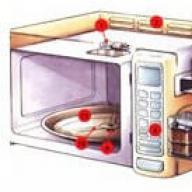
The main detail in any microwave oven is the magnetron. A magnetron is a special vacuum tube that generates microwave radiation. Microwave radiation has a very interesting effect on ordinary water, which is found in any food.
When irradiated with 2.45 GHz electromagnetic waves, water molecules begin to vibrate. Friction arises as a result of these vibrations. Yes, normal friction between molecules. Heat is generated by friction. It then heats up the food from the inside. This is how you can briefly explain the principle of the microwave oven.
Microwave design.
Structurally, a microwave oven consists of a metal chamber in which food is cooked. The chamber is equipped with a door that prevents radiation from escaping. For uniform heating of food, a rotating table is installed inside the chamber, which is driven by a motor-reducer (motor), which is abbreviated as T.T.Motor (Turntable motor).

Microwave radiation is generated by a magnetron and fed into the chamber through a rectangular waveguide. A fan is used to cool the magnetron during operation. F.M (Fan motor), which drives cold air through the magnetron. Then the heated air from the magnetron is directed to the chamber through the air duct and is also used to heat food. Part of the heated air and water vapor is discharged outside through special non-radiating openings.
In some models of microwave ovens, a dissector is used to form an even heating of food, which is installed at the top of the microwave chamber. Outwardly, the dissector resembles a fan, but it is designed to create a certain type of microwave wave in the chamber so that uniform heating of food is carried out.
Microwave wiring diagram.
Let's take a look at a simplified electrical diagram of an ordinary microwave (click to enlarge).

As you can see, the circuit consists of a control part and an executive part. The control part, as a rule, consists of a microcontroller, a display, a push-button or touch panel, electromagnetic relays, and a buzzer. These are the "brains" of the microwave. On the diagram, all this is shown as a separate board with the inscription Power and Control Curcuit Board ... A small step-down transformer is used to power the control part of the microwave. It is labeled L.V.Transformer in the schematic (only primary shown).
The microcontroller controls electromagnetic relays through buffer elements (transistors): RELAY1, RELAY2, RELAY3... They turn on / off the executive elements of the microwave oven in accordance with the specified operation algorithm.
Actuators and circuits are a magnetron (Magnetron), a stage gear motor T.T.Motor (Turntable motor), a cooling fan F.M ( Fan Motor), Grill heating element ( Grill heater), backlight O.L ( Oven lamp).
We especially note the executive circuit, which is a microwave radiation generator.
This circuit begins with a high-voltage transformer ( H.V.Transformer ). He is the healthiest in the microwave. Actually, this is not surprising, because through it you need to pump the power of 1500 - 2000 W (1.5 - 2 kW) required for the magnetron. The output (useful) power of the magnetron is 500 - 850 W.

An alternating voltage of 220V is supplied to the primary winding of the transformer. An alternating heating voltage of 3.15V is removed from one of the secondary windings. It is fed to the filament winding of the magnetron. Filament winding is necessary for the generation (emission) of electrons. It is worth noting that the current consumed by this winding can be up to 10A.
Another secondary winding of the high-voltage transformer, as well as the voltage doubling circuit on the high-voltage capacitor ( H.V. Capacitor ) and diode ( H.V. Diode ) creates a constant voltage in 4kV for feeding the anode of the magnetron. The anode current is small and is somewhere around 300 mA (0.3A).
As a result, the electrons emitted by the filament winding begin to move in a vacuum.
The special trajectory of the movement of electrons inside the magnetron creates microwave radiation, which we need to heat food. Microwave radiation is removed from the magnetron using an antenna and enters the chamber through a section of a rectangular waveguide.
Here is such a simple, but very sophisticated circuit is a kind of microwave heater. Do not forget that the microwave oven chamber itself is an element of this microwave heater, since it is, in fact, a resonator in which electromagnetic radiation occurs.
In addition to these elements, there are many protective elements in the microwave oven circuit (see KSD thermal switches and analogs.). For example, a thermal switch monitors the temperature of the magnetron. Its nominal temperature during operation is somewhere between 80 0 - 100 0 C. This thermal switch is attached to the magnetron. By default, it is not shown in the simplified diagram.
Other protective thermal switches are labeled on the diagram as OVEN THERMAL CUT-OUT(installed on the duct), GRILL THERMAL CUT-OUT(controls the grill temperature).

In the event of an abnormal situation and overheating of the magnetron, the thermal switch opens the circuit, and the magnetron stops working. In this case, the thermal switch is selected with a small margin - for a shutdown temperature of 120 - 145 0 С.

Very important elements of the microwave oven are three switches, which are built into the right end of the microwave oven chamber. When the front door is closed, the two switches close their contacts ( PRIMARY SWITCH- main switch, SECONDARY SWITCH- secondary switch). Third - MONITOR SWITCH(control switch) - opens its contacts when the door is closed.

Failure of at least one of these switches will cause the microwave to malfunction and trip the fuse (Fuse).
To reduce the interference that enters the power grid when the microwave oven is operating, there is a power filter - NOISE FILTER.

Additional elements of the microwave.
In addition to the basic structural elements, the microwave oven can be equipped with a grill and convector. The grill can be made in the form of a heating element (heating element "a) or infrared quartz lamps. These microwave elements are very reliable and rarely fail.
Grill heating elements: metal-ceramic (left) and infrared (right).

The infrared heater consists of 2 infrared quartz lamps connected in series at 115V (500 - 600W).
Unlike microwave heating, which comes from the inside, the grill creates heat radiation that heats the food from the outside to the inside. The grill heats up food more slowly, but without it, you cannot cook crispy chicken.
A convector is nothing more than a fan inside the chamber, which works in tandem with a heater (TEN "ohm). The rotation of the fan circulates hot air in the chamber, which contributes to uniform heating of food.
About fuse diode, high voltage capacitor and diode.
Elements in the magnetron power circuit have interesting properties that must be taken into account when repairing a microwave.

For those who wish to understand in more detail the structure of microwave ovens, an archive with service instructions for microwave ovens has been prepared (Daewoo, SANYO, Samsung, LG). The instructions contain schematic diagrams, disassembly diagrams, recommendations for checking elements, a list of components.
Even a child can easily operate a microwave oven today. She has become a familiar and reliable helper. And at the same time, we very rarely think about how food is heated in a matter of minutes. And this happens thanks to the microwaves that the magnetron produces. Let's figure out how the device works.
What is a microwave magnetron
The magnetron is the main component of the microwave oven... It is no coincidence that it is called the heart of the unit. The microwave operates properly only with a working magnetron. The main task of the part is to create electromagnetic fields. The ability to direct their emergence was established almost 100 years ago.
Reference. In 1921, physicist from the United States A. Hull, in the course of experiments and experiments, discovered the ability to change the mass of electrons.
He also introduced the very name of the magnetron. But high-frequency electromagnetic waves were discovered three years later, in 1924. Since that time, scientists have not only studied microwave frequencies, but also learned how to use them.
reference... These wave generators have been used in microwave ovens since the 1960s.
How a magnetron works in a microwave
The device of the part requires minimal knowledge of physics. The flow of electrons occurs in the space between the anode and cathode.
Anode
In the microwave, copper is used for the anode. The cylinder shell is made of it. It is hollow inside. The wall of the cylinder is thick, its inner surface is uneven. In section, the anode looks like a circle, along the entire length of which there are small half rings.
They are needed to create additional resonance. There is no air inside the anode; a vacuum space is created there. So that the created microwave waves do not remain inside, there is a special outlet in one of the half-rings-resonators.
Cathode
A cathode is laid through the center of the anode. A filament was used for it. Wires are provided for heating it. They connect the cathode to a heating source.
Important! The anode and cathode are housed in a special block that contains magnets.
How the magnetron works
So now we know that 2 different fields interact in the main part of the microwave .
- The first one is electronic... When the device is turned on and voltage is applied, electrons appear at the cathode, which move to the positive pole - to the anode.
- The second field is magnetic... It acts on the particles and returns them back to the cathode.
After the electrons form a ring, a charge arises inside the magnetron. Moreover, the number of charges increases, since additional electron rings are formed in each half-resonator. This causes high frequency vibrations to occur. Thus, The ultrahigh frequency wave field appears as a result of the interaction of electronic and magnetic fields. The resulting microwaves are used to process the food.
Microwave ovens (microwave ovens) have long become the most common household appliance, with which you can very quickly defrost food, reheat already prepared food or prepare a dish according to an original recipe, and even disinfect kitchen sponges and rags that do not contain metal.
The presence of a convenient, intuitive interface, as well as multi-level protection allow even a child to cope with the control of such a complex and high-tech device as a microwave oven. Some dishes can be quickly and easily prepared using the built-in programs. And possible malfunctions can be easily eliminated by doing.
The heating of the products placed in the microwave chamber occurs due to the impact on them of powerful electromagnetic radiation of the decimeter range. In household appliances, a frequency of 2450 MHz is used. Radio waves of such a high frequency penetrate deep into the food, and affect the polar molecules (mostly water in food), forcing them to constantly shift and line up along the lines of force of the electromagnetic field.
This movement raises the temperature of the products, and heating goes not only from the outside, but also to the depth to which radio waves penetrate. In household microwave ovens, waves penetrate 2.5-3 cm deep, they heat the water, and that, in turn, the entire volume of food.
Magnetron device - the main component
Radio waves with a frequency of 2450 MHz are generated by a special device - magnetron, which is an electric vacuum diode. It has a massive cylindrical copper anode, round in cross section and divided into 10 sectors with the same copper walls.
In the center of this structure is a rod cathode, inside of which there is a filament. The cathode is used for the emission of electrons. Powerful ring magnets are located at the ends of the magnetron, creating a magnetic field inside the magnetron, which is necessary for generating microwave radiation.
A voltage of 4000 volts is applied to the anode and 3 volts to the filament. An intense emission of electrons occurs, which are picked up by a high-strength electric field. The geometry of the resonator chambers and the anode voltage determine the generated frequency of the magnetron.
The energy is removed by means of a wire loop connected to the cathode and brought out into the radiator-antenna. From the antenna, microwave radiation enters the waveguide, and from it into the microwave chamber. The typical output power of magnetrons used in household microwave ovens is 800 watts.
If less power is required for cooking, this is achieved by turning on the magnetron for certain periods of time, followed by a pause.
To obtain a power of 400 W (or 50% of the output power), you can turn on the magnetron for 5 seconds within a 10-second interval, and turn it off for 5 seconds. In science it is called pulse width modulation.
The magnetron emits a large amount of heat during operation, therefore its case is placed in a plate radiator, which, during operation, must always be blown by the air flow from the fan built into the microwave. When overheating, the magnetron very often fails, therefore it is equipped with protection - a thermal fuse.
Thermal fuse and why is it needed
 To protect the magnetron from overheating, as well as the grill, which some models of microwave ovens are equipped with, special devices are used, called thermal fuse or thermal relay... They are available in different temperature ratings indicated on their body.
To protect the magnetron from overheating, as well as the grill, which some models of microwave ovens are equipped with, special devices are used, called thermal fuse or thermal relay... They are available in different temperature ratings indicated on their body.
The operating principle of the thermal relay is very simple. Its aluminum body is flanged to the place where the temperature needs to be controlled. This ensures reliable thermal contact. Inside the thermal fuse there is a bimetallic plate that has a setting for a certain temperature.
When the temperature threshold is exceeded, the plate bends and actuates the pusher, which opens the plates of the contact group. The power supply to the microwave oven is interrupted. After cooling, the geometry of the bimetallic plate is restored and the contacts are closed.
Purpose of microwave oven fans
The fan is an essential component of any microwave oven, without which its operation will be impossible. It performs a number of essential functions:
- Firstly, the fan blows on the main part of the microwave oven - the magnetron, ensuring its normal operation.
- Second, other components in the electronic circuit also generate heat and require ventilation.
- Thirdly, some microwave ovens are equipped with a grill, which must be ventilated and protected by a thermostat.
- Finally, the food being cooked in the cooking space also gives off a lot of heat and water vapor. The fan creates a slight overpressure in the chamber, as a result of which the air from the chamber, together with the heated water vapor, escapes through special ventilation holes.
In the microwave oven, from one fan, which is located at the rear wall of the case and sucks in air from the outside, a ventilation system is organized with the help of air ducts, directing the air flow to the magnetron plates, and then to the chamber. The fan motor is a simple single phase AC.
Microwave protection and locking system
Any microwave oven has a powerful radio-emitting device inside - a magnetron. Microwave radiation of such power can cause irreparable harm to the health of humans and all living beings, therefore, it is necessary to take a number of protective measures.
The microwave has a fully shielded metal work chamber, which is additionally protected from the outside by a metal case, which does not allow high-frequency radiation to penetrate outside.
The transparent glass in the door has a screen made of a metal mesh with a fine mesh, which does not transmit outward radiation of 2450 Hz, wavelength 12.2 cm, generated by the magnetron.
 The issue of saving energy consumption has always been relevant. one of the types of lighting devices that will greatly help reduce electricity consumption in everyday life are. To make the best choice, you just need to understand the advantages and disadvantages of each type of such lamps.
The issue of saving energy consumption has always been relevant. one of the types of lighting devices that will greatly help reduce electricity consumption in everyday life are. To make the best choice, you just need to understand the advantages and disadvantages of each type of such lamps.
Due to their characteristics, double switches are widely used at home. How to correctly connect such switches and what you need to know to prevent errors in this case, you can read in.
Microwave door fits snugly against the cabinet and it is very important that this gap maintains its geometric dimensions. The distance between the metal body of the camera and the special groove in the door should be equal to a quarter of the microwave radiation wavelength: 12.2 cm / 4 = 3.05 cm.
In this gap, a standing electromagnetic wave is formed, which has a zero amplitude value exactly at the place where the door adjoins the body, therefore the wave does not propagate outward. In such an elegant way, the issue of protection against microwave radiation is solved using the microwave waves themselves. This method of protection in science is called a microwave choke.
To prevent turning on the microwave oven with an open chamber there is a system of microswitches that control the position of the door. Usually there are at least three such switches: one turns off the magnetron, the other turns on the backlight lamp even when the magnetron is not working, and the third serves to "inform" the control unit about the position of the door.
The microswitches are located and configured so that they only work when the microwave oven is closed.
Door microswitches are also often referred to as limit switches.
The control unit is the brain of the device
 Any microwave oven has a control unit and it performs two main functions:
Any microwave oven has a control unit and it performs two main functions:
- Maintaining the preset power of the microwave oven.
- Switching off the furnace after the expiration of the set operating time.
On old models of electric furnaces, the control unit was represented by two electromechanical switches, one of which just set the power, and the other a period of time. With the development of digital technologies, electronic control units began to be used, and now they are microprocessor-based, which, in addition to performing two main functions, can also include many necessary and unnecessary service ones.
- Built-in clock that can certainly be useful.
- Power level indication.
- Changing the power level using the keyboard (push-button or touch).
- Cooking food or defrosting food using special programs "hardwired" into the memory of the control unit. In this case, the weight is taken into account, and the oven will select the required power itself.
- Signaling the end of the program with the selected soundtrack.
In addition, modern models have upper and lower grills, convection function, which are also "controlled" by the control unit.
The control unit has its own power source, which ensures the operation of the unit in both standby and operating modes. An important component is the relay unit, which commutes on commands from the power circuits of the magnetron and the grill, as well as the circuits of the fan, built-in lamp and convector. The control unit is connected by loops with the keyboard and the display panel.
An entertaining video with a story about the principle of operation of microwave ovens
See how easy it is to explain what makes this amazing device work.
Microwave ovens (microwave ovens) have long become the most common household appliance, with which you can very quickly defrost food, reheat already prepared food or prepare a dish according to an original recipe, and even disinfect kitchen sponges and rags that do not contain metal.
The presence of a convenient, intuitive interface, as well as multi-level protection allow even a child to cope with the control of such a complex and high-tech device as a microwave oven. Some dishes can be quickly and easily prepared using the built-in programs. And possible malfunctions can be easily eliminated by doing.
The heating of the products placed in the microwave chamber occurs due to the impact on them of powerful electromagnetic radiation of the decimeter range. In household appliances, a frequency of 2450 MHz is used. Radio waves of such a high frequency penetrate deep into the food, and affect the polar molecules (mostly water in food), forcing them to constantly shift and line up along the lines of force of the electromagnetic field.
This movement raises the temperature of the products, and heating goes not only from the outside, but also to the depth to which radio waves penetrate. In household microwave ovens, waves penetrate 2.5-3 cm deep, they heat the water, and that, in turn, the entire volume of food.
Magnetron device - the main component
Radio waves with a frequency of 2450 MHz are generated by a special device - magnetron, which is an electric vacuum diode. It has a massive cylindrical copper anode, round in cross section and divided into 10 sectors with the same copper walls.
In the center of this structure is a rod cathode, inside of which there is a filament. The cathode is used for the emission of electrons. Powerful ring magnets are located at the ends of the magnetron, creating a magnetic field inside the magnetron, which is necessary for generating microwave radiation.
A voltage of 4000 volts is applied to the anode and 3 volts to the filament. An intense emission of electrons occurs, which are picked up by a high-strength electric field. The geometry of the resonator chambers and the anode voltage determine the generated frequency of the magnetron.
The energy is removed by means of a wire loop connected to the cathode and brought out into the radiator-antenna. From the antenna, microwave radiation enters the waveguide, and from it into the microwave chamber. The typical output power of magnetrons used in household microwave ovens is 800 watts.
If less power is required for cooking, this is achieved by turning on the magnetron for certain periods of time, followed by a pause.
To obtain a power of 400 W (or 50% of the output power), you can turn on the magnetron for 5 seconds within a 10-second interval, and turn it off for 5 seconds. In science it is called pulse width modulation.
The magnetron emits a large amount of heat during operation, therefore its case is placed in a plate radiator, which, during operation, must always be blown by the air flow from the fan built into the microwave. When overheating, the magnetron very often fails, therefore it is equipped with protection - a thermal fuse.
Thermal fuse and why is it needed
To protect the magnetron from overheating, as well as the grill, which some models of microwave ovens are equipped with, special devices are used, called thermal fuse or thermal relay... They are available in different temperature ratings indicated on their body.
The operating principle of the thermal relay is very simple. Its aluminum body is flanged to the place where the temperature needs to be controlled. This ensures reliable thermal contact. Inside the thermal fuse there is a bimetallic plate that has a setting for a certain temperature.
When the temperature threshold is exceeded, the plate bends and actuates the pusher, which opens the plates of the contact group. The power supply to the microwave oven is interrupted. After cooling, the geometry of the bimetallic plate is restored and the contacts are closed.
Purpose of microwave oven fans
The fan is an essential component of any microwave oven, without which its operation will be impossible. It performs a number of essential functions:
- Firstly, the fan blows on the main part of the microwave oven - the magnetron, ensuring its normal operation.
- Second, other components in the electronic circuit also generate heat and require ventilation.
- Thirdly, some microwave ovens are equipped with a grill, which must be ventilated and protected by a thermostat.
- Finally, the food being cooked in the cooking space also gives off a lot of heat and water vapor. The fan creates a slight overpressure in the chamber, as a result of which the air from the chamber, together with the heated water vapor, escapes through special ventilation holes.
In the microwave oven, from one fan, which is located at the rear wall of the case and sucks in air from the outside, a ventilation system is organized with the help of air ducts, directing the air flow to the magnetron plates, and then to the chamber. The fan motor is a simple single phase AC.
Microwave protection and locking system
Any microwave oven has a powerful radio-emitting device inside - a magnetron. Microwave radiation of such power can cause irreparable harm to the health of humans and all living beings, therefore, it is necessary to take a number of protective measures.
The microwave has a fully shielded metal work chamber, which is additionally protected from the outside by a metal case, which does not allow high-frequency radiation to penetrate outside.
The transparent glass in the door has a screen made of a metal mesh with a fine mesh, which does not transmit outward radiation of 2450 Hz, wavelength 12.2 cm, generated by the magnetron.
 The issue of saving energy consumption has always been relevant. one of the types of lighting devices that will greatly help reduce electricity consumption in everyday life are. To make the best choice, you just need to understand the advantages and disadvantages of each type of such lamps.
The issue of saving energy consumption has always been relevant. one of the types of lighting devices that will greatly help reduce electricity consumption in everyday life are. To make the best choice, you just need to understand the advantages and disadvantages of each type of such lamps.
Due to their characteristics, double switches are widely used at home. How to correctly connect such switches and what you need to know to prevent errors in this case, you can read in.
Microwave door fits snugly against the cabinet and it is very important that this gap maintains its geometric dimensions. The distance between the metal body of the camera and the special groove in the door should be equal to a quarter of the microwave radiation wavelength: 12.2 cm / 4 = 3.05 cm.
In this gap, a standing electromagnetic wave is formed, which has a zero amplitude value exactly at the place where the door adjoins the body, therefore the wave does not propagate outward. In such an elegant way, the issue of protection against microwave radiation is solved using the microwave waves themselves. This method of protection in science is called a microwave choke.
To prevent turning on the microwave oven with an open chamber there is a system of microswitches that control the position of the door. Usually there are at least three such switches: one turns off the magnetron, the other turns on the backlight lamp even when the magnetron is not working, and the third serves to "inform" the control unit about the position of the door.
The microswitches are located and configured so that they only work when the microwave oven is closed.
Door microswitches are also often referred to as limit switches.
The control unit is the brain of the device
Any microwave oven has a control unit and it performs two main functions:
- Maintaining the preset power of the microwave oven.
- Switching off the furnace after the expiration of the set operating time.
On old models of electric furnaces, the control unit was represented by two electromechanical switches, one of which just set the power, and the other a period of time. With the development of digital technologies, electronic control units began to be used, and now they are microprocessor-based, which, in addition to performing two main functions, can also include many necessary and unnecessary service ones.
- Built-in clock that can certainly be useful.
- Power level indication.
- Changing the power level using the keyboard (push-button or touch).
- Cooking food or defrosting food using special programs "hardwired" into the memory of the control unit. In this case, the weight is taken into account, and the oven will select the required power itself.
- Signaling the end of the program with the selected soundtrack.
In addition, modern models have upper and lower grills, convection function, which are also "controlled" by the control unit.
The control unit has its own power source, which ensures the operation of the unit in both standby and operating modes. An important component is the relay unit, which commutes on commands from the power circuits of the magnetron and the grill, as well as the circuits of the fan, built-in lamp and convector. The control unit is connected by loops with the keyboard and the display panel.
An entertaining video with a story about the principle of operation of microwave ovens
See how easy it is to explain what makes this amazing device work.