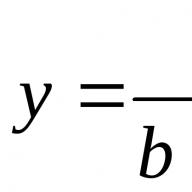Software examination is a study whose ultimate goal is to verify the completeness/completeness of a software product.
The tasks of software examination include:
- Checking for compliance with the requirements of the technical specifications (functionality, efficiency, reliability, etc.)
- Correct operation on planned hardware and software infrastructure
- checking the completeness of operational documentation
- checking the readiness of a software product for implementation into trial or industrial operation
The software examination process requires clear regulation. The whole process can be divided into several stages:
- internal software examination performed by the contractor’s employees at certain stages of development
- software acceptance examination performed on equipment and with the involvement of customer personnel to determine the degree of readiness of the product for implementation
Software examination within the project team is carried out in accordance with the regulations adopted by the performing company. When conducting an external examination, they are often guided by the following standards:
- GOST R ISO/IEC 12207-99,
- GOST R ISO/IEC 12119-2000,
- GOST R ISO/IEC 14764-2002,
- GOST R ISO/IEC TO 16326-2002,
- GOST R ISO/IEC 15408-2002
At the stage of acceptance testing, a document is drawn up: Test Program and Methodology, which determines quantitative indicators of product quality and testing methods. A program is being developed from the perspective of minimizing the amount of testing to verify that all document requirements are met.
The software examination program and methodology must contain the following sections (according to RD 50-34.698-90 AUTOMATED SYSTEMS, REQUIREMENTS FOR DOCUMENT CONTENT):
- description and purpose of the object
- list of documents based on which development is carried out (contract)
- purpose of the examination
- list of requirements and limitations of the technical specification that must be verified
- a program for testing the completeness of the software in accordance with the technical documentation and a test plan for checking all sections of the technical specifications (if additional requirements were identified during the development process, then a separate scenario is drawn up for them indicating the documents on the basis of which changes were made)
- all concepts of tested characteristics, testing conditions, tools used to automate tests, methods for processing and evaluating test results for each section of the examination program.
The software examination program and methodology are agreed upon with the developers and the Customer.
During the software examination process, the following indicators are checked:
- software size in different units of measurement (number of functions, lines in the program, disk memory size, etc.);
- system operation time;
- labor productivity
- number of errors and number of failures
The operating instructions for the software package are also checked and adjusted in all specified modes.
Software examination at the time of acceptance tests is carried out at the Customer's stands. The installation of software and debugging of stands is carried out by representatives of the developers.
During software examination, the use of automated testing tools is allowed.
The result of the software examination is recorded in the Test Report. The protocol must contain:
- date and place of examination
- list of documents on the basis of which the examination was carried out
- composition of the expert commission
- generalized test results with their assessment for compliance with the requirements of the technical specifications
- conclusions about test results and readiness of the software product for transfer to trial/industrial operation.
If during the software examination the need to change the requirements is identified, adjustments to the technical specifications are allowed by agreement of both parties. It is also possible to accept a software package with deviations from the original requirements. At the same time, the accepted assumptions are recorded in the software examination protocol.
If deviations from the requirements stated in the technical specifications significantly affect the achievement of the goals of the software, then the program is returned for revision. The examination protocol records the period for the retest.
Software expertise is a type of engineering expertise. This type of research is extremely relevant, since software is one of the most dynamically developing segments of the technological sphere. Another reason software expertise is in high demand is counterfeit products and unfair competition. It is this type of examination that makes it possible to establish whether the rights of a citizen (company) have been violated within the framework of the Code of Administrative Offenses (Chapter 7, Article 7.12 “Violation of copyright and related rights, inventive and patent rights”), as well as the Criminal Code (Article 146 “Violation of copyright and related rights"). Software forensics experts study, test, and analyze a computer product. They can also track instances of inappropriate software.
Specialists have to solve a wide range of issues:
- find out the degree of compatibility of the software being studied and the technical one;
- determine the functional purpose of the software product;
- draw conclusions about the composition of specific software files;
- identify programming languages used to develop a software product;
- identify signs of counterfeit software;
- determine forms of data input and output in a software product;
- establish the method of changes in the software (software failure, malware action, hardware failure, software environment errors).
What is the object of software examination?
Within the framework of this type of examination the following are subject to examination:
- utility programs;
- tools for debugging and developing programs;
- service system information.
What materials must be presented for software examination?
For analysis, a specialist examines system, application and proprietary software. Discs, computer and game discs, as well as DVD and Blue-ray discs are subject to examination. It is very important that all components are in good working order. The accuracy of the conclusion depends on this. However, if some information has been deleted, a specialist should try to restore it.
Software examination is carried out in two stages. The first stage includes conducting technological tests to ensure compliance with qualitative and quantitative indicators. The second stage includes functional testing, which allows us to determine the functional characteristics declared by the developer with the working version of the software product.
Our center has all the necessary equipment to carry out examination of software of any complexity. Our specialists will carry out all expert work at a high level and represent the customer’s rights at various stages of legal proceedings.
Cost and terms
Forensic examination
Extrajudicial research
Review of expert opinion
Receiving written expert advice (certificate)
Obtaining preliminary expert advice
Additional services
Frequently asked questions
Computer programs were installed in our company. There is a suspicion that they are counterfeit. How to conduct an inspection and, if the result is positive, make a claim?
To do this, you need to conduct a computer technical examination. The specialist will check whether the installed software has signs counterfeit products (the concept of counterfeiting is legal, therefore computer technical expertise does not answer the question of counterfeiting, but can only indicate the presence of signs that the installed software is counterfeit). Works are considered counterfeit, the production and distribution of which leads to a violation of copyright and related rights. Law enforcement officials should check whether such a violation occurred in your organization. To do this, you can provide them with a conclusion based on the results of a computer technical examination.
Is it possible to check the quality of a software product during software examination?
Yes, software examination allows you to track software of inadequate quality, determine the degree of its compatibility with equipment, identify the causes of failures and signs of counterfeit software. The ultimate goal of software quality assessment is to verify the completeness and acceptability of the program to the end user.
At the first stage of software examination, technological tests are carried out to check the compliance of quantitative and qualitative indicators. The second stage of software examination involves functional testing to compare the functional characteristics specified by the developer with the software product under study. The examination of the software ends with the preparation of an expert opinion.
Can computer forensics determine whether a certain program is malicious?
Computer forensics does not answer such questions. A malicious program knowingly leads to the unauthorized destruction, blocking, modification or copying of information protected by law. This definition indicates the actions of a person, the manifestation of his will and is associated with the functioning of the legal system. Consequently, the issue of software maliciousness is beyond the competence of a computer forensics specialist. The objects of study of computer technical expertise are computers, electronic storage media, systems for ensuring the implementation of information processes.
Should all documents found on the media being examined be printed as part of a computer forensic examination?
No, this is not a requirement. Computer technical forensics does not require printing out all found documents on a storage medium. For a computer forensics specialist, it is necessary to save the contents of the information carrier under investigation unchanged, create a copy, and then carry out computer forensics using it. This copy on a separate medium must be given to the investigator. The expert can print out a few small but important documents for him, but nothing more. Refusal of printing saves money, paper, printer consumables, time and allows the specialist to concentrate on conducting the actual computer-technical examination.
Does computer technical expertise resolve the issue of the functionality of a software product?
Yes, it does. Computer technical expertise is based in this case on the definition of operability contained in GOST 28195-89, which states that the operability of a program means its ability to function
- in specified modes;
- in given volumes of processed information;
- in accordance with program documents.
Based on this, a specialist in computer technical expertise, who has a question about the functionality of the program, requests additional materials - technical documentation. It is compiled by the program developer and may be called “Technical Specifications” or “Test Methodology”.
If the expert’s request is satisfied, he begins to conduct a computer technical examination, conducting a series of experiments and comparing the behavior of the program with the tests from the “Test Methodology”. Upon completion, a computer-technical examination report is drawn up. If the request is not granted, then the computer forensics specialist draws up a reasoned refusal to issue an expert opinion.
If the computer system unit is removed for computer forensic examination, will the information stored on it change?
Computer forensics involves preserving the contents of storage media unchanged. Moreover, this is required by the Criminal Procedure Code of the Russian Federation, which states that an expert is prohibited from performing actions that could lead to a change in the basic properties of the object under study. If this prohibition is violated, this will eliminate, if necessary, the possibility of verifying the expert’s conclusion - conducting a second computer-technical examination.
During a computer forensic examination, a specialist works through a so-called trusted operating system, which does not write anything unauthorized to the hard drive. On the computer under study, it can be physically protected from changes by connecting it through a special device.
To conduct the actual computer-technical examination, the researcher either creates a file image of the hard drive on his computer, or uses special software to copy it sector by sector to another hard drive. All information on the seized computer hard drive is stored unchanged.
There is a suspicion that the speed of the Internet connection via a USB modem is much lower than that stated by the provider. I would like to make a claim. Can computer expertise help in this case?
Yes, computer hardware examination may well resolve your issue. To do this, you will need to provide a USB modem for research. Within the framework of computer technical expertise, specialists will determine its technical characteristics: capacity, form factors, average data access time, data transfer speed, etc. Computer technical expertise will also check the data transfer speed for compliance with that stated in the contract. Based on the results of the study, you will be given a written conclusion in the prescribed form. The conclusions of an independent computer-technical examination can prove that the provider has failed to fulfill its obligations and become the basis for early termination of the contract.
There are photographs in the file (on a flash drive) that can confirm that I was in a different place at the time of the crime. To do this, you need to determine where, when and with what camera the photographs were taken. How to schedule an examination? What do you need for this?
The court can directly order a computer technical examination of photographs at our expert institution. When making a court order, it is necessary to provide photographs on electronic media and the camera with which the photographs were allegedly taken.
In addition, the research can be conducted at the initiative of one of the parties (at the request of a lawyer or a statement from a participant in the process). In such a situation, based on the results of the study, a specialist’s opinion will be provided, which can also be attached to the case materials. When conducting an expert study on their own initiative, participants in the process must also provide photographs on electronic media and a camera.
Is it possible to track whether the Internet was accessed using specific equipment (USB modem) and to which specific sites?
The ability to confirm that you are using a USB modem to access the Internet depends on the type of modem. If you are using a modem that works with a SIM card from a mobile operator, you must provide both the modem and the card for computer technical examination. If you use a modem without a SIM card (for example, yota), the fact of its use to access the Internet will be determined by the IMEI code of the modem.
Software product examination
differentiated and modernized
relatively high profitability

A– constant determined on the basis of statistics,
m– slope of the curve,
The pictures show a classic version of the life cycle. There are several varieties of it. Kinds:







The competitiveness of a product is a set of properties of a product that make it more preferable compared to the products of competitors in a given market.
The competitiveness of a product is assessed only taking into account the specific market for its sale. Otherwise, this work is useless, since a product that is competitive in certain competitive conditions may not be so in another market.
Competitiveness as a complex characteristic of a product does not remain constant over time. It begins to fall from the moment new products from competing enterprises appear on the market. There is a need to improve their products, change their structure, expand functionality and improve quality while consistently reducing the costs of production and operation of products.
The set of parameters that determine the competitiveness of a product is relatively stable, while at the same time their significance (weight) changes depending on the prevailing market conditions.
The basis for assessing competitiveness should be a comparative analysis of objects of the same functional purpose carried out by different enterprises.
The winner is the product that has the ratio of beneficial effect to the cost of its acquisition and use WITH(specific useful coefficient) is maximum compared to other similar products. Therefore, the condition for the preference of one of the goods over all others has the form:
 , Where
, Where
WITH– consumer costs,
Assessing the competitiveness of a product planned for sale includes the following steps:
defining the market and selecting the most competitive sample product as a basis for comparison and determining the level of competitiveness of this product;
determining a set of comparable parameters of both products;
calculation of the integral indicator of the competitiveness of a given product.
Assessment of product competitiveness TO carried out using the index method:
 ,
,
J n– free index according to standard parameters
 , l=
, l=
J tp– method, approach to determining technical parameters
 ,
,

p i– private parametric index. Reflects the degree of consumer satisfaction.

An ideal product is a product that satisfies the consumer 100%
Examination of the circumstances of the creation and use of files and databases
Examination of the circumstances of the creation and use of files and databases is a special type of computer technology research aimed at establishing the conditions accompanying the formation of files and databases, as well as the circumstances in which they were used. Carrying out this analysis requires special knowledge in the field of organizing data storage in computer systems. Computer memory is arranged hierarchically, information packets are organized in a special way and, in most cases, are arranged in an order that forms a branching tree. Files are placed in directories or, as they are commonly called, folders. The folders are in turn organized into larger folders. And so on. This is done for the convenience of the user - the system of nested folders makes it easier to find the desired file and access it.
At the digital level, a file contains not only the data that the user placed in it, but also a number of specific attributes, thanks to which the system recognizes this package of information and places it in the data warehouse. In addition to the access path to the file, its system part contains data about the user who generated the file, the size, type, time of creation of the file, and so on. You can get information about the last access to this file and the date of the last changes made. The extraction of these attributes, as well as their analysis, to put it simply, is the essence of examining the circumstances of the creation and use of files and databases. And, if some of this data can be obtained by an unqualified user, then to extract some characteristics of files or databases, special skills in the field of computer information are required, as well as the use of special modern technologies and, accordingly, equipment.
Databases are repositories of large amounts of data organized in a specific way. The method of organizing data depends on the content of the database, that is, on the type of data it contains, on the scope of the database, the specifics of the tasks solved with its help, on the number of users, and so on. The databases of large companies or government organizations contain huge amounts of attractive information, so such storage facilities often become targets for criminals who gain unauthorized access to data in order to use it for criminal purposes. To investigate such crimes, as well as to prevent them, an examination of the circumstances of the creation and use of files and databases is used. Research of databases may be required if errors are detected in their functioning, data is suspected of being used for other purposes, security system violations and other shortcomings.
An examination of the circumstances of the creation and use of files and databases is carried out both by decision of the investigative authorities or the court, and on the initiative of private individuals - citizens or organizations.
The procedure for conducting an examination of the circumstances of the creation and use of files and databases
To carry out this type of research, it is necessary to conclude an agreement for its conduct with an expert center or a specialist in the field of computer and technical expertise. Before concluding such an agreement, it is advisable to obtain preliminary consultation in person, by telephone or in another convenient way, especially if the need to conduct an examination has arisen for the first time and the specifics of its production raise questions or doubts. The consultation will help clarify the goals of the analysis, the subject of the study, the timing and cost of its implementation, as well as determine the specifics of the upcoming expert events. When concluding an agreement, you should check whether the goals and objectives of the study, its subject, the list of questions that the specialist will answer during the examination, the data of the parties, the timing and cost of the study are included in it. The contract must contain comprehensive information regarding all these points.
After signing the contract, the initiator of the study submits all the necessary materials:
- Documents confirming the identity of the initiator of the examination (for individuals). Documents confirming the existence of the organization and other title documents (for legal entities).
- A computer or computer system that contains files or databases.
- Printouts of the contents of files, printouts of the results of queries to the database, copies of such printouts - if available and relevant for the research (this is determined by a specialist at the stage of concluding a contract or preliminary consultation).
- Any documents related to the incident.
- A display of a computer screen (called a screenshot) containing some part of a file, a database interface, or confirming the presence of a file on the computer.
- Other documents or computer devices necessary for conducting the examination - at the request of the specialist performing it.
- For files and databases accessible on networked computer systems, it is necessary to provide information about the functioning of the network and access to the network architecture itself.
After carrying out the expert activities, the specialist summarizes the data obtained, answers the questions posed and begins to form an expert opinion, which is the main result of the research, has evidentiary value and can be included in the evidence base during the judicial hearing of the case.
Legal basis for the examination of the circumstances of the creation and use of files and databases
If the use of a file and databases is part of a computer crime, then responsibility for such acts is regulated by Chapter 28 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, which contains three articles describing the types of computer crimes and the corresponding preventive measures.
The rights and responsibilities of a specialist conducting an examination of the circumstances of the creation and use of files and databases are determined by Article 381 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Article 303 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation determines the punishment for the formation of a false conclusion by an expert, which, in essence, is falsification of evidence.
Examination of counterfeit products () (page 1 of 3)
Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation
Ural State Law Academy
Department of Legal Psychology and Forensic Expertise
Examination of counterfeit products
Performed: Berseneva O.V., student of group 512;
Checked: Associate Professor, Candidate of Legal Sciences Kuznetsov P.S.
It is difficult to imagine modern life without electronic computers, the prototype of which was ordinary abacus, especially since the life of each of us is somehow connected with electronics, be it an ordinary machine or, for example, an automatic machine for accepting payments on a cell phone.
The fourth part of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, which entered into force on January 1, 2008, detailed the regulation of rights to the results of intellectual activity and means of individualization. In addition, two Resolutions of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation were adopted on civil cases dated June 19, 2006 No. 15 and on criminal cases dated April 26, 2007 No. 14 on the practice of considering these cases on the protection of copyright and related rights, as well as an information letter from the Supreme Court Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated December 13, 2007 N 122 “Review of the practice of consideration by arbitration courts of cases related to the application of intellectual property legislation.”
But violations in the field of intellectual activity cause harm not only to authors and other copyright holders, but also to national interests, in particular, this is the legal aspect of the political and economic task of increasing GDP.
In this regard, in this work, I will try to reveal the basics of the examination of counterfeit products or software and hardware examination.
Chapter 1. Basic provisions for the purpose and production of software and hardware expertise.
Software examination is a system-forming piece of evidence in cases of copyright protection and is of fundamental importance. In both civil and criminal cases, an expert’s opinion is, in fact, a “qualifying” sign of copyright infringement. Thus, in civil cases, it is necessary to confirm the fact that the copyright belongs to the copyright holder and the fact of use of this right by the defendant; in criminal cases, it is necessary to confirm the defendant’s performance of a number (or one) of alternative actions (purchase, storage, transportation) performed for sales purposes, or the very use of copyrighted objects . Moreover, the latter is a common element in the subject of proof in both criminal and civil cases, in one case it is an objective side of the crime, in the other - a circumstance to which the plaintiff refers as the basis for his claims and objections (Article 56 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
The use of computer programs by the highest court is proposed, in particular, to be understood as “committed without the consent of the author. reproduction (production of one or several copies of a work or part thereof in any material form, including recording a work or phonogram in computer memory or on a computer hard drive). distribution on the Internet, translation of the work, its processing. modification of a computer program or database, as well as other actions performed without formalizing a contract or agreement in accordance with the law.” In connection with such a legal interpretation of copyright legislation in terms of the use of computer programs and the emerging law enforcement practice, the expert’s opinion becomes a necessary link in the subject of proof, since “the court must find out and indicate in the verdict exactly what actions violated the rights of the authors of the works, their heirs , performers, producers of phonograms, cable and broadcasting organizations, as well as other holders of these rights,” for example, by reproduction, distribution, modification, etc. It is also necessary because in all cases the expert’s opinion allows us to determine (confirm or refute) the period of use of computer programs (from the date of installation (creation) until the moment of deletion relative to real time), the exact and correct name and configuration, copyright ownership , as well as their volume in accordance with the technical characteristics of the program, the latter, as already noted, facilitates the task of establishing the correct cost of a copy of a work or copyright for its use.
However, the special knowledge required in carrying out the examination may not relate to any branch of knowledge - science, technology, art or craft. The exception is the legal knowledge that a law enforcement officer must have. Even the Plenum of the USSR Supreme Court, in its Resolution No. 1 of March 16, 1971 “On Forensic Expertise in Criminal Cases,” specifically stated that “courts should not allow legal issues to be raised before an expert as not within his competence.” Sometimes in practice, attempts by experts to resolve legal issues (for example, about the causes of a crime, the legal qualification of a crime) are unlawful. Therefore, investigative bodies and courts should not offer questions of a legal nature to experts, just as they, even having knowledge in any branch of science and technology, do not have the right to conduct research themselves to resolve issues that require special, but not legal knowledge. An expert can only examine the circumstances of a specific criminal case, which are reflected in the materials presented to him.
Due to the fact that copies of works are considered counterfeit, if the production, distribution or other use of them, as well as the import of such copies, violate copyrights protected in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, then the concept of counterfeiting is legal and the question of counterfeiting of copies of works is before the expert cannot be posed, since the questions posed to the expert and his conclusion on them cannot go beyond the special knowledge of the person entrusted with carrying out the examination, however, the opposite relationship is possible - the expert has the right to answer questions, although not posed to him, about the circumstances that are relevant to the criminal case, but within the limits of their special knowledge (see, for example, Part 2 of Article 204 of the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation).
Thus, the magistrate of judicial district No. 2 of the Oktyabrsky district of Yekaterinburg, when rendering an acquittal in a criminal case against B., unreasonably indicated:
The expert concluded that there are signs of counterfeiting of the 1C: Enterprise software product. Accounting. Typical configuration. 7.7 Network version,” the copyright to which belongs to 1C CJSC, while the question was raised only about the presence of signs of counterfeit software products, the copyright to which belongs to Microsoft Corporation. The question of the presence of signs of counterfeit software products, the copyrights of which belong to 1C CJSC, was not related to the subject of the expert study and was not indicated by the investigator in the resolution ordering the examination, and therefore the court believes that the expert went beyond his powers , since original samples of the products of the copyright holder, JSC 1C, were not provided to him.
In connection with these circumstances, the court considers that this expert opinion is unacceptable evidence, since it was obtained in violation of the requirements of criminal procedure legislation. An expert's conclusion about the presence of signs of counterfeit software cannot be used as the basis for a verdict.
When resolving the question of whether a copy of a work is counterfeit, the court must evaluate all the factual circumstances of the case, in particular, the circumstances and source of acquisition by a person of the specified copy, the legal grounds for its manufacture or import, the existence of an agreement on the transfer (granting) of the right to use (for example, copyright or a license agreement), compliance of the circumstances of use of the work with the terms of this agreement (payment of remuneration, circulation, etc.), conclusion of an examination of the seized copy of the work.
It is believed that the word “counterfeit” came into Russian from French and is formed from two components: contre (“against”) and faire (“to do”) - contrefacon, which translated from French means “fake, counterfeiting,” i.e. . in the lexical sense, counterfeit is a synonym for fake.
In this regard, in legal practice, apparently, due to the foreign origin of this concept, problems in law enforcement periodically arise, and problems are of such a level that they have to be brought to the attention of lower courts and the courts of a constituent entity of the Federation.
Thus, the deputy chairman of the Kurgan regional court was forced to make the following explanations to the chairmen of the district (city) courts of the region:
although the definition of the concept of a counterfeit copy of a work or phonogram given in paragraphs 3, 4 of Art. 48 of the Law of the Russian Federation “On Copyright and Related Rights” has nothing to do with the concept of forgery, however, in various manuals and publications that claim to cover the legal aspect of the application of Art. 146 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, recommendations are given for conducting special examinations in order to determine the counterfeitness of a copy of an audiovisual work or other object of copyright and related rights.
Thus, a false understanding of the issue of application of Art. 146 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation from the standpoint of proving the quality of a counterfeit copy, its forgery or falsification, while it is necessary to prove the very fact of violation of copyright and related rights by an individual who, based on the provisions of Part 2 of Art. 48 of the Law of the Russian Federation “On Copyright and Related Rights” is a violator of copyright and related rights on the sole basis of deliberate failure to comply with the requirements of this Law when using objects of copyright and related rights. And when determining whether copies are counterfeit and the presence or absence of a crime under Art. 146 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, it is necessary, first of all, given the blanket character of this norm, to simply check the activities of a person when using objects of copyright and related rights with the restrictions and requirements imposed on it by this Law and the relevant provisions of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, without raising questions of a legal nature to the expert, the resolution of which falls within the competence of the investigator, prosecutor and court.
Software expertise
Various questions may be raised for the consideration of the relevant expert. First of all, the set of such questions depends on the tasks that are solved during the research. This may be an examination of the work program, its compliance with certain criteria or the degree of similarity with another software product. Also, in certain cases, specialists are required to establish the functionality of a certain program and its technical elements.
Modern examination of professional programs allows you to carry out your defense in courts at a qualitatively new level, to operate with confirmed facts and conclusions of relevant specialists. Consequently, a forensic examination of the program will help establish the truth in the case and allow you to protect your rights.
Among other things, computer examination of the program will help identify possible flaws in its operation. Thus, you will have a unique opportunity to significantly improve the quality characteristics of your software product, to do everything to ensure that the final product pleases the consumer and does not cause any troubles during operation.
You can always contact us to get absolutely free advice on conducting examinations, preparing relevant documentation and many other issues related to software and research in this area.
A huge number of users have already entrusted us with conducting various types of research and were satisfied with the results of our cooperation. If you need software and technical expertise, you can always contact the accredited specialists of our company, who will help establish the truth in the matter, draw your attention to the essential points in the program’s operation and answer all your questions.
Positive customer reviews about the work of our specialists are the best advertising. We have been successfully competing in the market in this segment for a long time and can offer exceptionally high-quality services. Do you need computer program expertise? If so, you know where to turn! Our professionals and researchers in this field are waiting for interesting proposals and new materials to study. We are happy to provide assistance to everyone who decides to go deeper and immerse themselves in solving computer problems, comparing technical materials, and so on. Take advantage of a great offer from our company right now!
company's newsThe Moscow City Bureau of Commodity Expertise was founded on May 4, 1936. Since then, the Bureau's experts have conducted more than a million examinations. The bureau has unquestioned authority both among corporate clients and individuals.
Independent examination reviewsThe MGBTE company provides expert assessment services for all types of property with high quality and conscientiousness and has an excellent reputation among business partners.
Examples of auto examinationsAfter reading the articles in this section, you will be able to see with your own eyes the whole variety of automotive examinations performed by competent specialists of the Moscow City Bureau of Commodity Examinations.
Expertise of software for compliance with technical specifications
The purpose of the examination: examination of software to determine its compliance with the requirements and conditions of the specification.
Research part
To conduct the examination, access was provided to the software “...”, which was installed on the local network of XXX LLC for the duration of the study.
Software "..." is a system that is designed to maintain a unified database of the company's clients and manage: the full sales cycle, projects, marketing, as well as customer service.
Table 1 - Results of testing technical and functional characteristics
|
Functionality under study |
Conclusion |
|
|
1. Client management |
||
|
Unified database of company contacts and contractors |
Present, there is a connection between contacts and counterparties |
|
|
Possibility of multi-level segmentation of contacts and counterparties according to any direct and indirect criteria |
Multi-level segmentation is present in the system and works by contact and account fields |
|
|
Storing data and addresses with the ability to view on a map, careers and contact profiles on social networks |
The ability to store data and addresses is present, viewing addresses on an interactive map is supported, profiles of contact persons on social networks (twitter and facebook) are available |
|
|
2. Communication management |
||
|
Maintaining schedule and tasks |
Present in the corresponding tabs |
|
|
Possibility of flexible settings of reminders for various types of activities. Sending reminders to user email |
Present. There is a mechanism for setting up sending notifications from business processes. Letters are sent to users' emails |
|
|
13. System Administration |
||
|
Multilingual user and administrator interface |
On the test bench it is possible to change the language between Russian and English, and vice versa |
|
|
Setting up access rights to sections with distribution of rights to view, edit and delete down to the fields. The ability to configure access to individual records or operations, as well as specify which sections a user of a certain role will see in his workplace |
This functionality is available to the system administrator through the System Design section |
|
|
14. Other |
||
|
Availability of training materials |
||
|
Availability of applications for Android, iOS, Windows Mobile |
Applications for Android, iOS and Windows Mobile were found on the corresponding trading platforms |
|
*******************************************************************************************************************************************************
Conclusion
According to the subject of the agreement, it is established that the software complies with all technical and functional characteristics stated in Appendix No. 1 to the License Agreement.
If a person is involved in an accident, he can get fair insurance compensation according to OSAGO. Today, a special government methodology called EMRU is used to calculate damage. But what is the structure of this technique? What laws govern EMRU? And what formula is used to determine the amount of damage? Below we will find out the answers to these questions. We will also look at an example of calculating insurance damage according to EMRU.
The Unified Methodology for Calculation of Damage (UMRU) is a special method with which you can calculate the amount of insurance compensation under compulsory motor liability insurance.
In fact, EMRU is a set of formulas.
The unified calculation methodology is regulated by the following documents:
- Federal Law No. 432-P. Represents the main regulatory document in accordance with which the amount of monetary compensation is calculated.
- Federal Law No. 433-P. It is an additional regulatory document that regulates the rules for conducting an independent examination, with the help of which the amount of damage can be assessed and establish some details of the accident.
- BCZ. It is an electronic database that stores information about the cost of certain spare parts to most vehicles.
The draft laws were developed by the Ministry of Transport, the Central Bank and the Russian Union of Auto Insurers (RUA). Before the introduction of ERMU, there were more than 5 recommended state methods with which it was possible to determine the amount of damage.
The problem was that these techniques did not fit well with each other, which led to confusion. Another problem was that different methods produced different results, and the amount of recommended payments using different methods could vary. differ by 2-3 times .
Because of this confusion, many dissatisfied car owners sued the insurance company, and in 2013, before the law was adopted, the number of such lawsuits was more than 600 thousand.
The adoption of EMRU allowed us to solve many problems:
- Reducing the burden on the judiciary.
- Increasing the level of transparency between insurance companies and motorists.
- Unification of calculations.
- Stabilization of the economic model of compulsory motor liability insurance.
- Increasing the reliability of insurance companies.

EMRU is a document with which you can calculate the cost of insurance compensation. The EMRU contains the following information - definition of basic terms, calculation algorithms, formulas for calculations, reference materials, rules for drawing up expert reports, and so on. Using this information, you can accurately determine the amount of insurance payment for repairs.
The unified methodology for calculating damage contains information about all the main cars that can be found in the Russian Federation (the total number of car brands is more than 67, and the list itself is periodically updated).
It should also be remembered that EMRU can only be used if the client of the insurance company is an individual.
The methodology has the following structure:
- 7 main chapters, which contain basic information on the calculation of insurance compensation for compulsory motor liability insurance.
- 10 applications, which contain some additional information (correction factors, a list of parts for which a zero wear value is set, the average annual mileage of cars, and so on).
- There is also a special electronic database , which contains information about the average market cost of parts. This database is called BCZ.
| Type | Number | Short name | Information |
| Head of the Basic Law | 1 | Procedure for determining vehicle damage | Contains general information about EMRU. It is also indicated here that EMRU was created so that with its help it would be possible to calculate the amount of insurance compensation for damage to any vehicle. It also stipulates some basic concepts (evidence, vehicle examination, examination results) that are used to calculate insurance payments. Information is also indicated here that all examinations are divided into primary (carried out by an emergency commissioner or an insurer’s technician) and additional (carried out by forensic and independent experts). |
| 2 | Investigation of the circumstances of the accident | This chapter discusses the issue of studying the circumstances of an accident. The circumstances of the accident are studied with the help of special examinations, with the help of which it is possible to establish the key details of the accident (based on this information, in the future it is possible to establish the culprit of the accident, the degree of culpability, the type of violations that led to the accident, the amount of damage caused, and so on). Typically, two examinations are carried out to investigate the circumstances of the accident. The first examination is an expert-comparative analysis of the documentation that was drawn up after the accident. The second examination is a scientific expert analysis of an accident, with the help of which it is possible to establish the nature and type of damage caused; Based on this data, a computer model can be created that can be used to identify the culprit of the accident. If one of the parties does not agree with the conclusions of previous examinations, it can conduct an additional examination to clarify some details that may be important when considering the case. | |
| 3 | Determining the level of repair costs | Contains a number of algorithms that can be used to calculate the total cost of vehicle repairs. The following expense items are discussed here: the purchase of new auto parts (engine, headlights, bumper, etc.), the purchase of materials (paint, primer, abrasives, and so on) and the services of technicians. | |
| 4 | Determining wear levels when purchasing new parts | This chapter contains information on which you can calculate the wear of old parts. The fact is that many parts deteriorate over time, so when determining the level of compensation, the residual cost of the old part (taking into account wear and tear) should be subtracted from the full cost of each new part. | |
| 5 | Determining the cost of surviving parts if the vehicle is destroyed | This chapter describes a methodology with which you can calculate the cost of some spare parts, provided that the vehicle is completely destroyed (and there is the possibility of reusing these undamaged parts). The fact is that the damage caused may be so severe that the car will be almost impossible to repair, but some parts may be serviceable. Based on the data provided in this chapter, the cost of these serviceable spare parts can be calculated. | |
| 6 | Determining the value of a vehicle before damage | Contains information on how to use a methodology to calculate the pre-accident value of a vehicle. With the help of this information, you can understand whether it makes sense to restore the vehicle at all. The fact is that sometimes the damage can be so severe that repairing the vehicle does not make sense (for example, the value of the car before the accident may be much lower than the cost of repair). This chapter also specifies a method for calculating the average market value of a new car that is similar to a damaged one. If it turns out that a new car costs much less than repairing a damaged car, then the person is simply given money to buy a new vehicle (after all, in most cases it is quite difficult to calculate the cost of a car before an accident). | |
| 7 | The procedure for approving reference books for calculating the average cost of damaged parts | This chapter contains a list of sources that can help a technician or insurer estimate the cost of new parts. The fact is that when calculating damage, many parameters are used that can change (for example, the market value of parts). Some regulations of the Central Bank, an electronic database of spare parts, price standards and some other documents that do not contradict the EMRU are used as regulatory documents containing the necessary information. | |
| Appendix to the law | 1 | Photographing an accident and a damaged car | Contains information on how and in what cases it is necessary to record the consequences of an accident on photographic or video equipment. This information will be useful both in the case of drawing up a standard protocol with the involvement of traffic police officers, and in the case of drawing up a European protocol without the participation of traffic police officers. This information may also be useful in the event of litigation. |
| 2 | Typical vehicle damage | Contains information that can significantly simplify the procedure for classifying damage caused. This application also states that there are a total of 32 characteristic damages. | |
| 3 | Costs for restoring the body of some vehicles | This paragraph contains information on the basis of which you can calculate the cost of repairing non-metallic bodies of some vehicles. The fact is that the body of some foreign and domestic cars is made not of metal, but of some other materials (for example, special plastic), so an additional method is needed to calculate the repair of such a body. | |
| 4 | Commodity markets and boundaries of economic regions | Contains information about which economic regions certain areas belong to (13 regions in total). The fact is that the average market cost of parts is calculated taking into account the economic region (after all, for example, the price of a part in St. Petersburg may differ significantly from the price of the same part in Vladivostok). | |
| 5 | Size of correction factors for determining the degree of wear | When calculating the degree of wear, 2 special coefficients are used (depending on the type and brand of the vehicle). In this application you can find out the size of these coefficients in order to correctly calculate the degree of wear. | |
| 6 | Size of correction factors for determining the degree of wear of very old parts | In some cases, the values of the 2 correction factors (used to calculate the degree of wear) can be reduced. This annex provides information about the specific cases in which this may occur; The degree of reduction of these correction factors is also indicated here. | |
| 7 | List of parts for which wear value is set to zero | For some damaged parts, the wear value is set to zero. This appendix provides a list of these parts (brake discs, steering wheels, tie rod ends, etc.). | |
| 8 | Directory of average annual vehicle mileage (including regions) | When calculating the cost of repairs, the vehicle's mileage is also taken into account. In this application you can find out the average annual mileage of vehicles (taking into account the type of vehicle and region of residence). | |
| 9 | Reducing factor K, with which you can take into account the operating time of the vehicle | The cost of insurance payment may be slightly reduced depending on how long the vehicle is in use. This annex specifies the size of this reduction factor (the size of the factor depends on the type of vehicle and age of use). | |
| 10 | Additional coefficient K, which can be used to take into account the nature of mechanical damage | The cost of insurance payment may be changed depending on the nature of mechanical damage. This annex indicates the size of the correction factor, and the factor itself depends on the degree of mechanical damage. |
When can a unified methodology for calculating damages under compulsory motor liability insurance be used?
The following persons can use the unified methodology for calculating damage:
- Insurance companies and their official representatives who have the right to inspect damaged vehicles.
- Certified expert organizations (including independent ones).
- Private experts who have passed certification and are licensed.
- Forensic experts who have passed certification and are licensed.

After an accident, it is necessary to draw up a vehicle inspection report
(usually this document is compiled by experts with the participation of people who were involved in an accident).
The vehicle inspection report must include the following information:
- Reason for vehicle inspection(in our case it will be an accident).
- Exact start date and completion of the vehicle inspection.
- The exact address. If the accident occurred near a house - the street name and house number, if the accident occurred at an intersection - street names, if the accident occurred far from any populated areas - the name of the highway, kilometer number and direction of travel.
- Full information about the owner, as well as information about the person who was driving at the time of the accident (after all, in the general case, the driver may not be the owner of the car, but some other person, for example, a friend of the car owner).
- Vehicle information— equipment, start of operation, mileage, and so on.
- Information about damage that occurred before the accident. It is necessary to indicate not only all old damage, but also indicate the type of damage, their location, and so on. If repairs were made or spare parts were changed, this fact must also be reflected in the report.
- Information about damage that occurred as a result of an accident. It is necessary to indicate not only all existing damage, but also indicate the type of damage, their location, and so on.
- If any part was taken for analysis to conduct an additional examination, this fact must be reflected in the report.
- The current condition of the car should also be indicated in the report. If the car has been towed— information about where and how the vehicle was evacuated should be reflected in the report.

The unified methodology for calculating damage contains special rules that regulate the conduct of special examinations, with the help of which the amount of monetary compensation can be determined.
EMRU requires experts to meet the following requirements:
- They must have higher technical education.
- They must undergo special expert technical courses. At the end they must pass the exam successfully.
- They must take advanced training courses at least once every 5 years.
- The minimum professional experience is 12 months.
- After receiving a license to conduct an examination, information about the expert is entered into a special list of auto expert technicians. This list can be found on the RSA website . From this register you can find out the following information about the expert - full name, city, legal status, terms of accreditation, contact details, and so on.
Setting the amount of payments - the basic formula

The unified methodology for calculating damage contains information on how to correctly calculate the amount of insurance compensation.
The following formula is used for calculations:
- RK = SR + SM + SD.
- RK- This total amount of compensation.
- SR- This repair cost.
- CM- This Cost of materials.
- SD- This cost of parts that need to be replaced.
- When calculating these indicators, the average market cost of parts, materials and repair work is taken into account. The maximum degree of deviation from the average market value can be no more than 10%.
- When calculating the cost of work (CP) and materials (CM), the date and region of the accident are taken into account .
- Calculation of CP and SM occurs on the basis of standards specified in Appendix No. 3.
- Only damage caused by an accident is taken into account. . If, for example, someone scratched a car before an accident, then the insurance company will not give money to paint over the scratch.
- It should also be remembered that when calculating the cost of parts (CP), wear should be taken into account
. To do this, it is necessary to calculate the correction factor using a special complex formula; after this, you need to subtract this coefficient from unity, and the resulting result should be multiplied by the SD parameter.
It should be understood that the correction factor will always be less than one, so the full market value of the damaged part will not be returned to you.
And this is fair - after all, over time, many parts wear out, and if you are in an accident, the insurance company must only compensate for the market value of the old part.
- If the total amount of compensation exceeds the cost of a new car of the same make and model, then the insurance company will issue money not for repairs, but for the purchase of a new car . Often this approach is used when there is so much damage that it is much cheaper to buy a new car than to repair the old one.

Let's try to calculate the amount of damage ourselves:
- Let us have a car CHERY TIGGO (T11). Let's assume that the car was released in 2012. Its mileage was 70 thousand kilometers.
- In March 2016, an accident occurred.
- Let's Let's first calculate the degree of wear. To do this, you can use a special complex formula; You can also use a special online calculator. Regardless of the calculation method, we will get a wear rate of 0.35 (or 35%).
- Let us remind you that The amount of compensation is calculated according to the following formula : amount of compensation (RK) = cost of materials (CM) + cost of repairs (SR) + cost of parts (SD).
- Let's first calculate the SD parameter (cost of parts). Suppose we should buy a bumper, a right headlight and a mount for the right headlight. To do this, let's go to several sites and find out how much the same parts will cost on different sites (we will visit 3 sites). After this, you should calculate the arithmetic average (this will be the average market value). Let the bumper cost 3,600, 3,400 and 3,200 rubles on different sites - then the arithmetic average will be 3,400 rubles. Using the same scheme, we will calculate the cost of the headlight and headlight mount - let their average market price be 3,000 rubles and 800 rubles, respectively. Now let's add up these three numbers - we get 7,200 rubles. Now let's calculate the cost of parts taking into account wear: (1 - 0.35) * 7,200 = 4,680 rubles.
- Let us now calculate the parameter CP (repair cost). Let us only need to repair the wheel arch and carry out wheel balancing. Let the average market price of a standard hour in cases 1 and 2 be 1,000 rubles each. Now let’s open Appendix No. 3 - it states that the standard is 3.0 and 0.1 in the first and second cases, respectively. Let's calculate the CP: CP = 3.0 * 1.000 + 0.1 * 1.000 = 3.100 rubles.
- Now calculate the SM parameter (Cost of materials). Let's say we should paint the new bumper and bumper mount. Let's assume that the average market price for a standard hour is 1,200 and 500 rubles, respectively. Let's open the application - it states that the standard is 1.0 and 0.4, respectively. Let's calculate CM: CM = 1.0 * 1.200 + 0.4 * 500 = 1.200 + 200 = 1.400 rubles.
- Now we have all the data. Let us now calculate the amount of insurance payment: RK = SM + SR + SD = 1.400 + 3.100 + 4.680 = 9.180 rubles.
Video on the topic
Conclusion
Now you know what EMRU is. Let's summarize. Firstly, EMRU is the main method by which you can accurately determine the amount of insurance compensation in case of an accident. Secondly, EMRU is a document that consists of 7 chapters and 10 annexes, where contains all the basic information about the technique.
Leave a request for examination
Our professional services will help you protect your legitimate interests in court, as well as before law enforcement agencies.
What we can
Most often, we are contacted by software owners whose copyrights have been violated. To calculate the amount of damage caused by illegal actions of third parties, an assessment is necessary. The examination of the programs will record the fact you need, and the document issued based on the results of the study will have full legal force.
In addition, our specialists will analyze factors indicating the degree of security, including legal security, of your software product. The examination of programs will help to identify any weaknesses in this context, and the expert report will contain recommendations for eliminating them.
We also provide the following services:
- checking the quality of the developed software;
- checking the software for compliance with the technical specifications and terms of the contract.
Definition of concepts
Independent examination of information systems and software products is a whole complex of studies. Its goal is to solve problems of the identification level of information and software on appropriate media. Specialists discover patterns in the development and use of software, study the functional meaning and characteristics of the algorithm, structural features and current state, and also determine whether changes have been made to overcome the protection. Information research is carried out on the basis of an analysis of the media format and placement of data, where access to it is determined (degree of security, characteristics, ability to overcome protection), assessment of information created by a program or user to organize information processes.
Expertise of software and information systems involves research:
- system software
- application software
- data in multimedia formats
- text and graphic documents
- information in database formats and other applications of an applied nature.
When is software and information systems expertise needed?
An independent study is required in the following cases:
- if it is necessary to check various business systems, organizational management systems (ERP, CRM, etc.) for compliance with the standards of the technical specifications;
- if it is necessary to determine whether changes have been made to the program;
- if it is necessary to determine whether the software is protected from unlicensed use;
- if it is necessary to determine the essence of hidden information;
- if it is necessary to determine whether there are attempts in the data system to illegally access information;
- if it is necessary to determine the possibility of recovering deleted data;
- if it is necessary to determine the causes of software malfunction;
- if it is necessary to determine the type of storage medium;
- if it is necessary to determine the presence of a mechanism of damage to the storage medium;
- if it is necessary to determine the last correction of data on the storage medium;
- if it is necessary to determine the possibility of making changes to the storage medium;
- if it is necessary to determine an assessment of the quality of the information system;
- if it is necessary to determine the cost of the information system;
- if it is necessary to determine what type of hardware and software the document was produced on;
- if it is necessary to determine an assessment of the cost and quality of the software.
Expert actions
Our information systems and software specialists perform the following activities:
- analysis of related documentation and regulations;
- examination of the information system for compliance with the technical specifications;
- preparation of an evidentiary expert opinion (must be in writing).
Regions
If you want to seek services from our center, but do not live in Moscow or Voronezh, we offer you several options for interaction:
- our employees can travel to any region of Russia to conduct an examination;
- you or your representatives can contact the branches of our center in Moscow or Voronezh;
- Our specialists can conduct examinations based on the documents provided.
You can find out more about working with Russian regions.