Not the most common problem. Most users do not change the processor until the computer is completely replaced. However, sometimes due to a breakdown or upgrade, it becomes necessary to replace the installed processor. In this case, the question arises of how to choose a processor for the motherboard. In this article, we will analyze this problem and talk about how to choose the right processor.
In order to match the processor to the motherboard, you need to find out which socket it supports. A socket is a connector on the motherboard designed to install a processor. There are different kinds of sockets. Sockets differ in size, shape and number of legs. Therefore, it is not possible to install the processor in the wrong socket.
Now the most popular are the following sockets:
- For Intel processors
- LGA 1150
- LGA 1155
- LGA 1356
- LGA 1366
- For AMD processors
If you are on a motherboard that is installed in a working computer, then you can find out the name of the socket using special programs for viewing the characteristics of the computer. The most suitable program for our case is the CPU-Z program. With this program, you can find out all the main characteristics of the processor and motherboard.
The name of the socket will be indicated on the first tab of the CPU-Z program, opposite the inscription "Package". Also, using this program, you can find out the manufacturer and model of the motherboard. To do this, go to the "Mainboard" tab.

Just because a motherboard is equipped with a particular socket does not guarantee that it will support all processors with the same socket. Some newer processors may not work. That's why in order to select a processor for the motherboard, you need to go to the website of the manufacturer of this board and view the list of supported processors. Finding the information you need is not difficult. It is enough to enter the name of the motherboard into the search engine and go to the official website of the manufacturer.
If you have a motherboard to which you need to match the processor, but the computer does not work or is not assembled at all. Then you can see the name of the motherboard on its box. If there is no box, then carefully inspect the board itself, a name should be applied to its surface.
Once you know the name of the socket and the motherboard, choosing a processor is not difficult. First, choose a processor that is equipped with the desired socket, and then check if it is supported by your motherboard.
The motherboard is the main connecting link within the computer system unit.
That is why it is very important when buying to be able to select from a large assortment of motherboards exactly the one that suits your tasks and satisfies all your requirements. In this article, we will briefly review the main points that you should pay attention to when choosing a motherboard.
For convenience and quick transition, a summary is given:
Motherboard and its main components
In order to better navigate the main components and further visualize for ourselves directly what we will choose, I suggest that you familiarize yourself with the layout of the motherboard elements using a specific example. For the sample, we took a very original Sapphire Pure Z77K motherboard (original, because Sapphire), which is also aimed at the overclocking market. In fact, for the task of visually examining the main elements of the motherboard, neither the model nor the positioning is absolutely important. Therefore, we turn to the consideration of this system board:
Click on the picture to enlarge
Here, the main components are highlighted in numbers, but some rather specific elements inherent only in overclocking motherboards are also affected.
(1) Processor socket- one of the main elements of the motherboard. The processor is installed in the socket and it is very important that processor socket which it targets was compatible with the socket on the motherboard.
Under the number (0) was indicated "double" radiator, which is responsible for cooling the elements of the processor power converters, the integrated graphics core and the CPU VTT. Such heatsinks are often found only in overclocking motherboards. Regular motherboards are shipped without this cooling element.
(2) PCI-Express slots . On the printed circuit board of this motherboard, we see 3 PCI-Express X16 version 3.0 slots, these slots are designed for installing video cards (either one or several in SLI and Cross Fire modes). This also includes the number (3) - it's the same PCI-Express x16 slot, but already older version 2.0. Between PCI-E X16 slots, numbered (14) placed PCI-E X1 slots. These expansion connectors are designed to install devices that do not require a lot of bus bandwidth; one X1 line is enough for them. Such devices include TV tuners, audio and network cards, various controllers and many others.
Under the number (4) we have indicated chipset(In this case, Intel Z77), which is hidden under the heatsink that cools it. The set of system logic contains various controllers and is the connecting link between the control of a part of the components and the processor.
(5) Connectors for installation DDR3 RAM. These connectors are colored black and blue, for installing memory modules in dual-channel mode, which allows you to slightly increase their efficiency.
(6) CMOS memory battery. This battery powers the chip. BIOS CMOS so that it does not lose its settings after turning off the computer.
(8) , (12) 24-pin and 8-pin connectors respectively. The 24-pin is the main 24-pin power connector through which most motherboard components are powered.
Under the number (9) and (10) connectors are indicated SATA 3 (6Gb/s) and SATA 2 respectively. They are placed on the edge of the motherboard and are made in the style of motherboard connectors for overclocking (connecting devices on the side for open stands). SATA interface used to connect hard drives, SSD drives and drives. In conventional motherboards, they are deployed frontally and shifted closer to the center, which makes it convenient to use them within the system unit of "non-overclocking" systems.
Under the number (11) a rather specific element was designated, which is found only in motherboards for enthusiasts - this POST codes indicator. It also displays the temperature of the processor, but likes to lie a little.
(13)
Back panel motherboard with external connectors. The connectors on this panel connect a variety of peripheral devices such as a mouse, keyboard, speakers, headphones, and many others.
Now that we have gone through the layout of the components on the motherboard, we can proceed to the consideration of individual blocks and parameters for choosing a motherboard. Since this article is introductory, everything will be described briefly and already much more deeply discussed in separate articles. So let's go.
Choosing a motherboard manufacturer
The manufacturer of the motherboard is not a very important factor when choosing. Here the situation is absolutely identical, as with choice of manufacturer for the video card- everyone is good and the question here is rather "religious" - who believes in what. Therefore, you can safely choose from all non-"no name" manufacturers such as Asus, Biostar, ASRock, Gigabyte, Intel and MSI. Even the motherboard from an unknown in the motherboard market, Sapphire, which we took to review the main components, is a good example. Perhaps the layout of some boards is not very convenient, perhaps some manufacturer's package is not very extensive, and someone may have a box that is not as bright as we would like - but still, all this does not give us the right to isolate someone then one as an impeccable leader and answer the question: which motherboard is better in the manufacturer's assessment.

All motherboards will eventually come with the same chipsets from AMD and Intel, and will be functionally similar. The only thing, before buying, I advise you to review the reviews of motherboards and user reviews, so as not to run into a model with unsuccessful cooling, or something else. We will not linger on the choice of motherboard manufacturers for a long time, but rather we will move on.
Choosing the Right Form Factor
Initially, choosing the right form factor will save you a lot of problems in the future. At the moment, the most popular motherboard form factors are ATX and its stripped-down version, Micro-ATX.
It is very important that the form factor determines the further extensibility of the system. The Micro-ATX form factor usually has fewer PCI and PCI-E expansion slots for graphics cards and additional devices. Also, often, such motherboards have at their disposal only two slots for installing memory modules, which significantly limits the increase in RAM, both quantitatively and regarding issues related to convenience. But the main advantage of Micro-ATX lies in the price. Based on the description of these two standards, it can be argued that Micro-ATX is positioned as a budget solution for compact office and home systems.

Important is the size, which just follows from the form factor. ATX boards are much larger than their "Micro" brothers, so you should consider the size of the case in relation to the size of the motherboard.
More details regarding form factors and their features will be described in a separate article.
Motherboard socket selection
After you have decided on the processor, the selection of the motherboard begins. And the first factor of choice should be exactly the socket that ensures the compatibility of the processor and the motherboard. That is, if an Intel processor with an LGA 1155 socket was selected, then the motherboard must also be with an LGA 1155 socket. A list of supported sockets and processors can be found on the website of the motherboard manufacturer.
You can find more information about modern processor sockets in the article: processor socket .
Choice of motherboard chipset
The chipset is the connecting link for the interaction of the entire system. It is the chipset that largely determines the capabilities of the motherboard. Chipset- this was originally a "set of chips" of system logic, which consists of a north and south bridge, but now this is not so simple.
To date, the latest 7-series chipsets from Intel and the 900-series from AMD are popular, Nvidia also adjoins them, but the assortment in the field of chipsets is rather small there.
Intel's seventh series chipsets, such as the Z77, H77, B75 and others, slightly distorted the concept of "chipset", because they do not consist of several chips, but only of the north bridge. This does not cut down the functionality of the motherboard in any way, because some of the controllers were simply transferred to the processor. These controllers include a PCI-Express 3.0 bus controller and a DDR3 memory controller. The north bridge was given control of USB, SATA, PCI-Express, etc. What is tied to what and on which buses is clearly visible on the block diagram of the Z77 chipset:

Indexes Z, H, B - mean the positioning of one or another chipset for different market segments. The Z77 has been classified as a chipset for overclockers. H77 is a regular mainstream chipset with advanced features. B75 is a bit undercut in terms of H77 capabilities, but for budget and office systems. There are other letter indices, but we will not dwell on them in detail.
Chipsets from AMD continue the tradition of two-chip chipsets, and the latest 900-series is no exception. Motherboards with this set of system logic are equipped with north bridges 990FX, 990X 970, as well as south bridge SB950.

When choosing a northbridge for an AMD motherboard, you should also start from its capabilities.
The 990FX is a northbridge designed for the enthusiast market. The main curiosity of the chipset with this northbridge is support for 42 PCI-Express lanes. Therefore, on 32 lines reserved for video adapters, you can connect up to 4 video cards in a Cross Fire bundle. From this we conclude that a few users need such features, so the functionality of motherboards with this chipset will be redundant for most users.
990X and 970 are slightly reduced versions. The main difference, again, is in the PCI-Express lanes. Both of these north bridges support 26 lines each, but this is unlikely to be a disaster for anyone. It is worth noting that the 970 does not support SLI and Cross Fire, as a result of which it will not be of interest to users who plan to combine more than one video card in the system, but due to its reasonable price, the 970 will look very tasty for a wide audience of users limited to one video card.
More details about the capabilities of AMD and Intel chipsets will be discussed in a separate article.
Memory slots and PCI-Express
The number of memory slots and PCI-Express expansion slots is an important factor when choosing a motherboard. As we said above, the number of these same connectors is often determined precisely by the form factor. Therefore, if you seriously and conveniently plan to scale the amount of RAM, then it is better to look at motherboards with 4 and 6 slots for installing RAM. This also applies to PCI-Express slots: it's silly to take a Micro-ATX form factor motherboard if you are counting on installing three video cards in SLI or Cross Fire.
Also, it is very important to pay attention to the type of RAM that the motherboard supports. Now you can still find on sale motherboards with a supported type of DDR2 memory. When assembling a new system from scratch, it is better not to go back in time and take a motherboard with a DDR3 memory type.
The version of the PCI-Express bus is not an important factor, so don't go all out for PCI-Express 3.0 support. For modern video cards, version 2.0 is enough. Yes and backwards compatible Nobody canceled various versions of this interface.
External connectors
It is important enough to have certain connectors on the back of the motherboard. Also important is their number. If we take into account the USB ports, then there should be, let's say, not a few of them, since, in most cases, a mouse, keyboard, webcam, printer, scanner and a large number of other devices are connected there.

You should pay attention to the audio connectors of the integrated sound card: there can be either three or six of them. Three connectors are enough for a standard circuit: a microphone, headphones and a subwoofer. If you plan to use multi-channel acoustics, then you need to look towards motherboards with 6 connectors. But even if at the moment you are not planning to purchase such acoustics, the connectors will not interfere, and in the future they can be very useful. And for office and budget systems, 3 audio connectors are enough.
In addition, two LAN connectors may come in handy; for this, two network controllers must be soldered on the board. But for most users, one network connector will be enough.
Additional features
Additional features include functionality that is not in demand for the average user, but for some it can be very useful:
- ESATA is an interface for connecting removable drives, it is not present in all motherboards and for owners of external drives, it can be a very useful feature.
- Wi-Fi and Bluetooth module - integrated wireless network and data transmission modules, can greatly enhance the functionality of the motherboard.
- Thunderbolt is a new interface for connecting peripherals and provides data transfer at speeds up to 10 Gb / s, which is 20 times faster than the now popular USB 2.0, and 2 times faster than USB 3.0.
A very specific interface that units will need today, but promises to become very popular in the future.

- This also includes special buttons and indicators on motherboards for overclocking. It can also be various proprietary elements and technologies from the manufacturer.
conclusions
Choosing a motherboard is not such an easy task. Based on all the parameters, it is necessary to choose an option that will be satisfactory both in terms of functionality and in terms of cost. You need to be able to catch that fine line of price / performance ratio. It should be remembered that everything is very individual here and the best motherboard for your friend may turn out to be the worst option for your needs.
But if you navigate in the basic parameters and approach the issue comprehensively, then the choice will be correct and will fully satisfy all your expectations.
P.S. We will try to answer your questions like “which motherboard to buy?”, “Which motherboard is better?” etc., in the comments to the article or on our forum.
Thank you for your attention. Good luck choosing!
How to choose the right motherboard and what to look for when buying.
Motherboard (MP)- the largest and most important part in the computer. A lot depends on her choice. When replacing the MP, it is necessary to take into account its dimensions.
Sometimes you need to select a video card for MP and processor. This requires certain knowledge. This article will help you learn more about how to select a motherboard.
Motherboard elements
MP consists of: chipset, socket, slots, etc. Depending on the purpose of the MP, different components are used.
For different purposes, excellent motherboard models are used (for example, MP for must be much more powerful and have a good network card and.
For simple work, this level is not required. This difference determines the cost of the motherboard).
To choose the right motherboard
It is not recommended to put a powerful processor on a cheap MP (the motherboard simply cannot withstand such a load for a long time and it will have to be changed). It works and vice versa - a weak processor does not need a powerful MP - it's wasted money.
MP should be chosen only after you have selected all the components for yours (the class of the motherboard and the types of connectors for connection depend on the components).
Let us consider the elements of MP in more detail.
socket
This is a connector on the motherboard for connecting to the processor. It is of two types: nested or slotted.
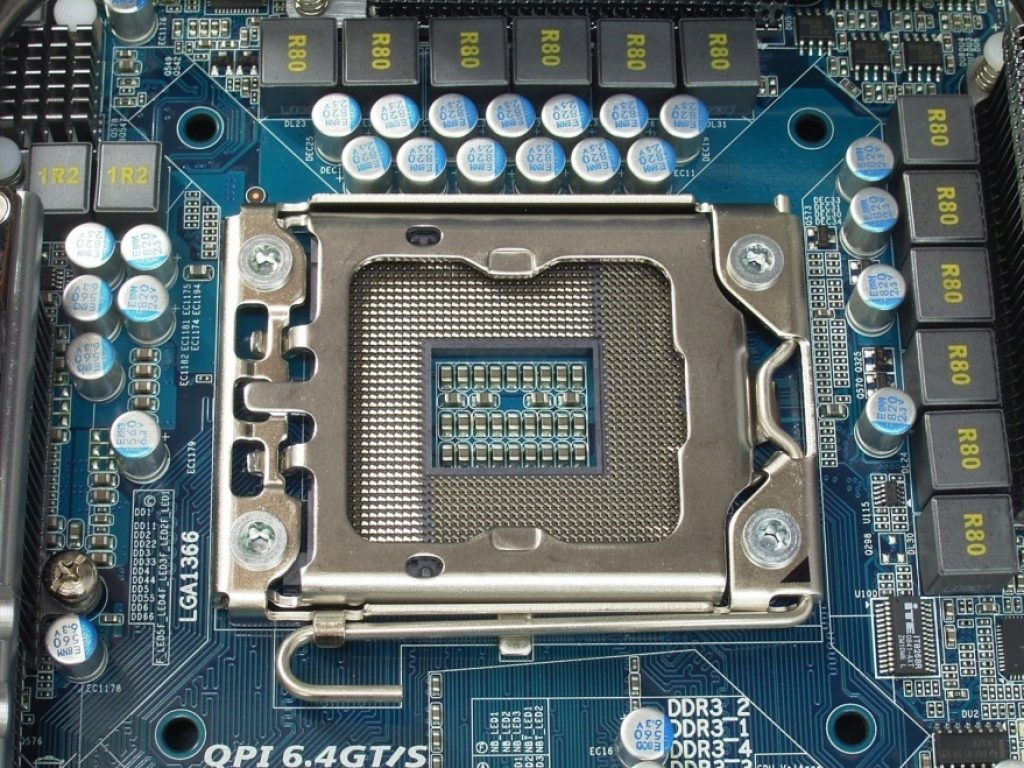
The shape of the socket depends on the type of processor. Currently, processors are produced by two companies: AMD and Intel. Current AMD sockets: FM2, FM2+, AM3, AM3+. Intel designates sockets with numerical values - 1150, 1155, 2011.
Differences between AMD and Intel processors:
- Various number and type of contacts;
- Different distance for fastening coolers;
- Different sizes of socket connectors;
- presence of controllers;
- The presence of integrated support in the graphics processor;
- Various connectors for system buses (a system bus is the total number of lines for transmitting all types of signals - addresses and control data - between the processor and other devices in your machine)
- Different types of processors
- Different number of USB ports and their types. For example, the number of USB0 and USB 3.0 ports (They differ in data transfer speed. USB 3.0 transfers information much faster)
- They differ in the amount of cache memory.
- Processors from different manufacturers vary in size.
- MPs from different manufacturers support different technologies and differ in performance parameters.
The reliability of AMD and Intel is approximately the same. The products of both companies meet the requirements of the US Department of Defense: 10 years of normal operation.
There is always a percentage of marriage, but the purchase guarantee evens it out.
Processors from different companies with the same characteristics cannot be put on the same motherboard.
How to determine socket type
It is important to know the manufacturer. This data can be found:
1 According to the documents. When buying a MP, the documents contain information about the manufacturer, characteristics, safety, operation, etc. Typically, a socket is denoted by the letter "S", or the word "Socket" with information about it.
2 By number. You can find the socket name and number near the CPU socket on the MP. You need to remove the side panel of the computer and the cooler. You can find the socket number on the Internet on the official website, in the catalog.
3 Compare. If there is no socket data, you can compare the processor socket and socket number.
4 With Everest. The program scans and displays the data of the computer system on the screen. Its interface is similar to a conductor (it forms information like a conductor)
To find out the scan results, you need to open the program and search through and DMI. Find a folder with processors and select the one you are interested in. In the last folder, find the "connector type", there will be information about the socket.
The CPU-Z program on the title page recognizes the data immediately. The advantage of this one is ease of use and speed, socket number, and processor socket.
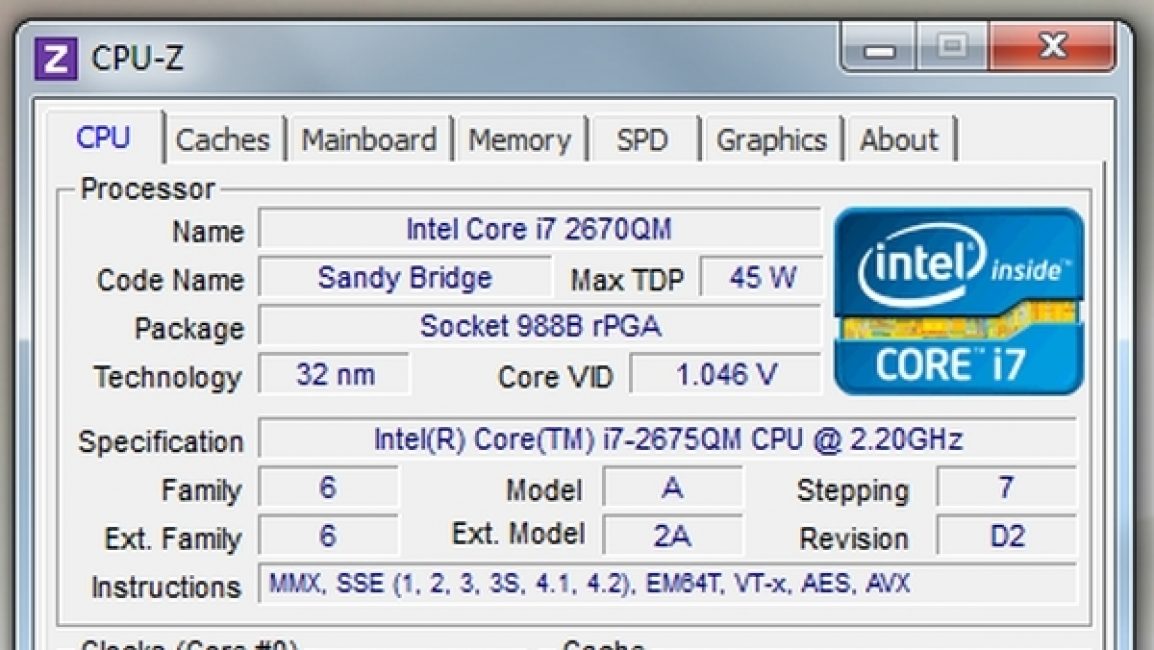
The socket type is not difficult to determine.
Chipset
Chipset- this is a block of microcircuits (from the English. Chip set - a set of chips). Each MP has a built-in processor, which is responsible for managing all components connected to the MP and their coordinated work. This processor is called a chipset.
In older models of MP microcircuits chipset are divided into two blocks — north and south bridge. The northbridge provides the processor with RAM (RAM controller) and video card (PCI-E x16 controller).
South - is responsible for the communication of the processor with: hard drives, optical drives, expansion cards, etc. via SATA, IDE, PCI-E x1, PCI, USB, sound controllers.
In modern models, the northbridge is under the processor, and the southbridge remains on the open surface. This improves performance.

There is a difference in the performance of the processor and chipset. The system will work according to the minimum performance of one of the devices.
For example, if the processor is weak, then its performance will determine the parameters of the system and vice versa.
The main manufacturers of processors are the same two companies: AMD and Intel.
To choose a chipset, you need to decide on its purpose. For home/office use, an Intel chipset (with built-in graphics card) or AMD (with built-in core) will do.
When working in graphic editors or for gamers, select devices with a discrete card.
Intel chipsets are marked with a number after the letter, this is a performance indicator. There are 3 types for this parameter: X (maximum), P (for those who want to upgrade their computer in the future), G (home / office version).
The new socket 1155 made changes to the marking: H (for ordinary users) and Z (according to the characteristics, this is P + H).
AMD chipsets have different notation systems. If only numbers are indicated, this is a budget product. G or V refers to the integrated video core.
Specifying X or GX means incomplete support for multiple video cards. FX can support multiple graphics cards.
Intel chipsets
Current representatives of the Intel chipset:
- H270/B250 - suitable for simple tasks, multifunction and gaming computers
- Q270 - suitable for network companies
- Z270 - suitable for powerful graphics editors and for gamers
- X299 / X99 - suitable for working in very powerful graphic editors
Most computers can be supplied with motherboards based on the H270 and B250 chipsets. The functionality of the Q270 is excellent, with the ability to support special security options and remote management (regular users will not need this).
The capabilities of the Z270 will allow you to change the processor multiplier (with the “K” index). This chipset supports memory over 2400 MHz (not available with other chipsets).
In addition, the Z270 chipset is in demand in powerful gaming PCs with support for multiple video cards due to the presence of a larger number of PCI-E lanes.
Motherboards based on X99/X299 chipsets will be required only by heavy-duty and expensive professional computers with processors on sockets 2011-3/2066.
AMD Chipsets
Current AMD chipsets include:
- A320 - suitable for simple tasks, multifunctional and gaming computers
- B350 - suitable for work in graphic editors and for gamers
- X370 - suitable for enthusiasts.
The processor cannot be overclocked on the A320 chipset, but the capabilities of the B350 allow it. X370, in addition to the basic functionality, has a larger number of PCI-E lanes (for mounting multiple video cards)
VIDEO: AMD. Choosing a Motherboard for Ryzen
AMD B450. Choosing a Motherboard for Ryzen
Slots

Slots are connectors on the MP. They allow you to connect additional boards (expansion cards) to them. DDR5 is the most current slot (the numbers at the end indicate the production period).
There are from two RAM slots on the motherboard and more (but rarely more than four). To increase the RAM, one slot is replaced with another one with higher RAM.
Slots for video cards have two types (different in bandwidth): AGP and PCI Express. The most commonly used slot is PCIe x16.
Large slot bandwidth provides better performance. It is worth knowing that the difference in domestic use is not felt.
Special purpose motherboards may not have video slots. Their capabilities are limited and not suitable for home PCs.
There are different sockets for different processor slots. There are slots for mounts and other functions (for example, a slot for expansion motherboards). There may be four SATA3 hard drive slots.
Video connectors
The video connector is an important element in the motherboard. The possibility and convenience of connection depends on it.
To connect monitors on video cards, VGA and DVI connectors are installed. The quality of the video signal and the price of the video card depend on the type of connector.

The MP has built-in connectors for the audio system. For ordinary speakers, without load, the budget version of the ALC8xx codecs is suitable. ALC1150 connector for higher quality codec.
Expensive motherboards for games are equipped with codecs with high sound quality. Three codecs are enough to connect speakers with a 2.0 and 2.1 audio system.
For multi-channel acoustics, five to six audio connectors with a 5.1 and 7.1 system are suitable.
To connect a high-quality audio system, you need an optical output with a digital Hi-Fi system.

Modern motherboards come with a built-in network card. You also need to have a router that, in the event of a failure, is able to protect the connection. Rj-45 connector image in the figure below.

Cheap network card options are indicated by the name of the Realtek manufacturer. Professional destinations require Killer or Intel.
A good network card does not guarantee the absence of network failures. Often problems occur due to poor signal quality.
Built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth
Some PCs are equipped with connectors for bluetooth and Wi-Fi ( budget options without such details). Consider this when choosing. But they can be installed additionally.

In order not to overheat the MP, fans (coolers) are placed on the board. There are no or few coolers on cheap versions of boards. With heavy loads in the operation of the MP system, additional coolers are provided.
An expensive motherboard does not guarantee high performance.
Introduction
It's no secret that a computer is a complex device, consisting of a huge number of parts. But what is its main part - the motherboard - responsible for? At the dawn of time, its function was utilitarian - a platform for other computer components that has a dozen elementary settings - and nothing more. Over time, the motherboard took on more and more functions, and now you will not surprise anyone with an integrated sound card and video card, USB and FireWire controllers. It would seem that since there is nothing more to integrate (after all, it is now rare to find expansion cards in a regular computer), then progress should have stopped. No matter how! We will prove the reliability of the last statement on the example of the motherboard of one of the patriarchs of the IT industry - Micro-Star International Co., Ltd.
We will talk about the configuration and diagnostic application software of modern boards, about the element base that affects reliability during intensive use, about proprietary technologies that simplify the setup and operation of a computer, about the fact that plug-ins for the VKontakte social network are by no means only for communicators and smartphones, but also for operating systems built into the BIOS, about processor overclocking and modern overclocking tools, about related features that help other computer components work more reliably and efficiently - in a word, about everything that the manufacturer has invested in his brainchild and about which sometimes it’s completely buyers are unaware.
The motherboard is big, but what can it do?
Can a new generation motherboard deliver significantly more than previous generation solutions? Yes!
The motherboard is the largest board in the computer, and various functions of the future computer depend on it - both basic and additional. So, with the main function - to combine all computer devices into a finished system that can perform the tasks assigned to it - all motherboards do an excellent job. Let's start with additional features that will make it easier to work with a computer, making it as comfortable as possible. Usually such technologies have a name that does not always reveal their essence. For example, what is “APS” and what is it for? Let's try to consider some of the most interesting features using the MSI MS-7760 X79A-GD65-8D as an example. For clarity, we will make the following table:
| Description | MSI MS-7760 X79A-GD65-8D |
| Increased current in USB ports for charging smartphones and tablets | Super Charger |
| A utility that simplifies BIOS settings | ClickBIOS II |
| Automatic overclocking | OC Genie II |
| BIOS update utility | M Flash |
| Energy Reduction Technology | APS |
| Component base with increased resource | Military Class III |
| Mini OS for quick access to the global Internet | Winki 3 |
| Software for updating firmware and drivers from under Windows | Live Update 5 |
| Ability to use disks larger than 2.2 TB | 3TB+ Infinity |
| Surround Sound Compliance | THX, HD Audio |
Although the above list, of course, does not claim to be complete, the listed technologies alone already allow us to conclude that a high-quality motherboard satisfies most of the needs of both ordinary users and specialists.

VKontakte can't wait!
Can the motherboard make it so that downloading the necessary applications from the HDD takes less time compared to the state-of-the-art SSD?
Typically, the startup time of the computer is associated with the drive installed in the system. At 75%, this is true: Windows starts many times faster from a modern SSD drive compared to a system installed on a hard drive. It is worth noting that before starting the installed operating system, the computer conducts self-diagnosis, the duration of which, sometimes reaching 10-15 seconds, sometimes is half (or even more) of the total computer startup time. With the introduction of the latest generation of UEFI BIOS into motherboards, the time from pressing the power button to transferring control to the operating system has been significantly reduced, so when choosing a new motherboard, you should pay attention to this parameter. In addition to reducing startup time, the UEFI BIOS allowed the introduction of a graphical interface into the BIOS Setup program. In addition, it became possible to change the interface language, and some manufacturers, for example, have Russian in the extensive list of languages.

However, this is not all. Quite often, a computer is turned on simply to check mail or communicate on popular social networks such as VKontakte or Facebook, for which you have to wait for the operating system to load and the browser to start - when using classic hard drives, this procedure takes quite a long time. To reduce latency, MSI motherboards support the Winki 3 mini operating system, which has minimal functionality but starts up in just a few seconds. When using it, you will have access to an Internet browser, a photo viewer, an Internet pager and an office suite. It is worth noting that such an opportunity is currently unique, and no other motherboard manufacturer offers such a set of applications, which increases the attractiveness in the eyes of potential buyers.

ATX, ITX, or maybe DTX? What are these abbreviations?
Does size matter? Is the functionality of the board related to its format? In "supercomputer" motherboards, "bigger" always means "better"!
. When choosing a motherboard, you should remember that modern cases have different sizes, and not every motherboard will fit in the chosen case. In order to simplify the selection of the motherboard, standards have been developed indicating the size of the board, the location of mounting holes and expansion slots. These standards are called the motherboard form factor. For desktop computers, the most common sizes are XL-ATX, ATX, microATX, mini-ITX. In the above list, the formats are presented in decreasing order of size. It should be remembered that a small board can be installed in a large case: all fasteners and expansion slots will be in the right places, but this should only be done as a last resort. For example, when upgrading, you have an ATX case, and you liked the microATX board. When buying a new computer, it is better to select components of the appropriate size. The photos below show boards with different sizes.

Please note: a computer built on a board of the smallest format (mini-ITX) is usually designed to work in office computers or media centers, therefore, such models do not have a PCI-E 16x slot for installing discrete video cards, as a result of which modern games will not be available .
In general, when miniaturizing a motherboard, additional slots for video cards are removed from it first of all, the cooling system is simplified, and sometimes the number of SATA connectors is reduced. When choosing a board, you should think about whether any components will be added to the system unit - if not, then microATX will be an excellent choice, because computers assembled on such boards take up much less space, but they are not suitable for a serious gaming computer.
"Chipset" - just a buzzword or something more?
What do manufacturers ask for money for when they offer more or less expensive boards based on one chipset: for marketing or for really useful things that make the computer more convenient to use?
When choosing a motherboard, you need to pay attention to such a component of the motherboard as the chipset. For a long time, this complex semiconductor device was practically the second processor of any home computer. Its functionality included a memory controller, a PCI-E or, even earlier, AGP controller, an integrated graphics adapter, USB and hard drive controllers, and more. As a result, computers assembled from the same components, but differing in motherboards and, accordingly, chipsets, had different performance.
Today, the situation has changed: the functions that are critical to performance have moved to the processor, so the impact on computer performance has been significantly reduced. Computers built on different chipsets of the same generation have the same performance, differing in such parameters as support for the video core built into the processor, overclocking capability, the number of SATA II/SATA 6 Gb/s and USB/USB 3.0 ports. Despite this, manufacturers quite often have several boards in their lineup, which are based on the same system logic. This is done to expand the functionality of the product by adding additional controllers or disabling functions that are not critical in terms of reducing the final cost of the product. A good example is the line based on the Intel Z68 chipset.
| Z68A-G45(B3) | Z68A-GD65 (B3) | Z68A-GD80 (B3) | |
| Intel Smart Response | + | + | + |
| Lucidlogix Virtu Switchable Graphics | + | + | + |
| Charging USB devices (iPod, iPhone, etc.), | + | + | + |
| Uses 100% solid polymer capacitors | + | + | + |
| Automatic overclocking | + | + | + |
| Heat pipe cooling system | - | + | + |
| Increased power USB ports | - | + | + |
| Driver-MOSFET (DrMOS) | - | + | + |
| Tantalum Capacitors | - | + | + |
| IEEE-1394 controller | - | - | + |
| Availability of two network cards 10/100/1000 Mbps | - | - | + |
| 3 PCI-E 16x slots | - | - | + |

If you look at the price list of the NIKS Computer Supermarket, it becomes obvious that the most functional motherboard has the highest price. Three computers assembled on the basis of the same components, but having three motherboards from the above example, will have the same performance, however, the functionality and reliability in this case will differ due to the use of high-quality components that have passed military acceptance in expensive models.

"I want Japanese capacitors." Is such a desire justified?
Stability in everything is the desire of most of humanity, and if in life its implementation largely depends on the state, then in a computer this role is assigned to the motherboard. But do all "computer governments" care about their "inhabitants" in the same way?
All motherboard manufacturers strive to increase the resource of their products using advanced scientific achievements, and the only limitation in this case is the promptness of engineers. Quite a long time ago, two or three years ago, many companies began to use expensive solid capacitors in the production of their boards. This step made it possible to significantly increase the reliability of the boards, since swollen electrolytic capacitors in the power supply circuit of the central processor were a fairly common cause of the failure of the entire computer.
Then ferrite coils and low resistance transistors began to appear, but progress did not stand still, and over time, components previously used only in the aerospace industry began to appear in desktop computer boards, which allowed reliability to be taken to a new level. Leading the way is MSI, which is the industry's first to use Hi-c polymer capacitors based on the rare earth tantalum.

Unlike conventional solid capacitors, which cannot operate when damaged, MSI HI-c capacitors can self-heal thanks to the Nobel Prize-winning polymers.

In addition, the low height of such capacitors minimizes the likelihood of damage when installing a bulky processor cooling system. The only drawback of these devices is the rather high price, so Japanese solid capacitors are used in less critical areas of the board, which have a very long service life. To confirm the reliability of its motherboards, MSI independently tests components to MIL-STD-810G, which is a testament to the highest quality and reliability. It is not for nothing that all US Army equipment is subject to such certification. To obtain the appropriate certificate, components must pass 7 tests:
- temperature fluctuations
- Can be used in high humidity
- Vibrotest
- Low pressure operation
- High temperature operation
- Low temperature operation
- Test for resistance to physical impacts


Overclock the processor? Easily!
Everyone knows that Russians love to drive fast. And what in motherboards is allied to this feeling?
There are situations when the performance of the processor used is not high enough. How to proceed in such a case? There are two options:
- Buy a faster processor
- Overclock existing

We use the word "usually" for a reason. Most modern boards provide the ability to automatically overclock, which makes this task quite simple and safe, but not everything is perfect here.
The most common way to automatically overclock is to run a specialized utility that gradually increases the processor frequency. In the future, there is a reboot and a subsequent increase in frequency - and so on until a certain safe level, according to the electronics of the board, is reached. Although this method is, of course, effective, the overclocking process takes quite a long time, and not everyone is satisfied with the need to install additional software. MSI took a different path with the development of OC Genie technology and its further development, OC Genie II.

To overclock the processor on the MSI board, just before turning on the computer, press the button on the motherboard that says "OC Genie" and turn on the computer. Immediately after turning on, the frequencies will be increased and the computer will be ready to work, and the stability of the system will not be affected due to the use of high-quality components.
And if you need to install more than one video card?
Since we are talking about performance, the mention of the computer's graphics subsystem will be a completely logical development of this topic. When choosing a high-performance gaming computer, first of all, you should pay attention to the video card, because the performance in games mainly depends on it. "What's with the motherboard?" - you ask. Let's figure it out.
Since modern gaming graphics cards are installed in a PCI-E 16x slot, Mini-ITX motherboards are the most suboptimal choice for a gaming computer due to the lack of such a slot. Quite often, motherboards have two or more PCI-E 16x slots. This configuration will be of interest to hardcore gamers and enthusiasts, since it will allow you to assemble a multi-GPU system, increasing the performance of the computer's graphics subsystem by a multiple of the number of video cards.
To implement such a scenario, just having the right connectors is not enough - you need to support Crossfire technologies for AMD Radeon video cards or SLI for nVidia GeForce video cards. Information about the support of these technologies can be found in the description of the motherboard you like on the website or on the manufacturer's website. If games as a class of software are not of interest to you, in this case it is quite possible to get by with a video card integrated into the motherboard or processor, the capabilities of which in most cases will be enough for office work and watching any movies, and this solution will save energy.
|
|
"Hybrid graphics". Did not hear? Let's tell!
 Your new computer can be noticeably quieter and more economical than the old one!
Your new computer can be noticeably quieter and more economical than the old one!If you want to not only play modern games, but also save electricity, then a motherboard with hybrid graphics is the best option. For the first time, such technologies appeared in laptops - the most critical devices in terms of power consumption, because battery life directly depends on this parameter. Over time, the turn came to desktop computers. The operation in this mode is quite simple to explain. In idle (for a video card, idle is any mode other than a game), the built-in video adapter works, and when a game or other application is started that actively uses the resources of the graphics adapter, a discrete video card is turned on.
Energy savings come from the fact that any discrete graphics card consumes more power when idle than integrated graphics, and the difference is quite significant. If you plan to use such a bundle, you should choose boards that support Lucidlogix Virtu Switchable Graphics technology, such as . You can find out about the board's support for this technology on our website in the description or by looking at the box, where the corresponding logo should be present.
If saving energy is not a priority, but when working with a computer you have to convert video materials, in this case, purchasing a board that supports Lucidlogix Virtu also has one very significant plus. The fact is that the graphics core built into Intel Sandy Bridge processors supports Intel Quick Sync technology, thanks to which the time required to convert a video is reduced by several times. Thus, by configuring discrete graphics for continuous operation, and the integrated video core for the video converter, you will get both the highest performance in games and the ability to encode video in minimal time.
What to choose?
So what do you end up choosing? Quality? It is at the proper level for all major manufacturers. Extended functionality? As we pointed out in the first part, the variety of features eventually translates into different names for the same features. Price? Perhaps this is indeed the right factor - however, you should not take the most expensive one, since for the most part this is a payment for a bigger name and the active work of marketers.
Founded more than a quarter of a century ago, MSI independently manufactures motherboards and components, so the prices for MSI products are among the most affordable, and we are talking about high-quality full-fledged products. Another important advantage of MSI solutions is a long warranty period and excellent support. For fans of online battles, the unique promotions held by MSI together with the developers of popular games will be a pleasant surprise. If you are a fan of the most popular MMO World of Tanks, then by purchasing you will receive some in-game gold and a premium account.
When assembling a computer, many are worried about which motherboard to choose, because there are a huge variety of models on sale that need to be chosen taking into account numerous characteristics. It is best to give preference to products of well-known brands, the quality of which cannot be doubted and it is officially sold in our country with a manufacturer's warranty. Reliability and quality are the main criteria when choosing a motherboard, because no one wants to buy a new one every year, or even earlier.
How to choose a motherboard for a computer?
The best motherboard manufacturers at the moment are the following brands:
- asus;
- gigabyte.
These are one of the most popular and well-known brands, in the range of which you are guaranteed to find a good model. Having decided on the choice of brand, we move on to how to choose a motherboard for a computer, taking into account its characteristics.
Features of the design of the motherboard
The motherboard is a special device that has slots for connecting other computer elements, including a video card, RAM, power supply, and much more. You won't be able to use your PC without it.
The basic set of elements present on the motherboard:
- A socket is a large slot that houses a processor;
- A chipset is a microchip that connects two bridges together. The northbridge connects the processor and graphics card. South is responsible for the functioning of the BIOS, hard drive, mouse, display, keyboard and other external devices;
- Slots to which RAM and video card are connected;
- Connectors for the drive and hard drive;
- Connectors designed for power supply, mouse, keyboard and other devices;
- USB pins, which can be internal or external. They are used to connect the power button on the system unit, reboot and more.

All components of the computer are connected to the motherboard. Thus, it is used to place them and ensure the interaction of the system components with each other.
Choosing a motherboard for Intel processors
When figuring out which motherboard to choose for intel, you probably already noticed that such solutions are significantly more expensive. More sophisticated models are intended for them, supporting the latest RAM standards with a frequency of up to 2864 MHz and even more. Often in such a motherboard there are SATA connectors with a bandwidth of 6 Gb / s. Of course, not every motherboard will have similar characteristics, there are also budget solutions, but in general motherboards for Intel are much better. When choosing them, you need to pay attention to the standard slot for the processor, otherwise it may simply not fit.

Advantages:
- Excellent throughput;
- Top-end video cards and high-frequency RAM are supported;
- A wide selection of boards from budget to expensive professional models.
Motherboard for AMD processors
When figuring out which motherboard to choose for a computer, many choose solutions for AMD chips, which is due to their affordable cost. But in terms of their parameters, they will be inferior to solutions for Intel. New models are equipped with slots for DDR4 RAM, but as a rule, their operating frequency is lower - within 2400 MHz. Bandwidth will also be lower - no more than 3 Gb / s, although this is a decent result. Often, such boards are equipped with a large number of slots for RAM and are much cheaper.

Advantages:
- Affordable price;
- Modern standards of RAM and video cards are supported;
- A large number of slots are available for expanding the amount of RAM.
Flaws:
- Often they turn out to be not as durable as motherboards for intel;
- They don't have that much bandwidth.
Chipset
The chipset is the processor integrated into the motherboard, which is responsible for controlling the equipment connected to it. It depends on it how functional and fast it will be - whether it will allow the filling to function at the limit of its capabilities or become a ballast that limits the capabilities of the system. Let's figure out how to choose the right motherboard for your computer, and what you need to consider. You should choose a chipset according to the company of the processor, but it is equally important that its characteristics correspond to your current needs for which the PC is being built.
Motherboards equipped with Intel chipsets:
- For mid-range computers, the B250 and H270 chipsets are ideal. A more simplified version - B150 and H170 is suitable for assembling a working PC;
- the Z270 chipset is suitable, which supports several top-end video cards at the same time;
- The X99/X299 boards are selected for programming.
AMD does not lag behind its competitor, releasing chipsets for various purposes. The only thing is that they are not as powerful and work slower. On the other hand, they are also cheaper.
- A320 motherboards are intended for assembling an office PC;
- For gaming computers, the B350 chipset was developed to improve processor performance;
- For professional PCs, the X370 chipset is used, which supports multiple video cards and is faster than others.
Computer Motherboard Form Factor
Choosing AMD or Intel motherboards will be easier if you know their form factor. It predetermines the physical dimensions of the panel, and with it the number of slots provided by the manufacturer. Smaller boards often have reduced capabilities because they can't fit a lot of connectors. According to the form factor, the models currently being produced are divided into several types, for each of which a certain system unit is suitable:
- ATX is the most popular format. It is a full-sized board, which can accommodate the maximum required slots. The dimensions are as follows: 30.5x24.4 cm;
- MicroATX is a reduced board, the size of which does not exceed 24.4x24.4 cm. The number of additional slots in it does not exceed 6;
- MiniATX is the smallest version with dimensions of 17x17 cm. Such a board can even fit into a compact system unit, but there is also a significant drawback - a very limited number of slots and problems with efficient cooling.
Socket
The socket is an important selection factor that determines which processor is usable.
- Intel offers several variants of the LGA1150 and LGA2011-3. This is an outdated format. which is still in use, but it is better to pay attention to the more modern socket 1151. In the future, it will be possible to easily replace the processor with a new, more efficient one;
- When figuring out how to choose a motherboard for an AMD processor, it is better to order a model with the current AM4 socket or the still in demand AM3 + and FM2 +. The newer the socket, the easier it will be to find a replacement processor in the future, so it is better to give preference to the newest socket.
Now you know how to choose a motherboard for a processor, let's move on.
Number of slots for RAM

The more slots, the better, because it opens up great opportunities for upgrading your PC in the future. If we talk about the memory standard, then it should be DDR4. DDR3 sticks may be cheaper, but they work less efficiently and may soon disappear from sale. When figuring out which motherboard to choose in 2018, you need to consider what frequencies it supports, otherwise the part may slow down the system.
- Budget models support a frequency of 2400-2600 MHz, which will be enough for the average user;
- To build a gaming and professional PC, the frequency must be above 3000 MHz. As a rule, motherboards of the middle price segment and premium models have it.
Of great importance is the number of slots, which are 4 in a full-sized board, and only 2 in Micro and Mini. Keep this in mind, the possibility of expanding the memory capacity will never be superfluous.
Other connectors that the board can be equipped with
Understanding the question of which gaming motherboard to choose, you can see that most models are available with slots for video cards such as PCI Express 16. There can be from 1 to 4 such slots, which is useful when assembling a computer for games and mining. A spare slot for an additional video card will never be superfluous. You can also connect additional equipment there, such as a modem, solid state drive, and much more.
You need to pay attention to other slots in order to work comfortably with a computer:
- USB 3.0 and 2.0 - used to connect external devices such as a keyboard and mouse. It is desirable that there be at least 5 of them;
- PS / 2 - an obsolete connector that was previously widely used to connect a keyboard. Now its presence does not make sense, since all peripherals are available with a USB connector;
- DVI - designed to connect a monitor and is present only in models with a built-in video card. HDMI is used for the same purpose, but you can also connect a TV to it;
- BIOS reset key. Used to reboot it;
- eSATA - connector for connecting external hard drives;
- RJ-45 - port for connecting an Internet cable;
- Audio output for headphones and microphone.
Built-in elements
Modern motherboards can be equipped with a wide range of modules, including a built-in Wi-Fi sound and video card, Bluetooth, and much more. Accordingly, if they are already integrated into the board, then you do not have to buy them separately. But as a rule, integrated modules turn out to be worse and weaker than those that can be bought separately and installed independently. Therefore, such savings are questionable.
Electronics
Inexpensive boards use simple capacitors that can behave unpredictably. In case of overheating or power outages, the electrolyte in them swells up, but the circuit continues to function. More reliable, but also expensive, will be solid capacitors.