL can be considered acceptable only for activities that do not require high access speed - e-mail exchange, study of graphic and text content. In most cases, the ADSL speed will not be enough for streaming music and watching videos. At the same time, downloading even 1 GB of information takes a significant amount of time, which is not comparable with the use of more modern access protocols.
Tariffs and services of Net By Net Holding LLC may be changed by the operator. Full up-to-date information about tariffs and services - in the "tariffs" section or by phone indicated on the site.
Designed to connect to the Internet through a telephone line. It can work as a bridge or a router. Many models have Wi-Fi. The device provides asynchronous data transfer. To configure it, you need information that the provider provides (DNS and IP addresses, PVC, login and password). It depends on the connection type. All parameters must be entered manually.
Rostelecom, for example, complete with its modems provides a disk that sets the settings itself. With it, you can quickly connect equipment to the network. And this does not require special knowledge or skills.
If your ADSL modem was previously used, it is better to reset its parameters to factory settings. It will also be useful if you do not remember the password for the web interface. Different operators have different connection methods. When changing providers (for example, you used Domolink, but moved to a new apartment located in the Rostelecom coverage area), it is easier to set up the device from scratch than to change individual options.
To return the default options:
- It is necessary to connect the ADSL modem to the electrical network.
- Find on its body a button or a hole labeled "Reset".
- If this is a button, hold it down for 30 seconds. The lights on the device may flash.
- If it's a hole, insert a pin or paperclip into it. Also hold for a few seconds.
- If none of the methods worked, hold down the On / Off button and wait until the indicators flash.
After the backup, the device will reboot. You can also reset the settings through the web interface. How to enter it is described in one of the following chapters.
Connecting to a computer
Before setting up an ADSL modem, it must be connected to a network and a computer. For this you will additionally need:
- Splitter. Frequency separator. It is a small box with three ports. Internet and telephony "are" in one wire. But they have different frequencies. The splitter eliminates their influence on each other.
- Ethernet cable. Needed to connect a PC to an ADSL device. You can also use Wi-Fi if you know the password. If you are connecting the modem via USB, you need a USB cable.

- Telephone cable with two connectors. For connecting router and splitter.
Many operators simultaneously provide Internet, telephony and television services (including Rostelecom). So all communications will work on one wire. Although there are other types of connections. Optical fiber cables are very popular now - they have a high bandwidth. Or twisted pair of various categories. They have different sizes and connectors. Therefore, they are not suitable for ADSL.
Setting up the modem begins with connecting it to a computer and a network.
- Get a splitter.
- In the slot called “Line”, insert the main telephone cable that is connected to the provider (Rostelecom, Domolink, MTS, and so on).
- The "Phone" (or "Tel") port is for a telephone set (if you have one). You can use outlets to connect multiple devices.
- Insert a telephone wire into the “Modem” jack, which you can route to the modem. The ADSL connector is intended for the Internet cable. There are slots of different sizes - do not confuse.
- Connect the router itself to the PC in any way convenient for you. To work via Wi-Fi, find the desired wireless network on your computer and enter the password (should be indicated on the modem case or in the instructions). To connect using an Ethernet cable, insert one end of it into the "LAN" slot, and connect the other end to the network card port. Or use a USB cable.
- Check if the corresponding indicators on the router are lit. The "Internet" light should not be on until you have established a connection.

Wiring diagram
Web interface. Setting up a network card
The ADSL modem is most often configured via the web interface. This is a visual display of device parameters and information about it. There you can see logs, statistics, options set. To enter the interface, open any browser and enter "192.168.1.1" or "192.168.0.1" without quotes in the address bar. The address may be different - this is always indicated in the instructions.
If the router page does not open, then it is not connected correctly, or it is not connected to the network card. In the first case, check the cables, see if they are properly fixed in the sockets. If everything is in order there, you need to configure the network card.
- Click on the connection icon in the taskbar (or open "Control Panel")

Click on the connection icon
- Go to the Network Sharing Center.
- Click on "Change adapter settings" (or "Manage connections" if you have Windows Vista).

- Right click on the required connection.
- Select "Properties".
- Find "Internet Protocol 4" in the list. Double click on it.
- A window will open in which you need to specify the IP and DNS.
There should be information that the provider will issue (in Rostelecom, for example, you need to automatically receive addresses). But for now, you need to configure the network card. To do this, set the following parameters:
- IP address - "192.168.1.2" (remove quotes).
- The subnet mask is "255.255.255.0".
Save your changes and try opening the web interface again. Upon login, it will ask for a username/password. The default is "admin/admin" or "admin/1234". The key is in the manual.
There you can reset the settings.
- Go to "Management" ("System").
- Section "Setting" ("Configuration").
- Click the "Restore Default Settings" button.
Internet connection
If the parameters are not set automatically, you must connect the device manually. The setting differs depending on the operator and router model. But the algorithm of actions is the same. For example, the situation with D-LINK DSL-2640U:
- Log in to the web interface.
- Open the "Net" or "Network" tab. In the 2500U model, it is called "WAN". In previous versions, located in the "Advanced Setup" section.
- Subsection "Connections".
- Click the "Add" button.

- Select "PPPoE" from the "DSL protocol" or "Connection Type" list.
- Enter the PVC parameters in the VPI and PCI fields. They vary by region and provider. For example, for Rostelecom in Moscow, VPI is 0 (zero), and VCI is 35. This information can be obtained from the operator.
- In "PPP Username" ("Username") write your login.
- In "Password" and "Password confirmation" ("Password" and "Confirm password"), copy the password.
- Check the "Keep Alive" and "IGMP" options.
- "LPC interval" and "LPC fails" ("Interval" and "Dips") are designed to set the intensity of authorization requests. If you set the interval to "20" and the failure to "3", after three unsuccessful connection attempts, the device will "wait" for 20 seconds. If the network is constantly interrupted, the interval can be reduced.
- Click the "Save" button at the bottom.
- Restart your ADSL modem.
Some models have so-called "Quick Settings" - "Quick Setup" or "Wizard". Just enter the data that the operator received - the system itself will select the appropriate parameters.
Titles and sections may vary. But the principle is the same. Consider the situation on a specific example. This is how the Rostelecom ADSL modem setup looks like:

- Log in to the web interface.
- Open Interface Setup - Internet.
- In the "Virtual Circuit" section, in the "Status" section, check the "Advanced" option.
- In "IP version" select "IPv4".
- In the "ISP" section, check "PPPoE/PPPoA".
- In the fields for entering "Username" and "Password" write your username and password.
- In the "NAT" list, set "Enable".
- In the "Direction" item, select "Both".
- Wi-Fi is configured in the "Wireless" section.
- "SSID" is the name of the network. "Pre-Shared Key" - password.
Rostelecom, like many other providers, provides an installation disk with its equipment. It makes it easier to connect to the internet. Just insert the CD into the drive and follow the instructions.
Connecting a Router to an ADSL Modem
You can use your modem as a link between your internet connection and your router. Then another device will “distribute” the Wi-Fi signal. To do this, it is necessary that all equipment is on the same network. This type of connection is called "Bridge Mode". This is convenient if you have several computers at home. After all, the router issued by the provider may not support a wireless connection.
Here's how to connect an ADSL modem to a Wi-Fi router:
- Set up your DSL device separately first. So that through it you can go online.
- Insert an Ethernet cable into its LAN port.
- Reset the parameters of the router from which you want to distribute the Internet. Even if it is new and has not been used before.
- Connect the other end of the Ethernet wire to the Wi-Fi router to the WAN slot. The port may be called "Internet". On the body, it is always highlighted in color.

- Connect it to your computer.
- Log in to the web interface.
- Open the "WAN" section.
- In the Connection Type list, select Dynamic IP.
- Set the option "PPPoE". Enter your login and password.
- Save your changes and restart your device.
The network must work. If this did not happen, then it has specific parameters that must be learned from the operator.
Setting up IPTV
Many providers provide Internet and television in one package (for example, the same Rostelecom). A Wi-Fi router is best suited for working with IPTV. But you can also use a regular ADSL modem. If it has several LAN connectors. To configure it, you need to create a bridge.
- Log in to the web interface.
- Open the Network - Connections section.
- Select Bridge from the Connection Type list.
- Specify VPI and VCI. If they are paired, you need two bridges.
- Click Save.
- Click the "Advanced" tab.
- Subsection "Interface grouping".
- "Create Group" button.
- Enter any name.
- Move the bridge and some LAN port to the right columns. For example, LAN3.
- Click Save and reboot your device.
After that, IPTV will work on the selected connector.
ADSL modems are ideal for working over telephone lines. But to install such devices, you need to understand the parameters. If your DSL does not have a wireless network, you can set it up to connect to your router.
Test Methodology for ADSL
The testing methodology is designed to evaluate and visualize the results of testing in case of problems when working on the Internet.
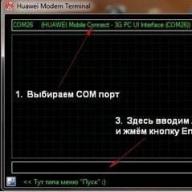
How to take a "screenshot" can be read
.
We draw your attention to some features of working on the Internet:
1) When the Subscriber is connected to its Data Transmission Network, the Provider is not responsible for the quality of communication outside the terminal subscriber device (if any) connected to the Provider's equipment.
The provider guarantees the speed of Internet access only if there is a direct connection, i.e. The Provider's cable connects directly to a laptop or personal computer. You can read more about the Procedure for the provision of services.
2) You can familiarize yourself with the division of areas of responsibility between the Provider and the Subscriber.
3) When using ADSL technology, the data transfer speed is always less than the connection speed by at least 13-15%. This is a technological limitation, which we will discuss in more detail below. It does not depend on the provider or the modem used.
Under ideal conditions, with a connection speed of 12 Mbps, you can expect a maximum real speed of ~ 10 Mbps.
Note!
You can read more about the factors affecting the data transfer rate when using ADSL technology.
Attention! If you use Wi-Fi wireless networks to work on the Internet, it will be useful for you to read the information below.
1. Sources of interference that affect the operation of wireless Wi-Fi networks can be as follows:
- material of walls and partitions in your apartment or office;
- the location of the Wi-Fi hotspot of your neighbors. For example, if the neighbor's point is located near the wall adjacent to your apartment, and your point, in turn, is located near this wall, then the signals of both points will interrupt each other;
- Wi-Fi module in your PC or other mobile device. A mobile device may not have the most modern module installed, which has a maximum speed limit;
- simultaneous downloading from different devices, both inside your apartment and at neighboring points outside your apartment;
- Bluetooth devices operating in the coverage area of your Wi-Fi device;
- various household appliances that use the 2.4 GHz frequency band while operating in the coverage area of your Wi-Fi device.
You can read more about possible sources of interference that affect the operation of Wi-Fi wireless networks.
2. To speed up the work on the Internet and make it more stable, you must:
- configure the router to work with mobile devices. How to do this on a TP-Link router, see ;
- choose a more free channel;
- choose the optimal location of the Wi-Fi point;
- purchase an external Wi-Fi adapter;
- use a dual-antenna wireless access point operating in the 2.4 GHz band;
- use a wireless access point operating in the 5 GHz band;
- work through an Ethernet cable.
You can learn more about ways to increase connection speed and Wi-Fi throughput.
- We measure the speed of the Internet.
A) We go by link and press the button Begin Test. We are waiting for the completion of the test.When the test is completed, you will be presented with a window similar to the following. Let's make it" screenshot” and attach to the results.
b) Download the file (about 75 MB in size) from here: http://www.apple.com/itunes/download/
Start downloading by clicking on the button "Download Now".
During the upload process, do "screenshot"
Attention! To display the download speed in the browser, go to the Downloads section by pressing the Ctrl + J key combination.With) Download a large file (about 2.3 GB) from here:
ftp://ftp.freebsd.org/pub/FreeBSD. During the upload process, do "screenshot" Your download manager or browser and attach to the test results.
Attention! You don't have to download the whole file! It is enough to wait a minute or two until a stable speed is established, then do 2-3 " screenshot» with an interval of 20-30 seconds and stop the download.d) Download the file using a torrent client. For correct speed testing it is necessary to exclude local retrackers. How to do this, you can see.
Attention! It is necessary to test the connection speed when downloading 3-4 files at the same time, in which the number of distributors is more than 100. During the download process, do " screenshot» of your torrent client and attach it to the test results. - We measure the speed from internal resources. For this Minsk subscribers go to the next link .
On the site click on "Change Server".
In the search bar write Atlant Telecom and select it as the server.
 Then we press the button "GO".
Then we press the button "GO".
We are waiting for the testing to be completed.As a result, a window with the results should appear.
We take a screenshot and attach it to the general results.
Regional subscribers go to the following links and download the file:
- link for Brest;
- link for Vitebsk;
- link for Grodno;
- link for Gomel;
- link for Mogilev.
During the download process, we take a “screenshot” of your download manager or browser (except for Internet Explorer) and attach it to the test results. - Download the program and install it (for modems of the D-link brand - the program).
Zyxmon is a free Windows program for managing and monitoring the status of Zyxel routers.
 Unpack the zip folder using some archiver. For example, WinRAR or winzip. Run the executable " ZyxMon". The program window will open. Click on the button " Settings(circled in red).
Unpack the zip folder using some archiver. For example, WinRAR or winzip. Run the executable " ZyxMon". The program window will open. Click on the button " Settings(circled in red).
The following window will appear. Fill in the fields Router IP And router password. Press " OK».
 After pressing " OK» we will return to the Main window of the program. We activate the connection with the modem. To do this, press the button " Telnet Router Connections” (circled in pink), while the indicators “ Telnet connection status" And " PPPoE session status» should change color from red to green .
After pressing " OK» we will return to the Main window of the program. We activate the connection with the modem. To do this, press the button " Telnet Router Connections” (circled in pink), while the indicators “ Telnet connection status" And " PPPoE session status» should change color from red to green . Description of bookmarks:
telnet: Modem connection status and PPPoE status.
Log: Modem text log;
SyslogD: Messages received from modem by Syslg Daemon;
SNMP: RealTime channel filling statistics;
DynDNS: Dynamic DNS state (not used);
line: Data required for line testing: noise margin , attenuation . To get the data, you need to press the button “ Get ”. Doing " screenshot» of the result and attach it to the test results.
Doing " screenshot» of the result and attach it to the test results.
Test Methodology
Attention! If you are connected through additional equipment or use wireless Wi-Fi networks, you must first connect the Internet cable directly to your laptop or personal computer without additional devices, and then perform the speed test method.
To obtain adequate results during each of the points of the test, NO work on the Internet should be conducted!
For Windows OS
Downloading the archive. Unzip it to any folder on your computer. The file should appear in the same folder TEST.bat. We launch it and wait from 10 to 20 minutes (depending on the quality of the DSL connection).
Attention! For Windows 7 and Windows 8, you need to run the file as an administrator (right-click on TEST.bat and select "Run as Administrator"). When the BAT file performs all the actions, you will see the following window.
Press any key on the keyboard - the window will close. After that we go to Disk C and find text files there PING.txt, PATHPING.txt And CONFIG.txt . We attach these files to the results.
For Mac OS X
Downloading the archive. Unzip it to any folder on your computer. After unpacking, a file should appear in the same folder test.app. We launch it and wait from 10 to 20 minutes. After completing the test, press any key on the keyboard - the window will close.
Upon completion of testing, three text files will appear on the desktop - CONFIG, PING, TRACEROUTE. We attach these files to the results.
We check at what speed the modem receives / gives data.
a) telnet.
We go to the command line: Start -> Run -> cmd -> Ok
. In the window that appears, write the command telnet
From the main menu of the modem, go to the menu 24.1 - System Maintenance - Status
. To do this, press on the keyboard 24 - "Enter", 1- "Enter".
Take screenshots of this window:
Explanations to the fields of interest to us in this menu:
Tx B/s
- transmission speed in Bytes per second;
Rx B/s
[Receiving speed, Byte/s] - receiving speed in Bytes in seconds;
Up Time
[Connection time] - the duration of the connection between the modem and the provider;
My WAN IP (from ISP)
[my ip-address in the global network (from the provider)] - ip-address received by the modem from the provider;
line status
[Line state] - current state of the xDSL line: Up - up, Down - not up;
Upstream Speed
[Outgoing speed] - transmission speed of outgoing traffic in Kbps;
downstream speed
[Incoming speed] - transmission speed of incoming traffic in Kbps;
CPU Load
[CPU load] - percentage of modem CPU load.
b) For modems ZyXel 660R, ZyXel 660R-T1, ZyXel 660RU-T1, ZyXel 660HT1, ZyXel 660HW-T1 via WEB interface.
192.168.1.1
and press the key Enter.
1234
and press the button "login".
Ignore.
In the main menu of the modem, select System Status.
In the window that opens, find the button "Show Statistics"
and press it. Doing " screenshots» last window:
- first: during download from the Internet;
- second: during download from internal resources.
We name the files accordingly and attach them to the results.
c) For modems ZyXel 660R-T2, ZyXel 660RU-T2, ZyXel 660HT-2, ZyXel 660HW-T2.
Type in the address bar of your Internet browser (Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, etc.) the address 192.168.1.1
and press the key Enter.
Next, a window will appear asking for a password. Prescribe 1234
and press the button "login".
A window will appear in which you are advised to change the password for logging into the modem. Click the button Ignore.
In the main menu of the modem, press Status,
and in the window that opens, click the link Packet Statistics.
As a result, a statistics window will open, do it " screenshot»:
- first: during download from the Internet;
- second: during download from internal resources.
We name the files accordingly and attach them to the results.
d) For D-Link 2500/2540/2600/2640U v.2 modems
Type in the address bar of your Internet browser (Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, etc.) the address 192.168.1.1 and press the " Enter
". Next, a window will appear asking for a username and password. We register the user - admin
and password - admin
, press the button " Ok
».
Next, go to the menu Device Info -> Statistics -> WAN
As a result, a window will open, do it " screenshot»:
- first: during download from the Internet;
- second: during download from internal resources.
We diagnose the connection of the DSL channel.
For this we go: Start -> Run -> cmd -> Ok.
In the window that appears, write commands one by one (after each press the key "Enter"
):
netsh("Enter")
ras("Enter")
set tracing ppp enable("Enter")
exit("Enter")
Next, go to the Windows folder (usually c: Windows) and create a folder there tracing
. If you are told that such a folder already exists, do not be alarmed. We go into it (the path for the example: c: Windowstracing) and copy the ppp.txt file from there with the results of the commands we entered earlier. We attach this file to the results of the methodology.
We analyze the DSL channel on the modem.
a) For modems ZyXel 660R, ZyXel 660RT1, ZyXel 660RU1, ZyXel 660HT1, ZyXel 660HW-T1
We go to the modem configurator, as shown in paragraph 6-a, go to the menu
- modem command line. We write commands one by one (after each press the key "Enter"
):
wan adsl chandata ("Enter")
wan adsl opmode("Enter")
wan adsl linedata far("Enter")
wan adsl linedata near("Enter")
wan adsl perf("Enter")
wan hwsar disp ("Enter")
Doing " screenshots» obtained results. First of all, the state of the 1st (physical) level is analyzed. This information is retrieved by the commands "xdsl state", "wan adsl linedata far", "wan adsl linedata near". Link for information: http://zyxel.ru/kb/1543.
The main parameters to control are "SNR margin value", "Loop attenuation" for 782 and 791, and "noise margin downstream", "attenuation downstream" for 642, 650, 650, 660. Both values are measured on the receive channel of the transceiver. The first universally characterizes the noise immunity margin of the line. Level 6 db roughly corresponds to an error rate of 10E-6 and is the threshold for reliable communication. This parameter obviously depends on the speed, i.e. the higher the speed, the lower the margin. It is also worth noting that the measured values at each end of the line may differ. This indicates that the source of interference is located closer to one of the ends of the line.
Attenuation downstream - signal attenuation in the line and clearly depends on the active resistance of the wire. The influence of noise on the quality of communication and the maximum speed is higher than that of attenuation. You need to do this several times at different times of the day. Attach the results to the results of the methodology.
b) For modems ZyXel 660RT2, ZyXel 660RU2, ZyXel 660HT2, ZyXel 660HW-T2, ZyXel 660RT3, ZyXel 660RU3, ZyXel 660HT3
When entering the modem settings through telnet
(as shown in paragraph 6-a), you will immediately be taken to the modem's command line, where you need to enter the commands indicated above.
c) For ZyXel 700 series modems (782 and 791)
In a similar way, go to the modem configurator (see paragraph 6-a) and go to the menu 24.8 - Command Interpreter Mode.
We write commands one by one (after each press the key "Enter"
):
xdsl cnt disp("Enter")
wan hwsar disp ("Enter")
xdsl state("Enter")
Doing " screenshots» obtained results and attach to the test results.
d) For D-Link 2500/2540/2600/2640U v.2 modems
We go into the modem configurator, as shown in paragraph 6-d, go to the menu Device Info -> Statistics -> ADSL
.
We take a screenshot and attach it to the results.
We save all the results of the testing methodology in one archive and send it to the technical support e-mail address [email protected] indicating client data (personal account number/organization name, contact phone number/e-mail address) for feedback.
Almost everyone needs internet access these days. Whether it's work, entertainment, communication - the global network has entered our lives everywhere. To provide Internet access at home or in the office, you need a modem that will allow you to connect all the necessary devices to the network. In large cities, providers offer fiber-optic and fiber-coaxial systems that allow you to get a fast and stable connection. However, in order to run such cables, it is necessary that the number of users allows filling the entire bandwidth of the cable - otherwise it is simply not profitable. Therefore, the possibility of such a connection is not provided by business everywhere. This is especially true for small towns, towns and villages. But what if such services are not provided, but the Internet is still needed?
There are different options, and one of the best is the use of twisted-pair subscriber telephone wires. Many will recall with horror a non-working phone while using the Internet. However, technology has come a long way. Today, xDSL technologies are the most widespread and effective. DSL stands for Digital Subscriber Line. This technology allows you to achieve a fairly high data transfer rate over copper pairs of telephone wires, while not occupying the phone. The fact is that the frequency range from 0 to 4 kHz is used for voice transmission, while signals with a frequency of up to 2.2 MHz can be transmitted over a copper telephone cable, and it is the section from 20 kHz to 2.2 MHz that uses xDSL technology . The speed and stability of such a connection is affected by the length of the cable, that is, the farther the telephone center (or another modem if a network is created) is from your modem, the lower the data transfer rate will be. The stability of the network is due to the fact that the data flow goes from the user directly to the node, its speed is not affected by other users. An important factor: to provide an xDSL connection, it is not necessary to change cables, which makes it theoretically possible to connect to the Internet wherever there is a telephone (depending on the availability of such a service from the provider).
The xDSL modem will act as the link between the phone cable and your devices (or router), but there are a number of features to consider when choosing a particular model that will work for you.

What is the difference between xDSL modems
xDSL technologies
In the acronym xDSL, the "x" stands for the first letter of the DSL technology. xDSL technologies differ in signal transmission distance, data transfer rate, as well as the difference in the transfer rates of incoming and outgoing traffic.ADSL technology is translated as asymmetric digital subscriber line. This means that the transmission speed of incoming and outgoing data is different. In this case, the data reception rate is 8 Mbps, and the transmission rate is 1.5 Mbps. In this case, the maximum distance from the telephone node (or another modem in the case of a network) is 6 km. But the maximum speed is possible only at a minimum distance from the node: the farther, the lower it is.
ADSL2 technology makes much better use of wire bandwidth. Its main difference is the ability to distribute information across multiple channels. That is, it uses, for example, an empty outgoing channel when the incoming is overloaded, and vice versa. Due to this, its data reception speed is 12 Mbps. The transmission speed remained the same as in ADSL. At the same time, the maximum distance from the telephone exchange (or other modem) is already 7 km.
ADSL2+ technology doubles the downstream speed by increasing the usable bandwidth to 2.2 MHz. Thus, the data reception rate is already equal to 24 Mbps, and the transmission rate is 2 Mbps. But such a speed is possible only at a distance of less than 3 km from the node - further it becomes similar to ADSL2 technology. ADSL2+ equipment has the advantage of being compatible with previous ADSL standards.
SHDSL technology is a standard for high-speed symmetrical data transmission. This means that the download and upload speeds are the same - 2.3 Mbps. At the same time, this technology can work with two copper pairs - then the speed doubles. The maximum distance from the telephone exchange (or other modem) is 7.5 km.
VDSL technology has the maximum data transfer rate, but is significantly limited by the distance from the node. It works in both asymmetric and symmetrical modes. In the first variant, the data reception speed reaches 52 Mbps, and the transmission speed - 2.3 Mbps. In symmetrical mode, speeds up to 26 Mbps are supported. However, high speeds are available at a distance of no more than 1.3 km from the node.
When choosing an xDSL modem, you need to focus on the distance to the telephone exchange (or other modem). If it is small, you can safely focus on VDSL, but if the node is far away, you should choose ADSL2+. If there are two copper pairs of wires, you can pay attention to SHDSL.

Annex Standards
Annex - a kind of ADSL standards for high-speed data transmission in conjunction with analog telephony (ordinary telephone).The Annex A standard uses frequencies from 25 kHz to 138 kHz for data transmission, and from 200 kHz to 1.1 MHz for receiving data. This is a common standard for ADSL technology.
The Annex L standard extends the maximum communication distance to 7 km by increasing the power at low frequencies. But not all providers use this standard due to interference.
The Annex M standard allows you to increase the speed of the outgoing stream up to 3.5 Mbps. But in practice, the connection speed ranges from 1.3 to 2.5 Mbps. For an uninterrupted connection, this standard requires a telephone line without damage.
DHCP server

DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. A DHCP server is a program that allows you to automatically configure local computers to work on a network. It gives clients IP addresses (unique identifiers of a device connected to a local network or the Internet), as well as additional parameters necessary for working on the network. This will allow you not to manually enter the IP, which will make it easier to work on the network. However, it should be noted that for devices such as network printers, and for permanent remote access to a computer using special programs, a static rather than a dynamic IP will be desirable, since the constant change of IP will cause difficulties.
USB ports
Today, there are two options for organizing an Internet connection using ADSL technology: via a USB port and via an Ethernet port.An external USB ADSL modem is connected to the computer via a USB port. It receives power from the computer. The advantages of such modems are low cost and ease of use. The disadvantages include compatibility not with all computers, the need for regular reinstallation of drivers, and work with only one device.
An ADSL modem connected to the device via an Ethernet port will work more stable. But for use with multiple devices, it must have a router function or Wi-Fi technology.
Setup and management

Modems are most often configured and managed using three technologies: Web interface, Telnet, and SNMP.
The web interface is a feature that allows configuration and control through a computer browser. This option will be enough for home use of the modem.
Telnet is a network protocol for remote access to a computer using a command interpreter. With it, you can configure the modem from devices that are not connected to it. This is useful for small chains of modems at home and in the office.
SNMP is a standard Internet protocol for managing devices on IP networks based on the TCP/IP architecture (means for exchanging information between networked devices). Using the SNMP protocol, network device management software can access information stored on managed devices. Due to this, it is most often used in the construction of office networks.

Criterias of choice
xDSL modems differ in a number of characteristics, the most important of which are the maximum distance from the telephone exchange, the speed of receiving and transmitting data, the presence of symmetric or asymmetric transmission. Understanding in what conditions and how exactly the modem will be used, you can choose the right device for you.Recall that when choosing an xDSL modem, it is important to know the characteristics of the telephone network: the length of the cable to the telephone exchange, the number of copper pairs of the cable and its quality, the offers and capabilities of the provider. It is important that there is no interference on the line, which is caused by the intersection of cable pairs or its poor quality.