The most affordable model of the "new Nokia"
At the beginning of the year, during the MWC 2017 exhibition, the first three models from the new model line of Nokia smartphones were announced, they were Nokia 3, Nokia 5 and Nokia 6. Later, other new items were presented, including the powerful flagship Nokia 8, but it is only just went on sale. Today we will talk about the most affordable model in the new line, costing only $ 150: Nokia 3. For its level, this is a rather interesting device, moreover, it has long been sold in official Russian retail for 10 thousand rubles.
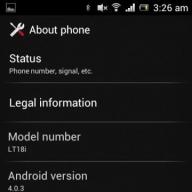
Main Features of Nokia 3 (Model TA-1032)
- SoC MediaTek MT6737, 4 cores @ 1.25 GHz (ARM Cortex-A53)
- GPU Mali-T720
- Operating system Android 7.0
- 5 ″ IPS touchscreen display, 1280 × 720, 293 ppi
- Random access memory (RAM) 2 GB, internal memory 16 GB
- Nano-SIM support (2 pcs.)
- MicroSD support up to 128GB
- GSM / GPRS / EDGE networks (850/900/1800/1900 MHz)
- WCDMA / HSPA + networks (850/900/1900/2100 MHz)
- LTE Cat.4 FDD (B1 / 3/5/7/8/20/28), LTE TD (B38 / 40)
- Wi-Fi 802.11a / b / g / n (2.4 and 5 GHz)
- Bluetooth 4.1
- GPS, A-GPS
- Micro-USB, USB OTG
- Main camera 8 MP, f / 2.0, autofocus, 720p video
- Front camera 8 MP, f / 2.0, autofocus
- Proximity sensor, lighting, accelerometer, gyroscope, compass
- Battery 2630 mAh
- Dimensions 143 x 71 x 8.5mm
- Weight 142 g
Contents of delivery
A unified packaging design was chosen for the entire new Nokia line. This is a rather simple flat box made of thin inexpensive cardboard, brightly decorated in a youth style.

The kit consists of a connecting cable, a power adapter with an output current of 1 A and a maximum voltage of 5 V, a key for removing cards, very simple headphones without rubber pads, and a bundle of paper documentation.


Appearance and usability
This is not to say that Nokia 3 looks expensive or even more expensive than its level. The Chinese now manage to offer much cheaper models in spectacular all-metal cases. Here everything is simpler: the device has got a neat but simple design with a plastic back panel and a metal side rim.

The bezel is matte and is as plain as all the other elements that make up the outer part of the Nokia 3. One can of course say that the device continues the design traditions laid down by Nokia and Microsoft in the Lumia family. But still, this model is more reminiscent of a Sony smartphone, since here the corners are very little rounded in plan, the device turned out to be clearly not “iPhone-like”.

Nokia 3 practically does not differ from the older Nokia 5 in size, but due to the slightly rougher matte sides and less weight, the device is more secure in the hand and does not slip out. There are practically no fingerprints on its matte surfaces either, the smartphone always looks neat. On the whole, the device is practical in everyday life, but it is difficult to promise that it will retain its presentable appearance for a long time, the materials are obviously prone to scratches.
 |
 |
On the side of the device there are two slots for cards: one provides space for two Nano-SIM cards, and the other can accommodate a microSD memory card. It's very convenient, you don't have to sacrifice one thing.

The front panel is completely covered with transparent 2.5D Gorilla Glass. The edges of the glass are sloping, and in combination with the slightly rounded corners of the case, this does not look very natural. Such glass is well suited for streamlined "remnants" - in fact, Apple with its sixth iPhone, and once introduced it into use. Here, perhaps, a flat "classic" would have looked better. But the tribute to fashion forces all manufacturers to follow the same path, what can you do.

Above the screen, sensors and a front camera peephole are habitually installed, but there is no front flash or LED event indicator.

At the bottom there is the same sad situation: there are touch buttons, but they do not have a backlight. There is no fingerprint scanner on the front or back - it was considered an unnecessary luxury for a budget phone.

The buttons on the right side edge do not differ in texture, they are the same matte and solid color as the bezel itself. The keys are harsh and have a distinct response.

On the back, the camera is combined with a flash under a transparent oval glass. The flash, unlike the Nokia 5, is single, but it shines just as brightly. Modern Nokia smartphones can work with some of the most powerful flashlights.

The top end is for a 3.5 mm headphone jack and an auxiliary microphone hole.

The bottom end contains a standard Micro-USB connector that supports connecting external devices in USB OTG mode, as well as a conversational microphone and main speaker.

The Nokia 3 comes in four color options. Three of them are completely ordinary (black, white and dark blue), but the last one, having a body like the white one, has a side frame not silver, but orange. It turns out a kind of sports orientation for people leading an active lifestyle.

Screen
The Nokia 3 features an IPS display covered with 2.5D Gorilla Glass with sloping edges. The physical dimensions of the screen are 62 × 110 mm, the diagonal is 5 inches. The resolution is 1280 × 720, which is often found in budget solutions, especially with a relatively small screen, option. Accordingly, the dot density is about 293 ppi. The frame around the screen is standard: the total width on the sides is 4.5 mm, on the top - 15 mm, on the bottom - all 17 mm.
The brightness of the display can be manually adjusted or use automatic settings based on the operation of the ambient light sensor.
 |
 |
A detailed examination using measuring devices was carried out by the editor of the "Monitors" and "Projectors and TV" sections Alexey Kudryavtsev... Here is his expert opinion on the screen of the test sample.
The front surface of the screen is made in the form of a glass plate with a mirror-smooth surface, resistant to scratches. Judging by the reflection of objects, the anti-glare properties of the screen are better than that of the Google Nexus 7 (2013) (hereinafter simply Nexus 7). For clarity, here is a photo in which a white surface is reflected in the turned off screens (on the left - Nexus 7, on the right - Nokia 3, then they can be distinguished by their size):

The Nokia 3's screen is slightly darker (photo brightness is 107 versus 118 for Nexus 7). The doubling of reflected objects in the Nokia 3 screen is very weak, which means that there is no air gap between the layers of the screen (more specifically, between the outer glass and the surface of the LCD matrix) (OGS type screen - One Glass Solution). Due to the smaller number of boundaries (such as glass / air) with greatly different refractive indices, such screens look better in conditions of intense ambient light, but their repair in the case of cracked outer glass is much more expensive, since the entire screen has to be changed. On the outer surface of the screen there is a special oleophobic (grease-repellent) coating (better than the Nexus 7 in terms of efficiency), so fingerprints are much easier to remove, and appear at a slower speed than in the case of ordinary glass.
With manual brightness control and with output full screen white field the maximum brightness value was about 520 cd / m², the minimum - 18 cd / m². The maximum brightness is very high, and given the excellent anti-glare properties, readability even on a sunny day outdoors should be good. In complete darkness, the brightness can be lowered to a comfortable value. In the presence of automatic brightness control according to the light sensor (it is located to the left of the front speaker slot). In automatic mode, when the ambient light conditions change, the screen brightness both increases and decreases. This function depends on the position of the brightness adjustment slider. If it is 100%, then in complete darkness the auto-brightness function reduces the brightness to 170 cd / m2 (too bright), in an office illuminated with artificial light (about 550 lux) it sets at 330 cd / m2 (also a lot), in a very bright environment (corresponds to illumination on a clear day outdoors, but without direct sunlight - 20,000 lux or slightly more) the brightness rises to 520 cd / m² (to the maximum, this is what you need); if the adjustment is about 50%, then the values \u200b\u200bare as follows: 19, 130 and 520 cd / m² (suitable values), if the regulator is at 0% - 4, 8 and 520 cd / m² (the first two values \u200b\u200bare too low, which is logical). It turns out that the automatic brightness control function works adequately and to some extent allows the user to customize his work for individual requirements. At any brightness level, there is no significant backlight modulation, so there is no screen flicker either.
This smartphone uses an IPS-type matrix. The micrographs show the typical IPS sub-pixel structure:

For comparison, you can see the gallery of photomicrographs of screens used in mobile technology.
The screen has good viewing angles without significant color shift, even with large gaze deviations from the perpendicular to the screen, and without tint inversion. For comparison, here are some photos showing the same images on the screens of Nokia 3 and Nexus 7, while the brightness of the screens was initially set to about 200 cd / m², and the color balance on the camera was forced to 6500 K.
White field perpendicular to screens:

Note the good uniformity of brightness and color tone of the white field.
And the test picture:

The color saturation on the Nokia 3 screen is normal, the colors are close to natural. The color balance between the Nexus 7 and the tested screen is clearly different.
Now at an angle of about 45 degrees to the plane and to the side of the screen:

It can be seen that the colors did not change much on both screens, but in Nokia 3 the contrast decreased to a large extent due to the strong black lightening.
And the white box:

The brightness at an angle of the screens decreased (at least 5 times, based on the difference in exposure), but the Nokia 3 screen is still slightly darker at this angle. When deviated diagonally, the black field is strongly lightened and acquires a bluish or yellowish tint. The photos below demonstrate this (the brightness of the white areas in the direction perpendicular to the plane of the screens is the same!):

And from a different angle:

At a perpendicular view, the uniformity of the black field is average:

The contrast (approximately in the center of the screen) is high - about 1050: 1. The response time for the transition black-white-black is 22 ms (11 ms on + 11 ms off). The transition between gray tones of 25% and 75% (based on the numerical value of the color) and back takes 33 ms in total. The gamma curve, plotted using 32 points at equal intervals in terms of the numerical value of the shade of gray, did not reveal any blockage in either the highlights or the shadows. The exponent of the approximating power function is 2.20, which is equal to the standard value of 2.2, but in this case it does not really matter. In this case, the real gamma curve deviates somewhat from the power dependence:

This device has an aggressive dynamic adjustment of the backlight brightness in accordance with the nature of the displayed image - the brightness of the backlight decreases in dark images in the middle. As a result, the obtained dependence of brightness on the hue (gamma curve) does not correspond to the gamma curve of a static image, since the measurements were carried out with sequential display of shades of gray on almost the entire screen. For this reason, a number of tests - determining the contrast and response time, comparing black illumination at angles - we carried out (however, as always) when displaying special templates with a constant average brightness, and not monochromatic fields in full screen. In general, such a non-switchable brightness correction does nothing but harm, since a constant change in screen brightness can at least cause some discomfort, reduce the visibility of gradations in the shadows in the case of dark images and the readability of the screen in bright light, since the brightness of the backlight is not the brightest in average images underestimated.
The color gamut is close to sRGB:

The spectra show that the matrix light filters mix the components together to a moderate extent:

As a result, the visual colors on this screen hardly differ from natural ones. The balance of shades on the gray scale is not very good, since the color temperature is significantly higher than the standard 6500 K, but the deviation from the spectrum of the absolute black body (ΔE) is below 10, which is considered an acceptable indicator for a consumer device. At the same time, the color temperature and ΔE do not change much from shade to shade - this has a positive effect on the visual assessment of the color balance. (The darkest areas of the gray scale can be ignored, since the color balance is not very important there, and the error in measuring color characteristics at low brightness is large.)


Let's summarize. The screen has a very high maximum brightness and excellent anti-reflective properties, so the device can be used outdoors without any problems even on a sunny summer day. In complete darkness, the brightness can be lowered to a comfortable level. It is also acceptable to use a mode with automatic brightness adjustment, which works adequately. The advantages of the screen include an effective oleophobic coating, no air gap in the layers of the screen and no flicker, high contrast, color gamut close to sRGB. The disadvantages are low stability of black to deviation of gaze from the perpendicular to the plane of the screen and aggressive dynamic adjustment of the backlight brightness in accordance with the nature of the displayed image. Nevertheless, given the importance of characteristics for this particular class of devices, the screen quality can be considered high.
Camera
The front module of the Nokia 3 takes pictures with a maximum resolution of 8 megapixels, but the quality of the pictures is not very high. The detail is not maximum, the images are darkish. The lens here is wide-angle, so a single subject looks unusually small in the picture.

The main camera uses an 8-megapixel sensor with a pixel size of 1.12 microns and an f / 2.0 aperture lens. There is a fairly fast autofocus and a single very bright flash. There is no stabilization system.
The camera application is quite simple, the settings menu, represented by a single drop-down list, is convenient and concise. Curiously, the aspect ratio and resolution of photos and videos are set in a single subsection for both cameras. You can manually set the white balance and perform exposure compensation, choose focusing options. Otherwise, the shooting parameters are determined by the machine with a ready-made list of scene modes.
 |
 |
 |
 |
The camera can shoot video in a maximum resolution of 720p, there is no Full HD, there is no stabilization function either. With such a resolution, you don't have to wait for a detailed and rich picture, the image is loose, but in general the camera produces the maximum possible for such conditions. There are no complaints about sound recording, the sound is recorded with high quality.
- Movie # 1 (20 MB, 1280 × [email protected] fps, H.264, AAC)
- Movie # 2 (29 MB, 1280 × [email protected] fps, H.264, AAC)
 |
The camera is good at macro photography in room lighting. |
 |
Details in the background merge. |
 |
The camera copes with macro photography. |
 |
Good sharpness across the field and across plans. |
 |
The text has been worked out well. |
 |
Not bad detail in the foregrounds, but in the middle the details are already merging. |
With its relatively low resolution, the camera sometimes fulfills the details well, but with the slightest lack of lighting, they begin to merge. As for the rest, the pictures are quite decent: sharpness across the field and according to plans is not bad, there are practically no noticeable areas of blur, and the program works very neatly in the light. As a result, the camera will do well with documentary and sometimes artistic photography.
Telephone part and communications
The communication capabilities of Nokia 3 include support for LTE Cat.4 (up to 150 Mbit / s), as well as support for a number of LTE FDD and TDD frequency bands, including all 3 interesting FDD LTE bands (band 3, 7, 20). In the city limits of the Moscow region the device behaves confidently, the signal reception quality raises no objections.
In addition, Nokia 3 supports both Wi-Fi bands (2.4 and 5 GHz), and there is even an NFC module that can work with travel cards. You can standardly organize a wireless access point via Wi-Fi or Bluetooth 4.1 channels. The Micro-USB connector supports connecting external devices in USB OTG mode. The navigation module only works with GPS (with A-GPS). The first satellites during a cold start are detected within half a minute, the positioning accuracy is not bad. There is a built-in magnetic field sensor for compass navigation programs.
Software and multimedia
As a software platform, Nokia 3 uses Google's Android 7.0 version - unlike older Nokia models, which received Android 7.1.1. In principle, this is all the difference, since the rest of the interface is identical. The manufacturer is proud to announce that the new Nokia smartphones run on a completely pure Android OS. There are practically no third-party programs, everything you need is achieved using Google Apps.
To listen to music, a regular Google Music player with sound settings and built-in equalizer presets is used. Both in headphones and through the speaker the device sounds rather modest, whistling and hissing prevail, the sound is noisy, not very clear, but the volume is generally enough for any environment. There is also an FM radio, but there was no built-in voice recorder in the device.
 |
 |
 |
 |
Performance
The hardware platform of Nokia 3 is based on SoC MediaTek MT6737, made according to the 28 nm process technology. This 64-bit platform is configured with 4 Cortex-A53 processor cores operating at up to 1.25 GHz. The Mali-T720 video accelerator is responsible for graphics processing. RAM is 2 GB and user storage is 16 GB. Of these, on average, less than 500 MB of RAM and less than 10 GB of flash memory are free. It is possible to connect external flash drives in USB OTG mode.
MediaTek MT6737 is one of the most modest in terms of capabilities of modern platforms for entry-level mobile devices. It is quite weak, focused on the ultra-budget class of devices. It is pointless to expect high performance from this SoC, the hero of the review gains less than 30K points in AnTuTu, and in all other tests the Nokia 3 shows a low level. Demanding games like Mortal Kombat X and graphical tests slow down noticeably. Such a device certainly has no power reserve for the future.


Benchmarking AnTuTu and GeekBench:
All the results obtained by us when testing the smartphone in the latest versions of popular benchmarks, we summarized for convenience in tables. Several other devices from different segments are usually added to the table, also tested on similar latest versions of benchmarks (this is done only for a visual assessment of the obtained dry numbers). Unfortunately, within the framework of one comparison it is impossible to present the results from different versions of benchmarks, so many worthy and relevant models remain behind the scenes - due to the fact that they once passed the "obstacle course" on previous versions of test programs.
 |
 |
Testing the graphics subsystem in gaming tests 3DMark, GFXBenchmark and Bonsai Benchmark:
When testing in 3DMark for the highest performing smartphones, it is now possible to run the application in Unlimited mode, where the rendering resolution is fixed at 720p and VSync is disabled (which can cause the speed to rise above 60 fps).
| Nokia 3 (MediaTek MT6737) |
Micromax Canvas Juice A1 (Qualcomm Snapdragon 210) |
Honor 6C (Qualcomm Snapdragon 435) |
HTC One X10 (MediaTek Helio P10 (MT6755)) |
Honor 8 lite (HiSilicon Kirin 655) |
|
| 3DMark Ice Storm Sling Shot ES 3.1 (more is better) |
103 | — | 254 | 421 | 398 |
| GFXBenchmark Manhattan ES 3.1 (Onscreen, fps) | 3 | — | 11 | 5 | 5 |
| GFXBenchmark Manhattan ES 3.1 (1080p Offscreen, fps) | 1 | — | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| GFXBenchmark T-Rex (Onscreen, fps) | 10 | 9 | 28 | 17 | 19 |
| GFXBenchmark T-Rex (1080p Offscreen, fps) | 6 | 5 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
 |
 |
Browser cross-platform tests:
As for benchmarks for evaluating the speed of the javascript engine, you should always make allowances for the fact that the results in them significantly depend on the browser in which they are launched, so that the comparison can be truly correct only on the same OS and browsers, and this possibility is available when testing not always. In the case of Android OS, we always try to use Google Chrome.
 |
 |

AndroBench memory speed test results:

Thermal images
Below is a thermal image back surface obtained after 10 minutes of battery test in GFXBenchmark program:

Heating is more localized in the upper part of the device, which, apparently, corresponds to the location of the SoC chip. According to the heat chamber, the maximum heating was 37 degrees (at an ambient temperature of 24 degrees), which is not very much.
Video playback
To test the "omnivorous" video playback (including support for various codecs, containers and special features, such as subtitles), we used the most common formats, which make up the bulk of the content available on the Web. Note that it is important for mobile devices to have support for hardware decoding of video clips at the chip level, since it is often impossible to process modern versions at the expense of processor cores alone. Also, do not expect a mobile device to decode everything, since the leadership in flexibility belongs to the PC, and no one is going to challenge it. All results are tabulated.
| Format | Container, video, sound | MX Video Player | Native video player |
| 1080p H.264 | MKV, H.264 1920 × 1080, 24 fps, AAC | reproduced normally | reproduced normally |
| 1080p H.264 | MKV, H.264 1920 × 1080, 24 fps, AC3 | reproduced normally | video plays normally, no sound |
| 1080p H.265 | MKV, H.265 1920 × 1080, 24 fps, AAC | not reproduced | |
| 1080p H.265 | MKV, H.265 1920 × 1080, 24 fps, AC3 | reproduced with significant delays (only in SW) | not reproduced |
Further testing of video playback by Alexey Kudryavtsev.
We did not find the MHL interface, like the Mobility DisplayPort, in this smartphone, so we had to limit ourselves to testing the output of video files on the screen of the device itself. For this, we used a set of test files with an arrow and a rectangle moving one division per frame (see "Testing methods for video playback and display devices. Version 1 (for mobile devices)"). Screenshots with a shutter speed of 1 s helped to determine the nature of the frame output of video files with different parameters: the resolution varied (1280 by 720 (720p), 1920 by 1080 (1080p) and 3840 by 2160 (4K) pixels) and the frame rate (24, 25, 30, 50 and 60 fps). In our tests, we used the MX Player video player in the "Hardware" mode. The test results are summarized in the table:
720 / 30pNote: If both columns Uniformity and Skips green marks are set, this means that, most likely, when watching movies, artifacts caused by uneven alternation and skipping of frames will either not be visible at all, or their number and visibility will not affect the viewing comfort. Red marks indicate possible problems with the playback of the respective files.
According to the criterion for outputting frames, the quality of video files playback on the screen of the smartphone itself is good, since in most cases frames (or groups of frames) can (but are not required) to be displayed with more or less uniform alternation of intervals and without frame drops. Note that, most likely, the refresh rate of the screen is slightly higher than 60 Hz (about 62 Hz), so perfect playback smoothness is not obtained at any standard frame rates in a video file. When playing video files with a resolution of 1280 by 720 pixels (720p) on a smartphone screen, the image of the video file itself is displayed exactly along the edge of the screen, one to one pixel by pixel, that is, in the original resolution. The brightness range displayed on the screen corresponds to the standard range of 16-235: in shadows and highlights, only a couple of shades merge with black and white, respectively.
Battery life
The non-removable battery installed in the Nokia 3 has a slightly lower capacity of 2630 mAh than the older Nokia 5 with its 3000 mAh. It is logical that the younger model also demonstrates a slightly worse level of autonomy. However, the level of both models is quite satisfactory, just not outstanding. As a standard, the hero of the review is able to live until the evening charge, but the smartphone will have to be charged every night.
Testing has traditionally been conducted at typical power consumption levels without using power saving features.
Continuous reading in the Moon + Reader program (with a standard, light theme) at a minimum comfortable brightness level (the brightness was set to 100 cd / m2) with auto-scrolling lasted about 13 hours until the battery was fully discharged, and with continuous video viewing in high quality (720p) with the same brightness level via a Wi-Fi network, the device operates for about 10 hours. In 3D games mode, the smartphone can work up to 5 hours.
The Nokia 3 is charged for 3 hours with a current of 0.9 A at a voltage of 5 V. The smartphone does not support wireless charging either.
Outcome
The most affordable of the new Nokia smartphones has got the most modest cameras and sound system in the family. The device was obviously not intended as a multimedia solution, it is a workhorse with a practical body, quite good communication capabilities for its level (which even surprised us), and a good bright screen. Autonomy is average. Unfortunately, the hardware platform for the smartphone was chosen very weak, its capabilities are only enough for the interface and applications to work without delays, but this is not bad either. In official retail, a smartphone costs only 10 thousand rubles, this is not much. Taking into account the fact that many still remember their favorite old Nokia phones, the unpretentious new Nokia 3 will surely find its buyer.
Exquisite design and high quality workmanship
The Nokia 3 embodies all the classic hallmarks of our brand: an exquisitely beautiful polycarbonate casing, a sturdy aluminum frame, meticulously crafted details and optimal performance for everyday use.
Practical technology and quality materials
Correctly selected technologies and materials are a guarantee of convenience in everyday use of the device. The ruggedized Corning Gorilla Glass display and meticulously machined aluminum frame provide superior protection.
Phones for real life
For many years, Nokia devices were unmatched in terms of design and workmanship. And this phone has many important advantages: durable, eye-catching materials, ergonomics, the perfect balance between performance and battery life.
Regular software updates to ensure your Nokia phone is secure and has the latest features.
Consistently high quality photos
The Nokia 3 lets you take cool selfies and photos with your friends using the 8MP front or main camera with autofocus. With Google Photos, you can save and share all your photos.
Polarized display for easy visibility
No need to squint: The Nokia 3's polarized HD display is fully laminated to let you watch videos, read and use apps even in bright sunlight.
Simplicity, safety and compliance with modern requirements
The Nokia 3 comes with a pure Android Nougat operating system and all Google services without unnecessary add-ons and skins. You get a simple, clean interface for the latest version of Android, which is constantly updated to provide you with high security and support for new features.
Communication
LTE (bands 1, 3, 5, 7, 8, 20, 28, 38, 40)
WCDMA (bands 1, 2, 5, 8)
GSM (850, 900, 1800, 1900 MHz)
LTE 4 Network Speed, 150 Mbps (Upload) / 50 Mbps (Upload)
micro-USB (USB 2.0), USB OTG
Bluetooth wireless technology
Display
Display type: LCD, IPS technology
Display diagonal (inch): 5
Display Resolution (pix): HD (1280x720, 16: 9)
Rugged display Corning® Gorilla® Glass 2.5D
Brightness up to 450 cd / m², with lamination
Features: polarizer
Main camera
LED flash
Front-camera
8 MP, autofocus, 1.12 microns, f / 2
Field of view 84 °
CPU
Mediatek MT6737 processor, 1.3 GHz, 4-core
Memory
Built-in memory: 16 GB
RAM: 2 GB
System
Operating System: Android ™ 7.0 Nougat
MicroSD card slot
Supports cards up to 128GB
Sound
3.5mm headphone jack
One speaker
Sensors
Accelerometer (screen rotation sensor)
Ambient light sensor
Electronic compass
Gyroscope
Proximity sensor
Nutrition
Built-in battery
Battery capacity, mAh: 2630
Housing
Height (mm): 143.4
Width (mm): 71.4
Device type:
Smartphone / Communicator
2G standards:
The mobile communication standard defines the technologies used and the principle of building mobile communication networks. It is customary to divide mobile communication networks into analog (NMT, AMPS) and digital (D-AMPS, GSM, CDMA, WCDMA, UMTS), as well as to classify the stages of development of the standards themselves by generation.
GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) is the most popular and widespread second generation 2G cellular communication standard practically all over the world. In our country, as in most European countries, frequencies of 900 and 1800 MHz are allocated for this standard. In the countries of the American continent, it is customary to use frequencies of 850 and 1900 MHz.
The widespread introduction of GSM instead of outdated analogue networks has made it possible to significantly expand the subscriber base and the range of services provided, making cellular communications massively available. However, the specificity of GSM limits the currently demanded services based on high-speed Internet access.
GSM 1800 / GSM 1900 / GSM 850 / GSM 900
3G standards:
3G (Third Generation) - Third generation mobile communication technologies based on packet data transmission. Third-generation 3G networks typically operate in the around 2 GHz range, allowing data transfer speeds comparable to dedicated home Internet. In addition to standard voice telephony services, 3G networks were initially focused on various multimedia services, such as video telephony and video conferencing, on-line watching of terrestrial television and films, listening to Internet radio, etc. The most common third-generation communication standard is WCDMA (UMTS) operating in most European countries, incl. in Russia and the CIS countries.
UMTS 2100 / UMTS 900
4G (LTE) standards:
4G (Fourth generation) - The fourth generation of mobile communications, characterized by high data rates and improved voice quality. The fourth generation networks include mobile data transmission technology LTE (Long Term Evolution). The data transfer speed according to the LTE standard in theory reaches 173 Mbps for download (download), and 58 Mbps for upload.
LTE 1800 / LTE 2100 / LTE 2300 / LTE 2600 / LTE 800 / LTE 850 / LTE 900
VoLTE:
VoLTE (in English Voice over LTE - voice over LTE) - Voice over LTE technology, which allows the provision of voice services and their delivery as a data stream over LTE. MegaFon is the first telecom operator in Russia to launch VoLTE without restrictions on the type of users: all subscribers of the Moscow Region only, regardless of the tariff plan and the payment system used, can connect to the HD voice in 4G service and make calls using the new technology. using mobile devices with VoLTE support of the MegaFon network.
Generation of SIM:
Each new generation of SIM cards is smaller than the previous one. Format Mini-SIM (2FF) appeared in the 1990s and is now used primarily in simple push-button telephones. Cards Micro-SIM (3FF) have been used in smartphones since 2003 to this day. Nano-SIM (4FF) is the most compact card installed in modern smart devices. eSIM is a chip built into the device, on which you can write a virtual SIM card. This format is not supported by all telecom operators.
Number of SIM-cards:
Accumulator battery:
The difference in the chemical composition of batteries determines their physical and consumer parameters.
Ni-Cd (Nickel - Cadmium) and Ni-Mh (Nickel - Metal Hydride) batteries are quite heavy and bulky. If they are not fully discharged before recharging, they are prone to loss of capacity (memory effect), and therefore require periodic maintenance (charge-discharge, so-called training).
On the contrary, Li-Ion (Lithium - Ion) and Li-Pol (Lithium - Polymer) batteries are free from these disadvantages. However, they lose their charge faster at low temperatures and are poorly resistant to drops. Low maintenance and comparatively smaller size and weight were decisive factors for their active use.
Li-Ion, 2650 mAh
Wireless charging function:
The wireless charging phone can be charged without connecting a cable, just place it on the induction hob. A wireless charger is usually not included with your phone and must be purchased separately.
When choosing a charger, pay attention to the wireless charging standard (the most common is Qi).
NFC module:
NFC (Near Field Communication, "near field communication") - a wireless communication technology that allows the exchange of data between devices located at a distance of up to 20 centimeters. There are many uses for NFC technology: transferring files between devices, connecting to accessories, using the device as a payment card, etc.
Equipment:
Phone, network charger, USB cable, wired stereo headset, key for removing the SIM card, warranty card, instructions, packaging
Warranty period:
Memory and processor
The amount of random access memory (RAM):
Random access memory used by programs and applications in the device. The speed of the device depends on its size. Actual free memory space may differ from the manufacturer's specifications.
Built-in memory:
Built-in device memory - the total amount of memory intended both for storing user data and for applications installed by the manufacturer, and also includes a section with the Operating System. Actual free memory space may differ from the manufacturer's specifications.
Display and keyboard
Display type:
TFT IPS - High quality liquid crystal matrix. It has wide viewing angles, one of the best indicators of color and contrast quality among all that are used in the production of displays for portable equipment.
Super AMOLED - if a conventional AMOLED screen uses several layers, between which there is an air gap, then in Super AMOLED there is only one such sensor layer without air gaps. This allows you to achieve a brighter screen for the same power consumption.
Super AMOLED HD - differs from Super AMOLED in high resolution, thanks to which it is possible to achieve a size of 1280x720 pixels on a mobile phone screen.
Super AMOLED plus - this is a new generation of Super AMOLED displays, which differs from the previous one by using more subpixels in a conventional RGB matrix. The new displays are 18% thinner and brighter than the older PenTile technology.
AMOLED - an improved version of OLED technology. The main advantages of the technology are significantly reduced power consumption, the ability to display a wider color gamut, smaller thickness and the ability of the display to bend slightly without the risk of breaking.
Retina -display with high pixel density, designed specifically for Apple technology. The pixel density on Retina displays is such that individual pixels are invisible to the eye at a normal distance from the screen. This provides the highest picture detail and dramatically improves the overall viewing experience.
Super Retina HD - the display is made using OLED technology. The pixel density is 458 PPI, the contrast ratio reaches 1,000,000: 1. The display has a wide color gamut and unrivaled color accuracy. Pixels in the corners of the display are anti-aliased at the sub-pixel level, so the edges are smooth and smooth. 50% thicker Super Retina HD gain layer. It will be harder to break the screen.
Super LCD is the next generation of LCD technology and features improved performance over earlier LCD displays. The screens have not only wide viewing angles and better color reproduction, but also lower power consumption.
TFT- A common type of liquid crystal displays. With an active matrix controlled by TFTs, display performance and contrast and clarity are significantly improved.
OLED - organic electroluminescent display. Consists of a special thin-film polymer that emits light under the action of an electric field. This type of display has a large margin of brightness and consumes very little power.
Touchscreen:
A touchscreen display is a conventional graphic display over which either a pressure-sensitive substrate or infrared sensors are placed. Such a display responds appropriately to pressing with a stylus (pen) or fingers and is a more convenient way to interface with a device than a keyboard.
Additional display:
As a rule, an additional display is installed in folding phones. Depending on the model of the device, the secondary display may show the caller's number, time, signal reception strength and battery charge level.
Multimedia
FM radio:
Your favorite radio stations or news programs will accompany you on a long journey and on the way to work. In some cases FM radio tuner can also be used as an alarm clock.
However, it should be remembered that due to the design features, for the radio to work on almost all phone models, a wired portable headset must be connected.
Photo / Video Camera
Main camera:
Built-in digital camera it is very easy to capture important moments from life or shoot a video. Modern smartphone cameras are often not inferior in the quality of shooting to real cameras. The use of two, three or even four modules allows you to take wide-angle shots, photograph distant objects and achieve the effect of artistic background blurring - bokeh.
Autofocus:
Photo flash:
Designed for short-term and intense illumination of objects during shooting. Cell phones are either xenon (based on an electric discharge lamp filled with xenon) or LED (LEDs act as a light source).
LED
Main camera image size:
Front camera image size:
The maximum resolution of pictures taken when photographing with the built-in camera. Measured in the number of pixels horizontally and vertically. The higher the number of pixels, the clearer the photos will be.
Communications and interfaces
Wi-Fi:
Wi-Fi (IEEE 802.11) is a high-speed wireless connection technology aimed at building corporate, private or public networks. The technology is based on the use of so-called multiple access points (hot-spots), to which client terminals are connected. Wi-Fi technology is described by many specifications (standards), which is displayed in their name with the last letter (for example, IEEE 802.11g).
On the basis of Wi-Fi technology, public access points to the Internet have been created in cafes, hotels, airports and other places. Connecting the device to such points is simplified as much as possible and requires entering the network identifier (SSID), username and password.
Bluetooth module:
Technology Bluetooth implements wireless connection of devices via a secure radio channel in the 2.4 GHz band. The technology is based on the use of profiles (services) as tools for performing specific tasks (audio gateway, hands-free, headset, file transfer, dial-up networking, serial port, etc.). Each profile contains a specific set of operations and defines the possible areas of interaction between devices.
With a Bluetooth connection, the devices can be at a distance of up to ten meters from each other, and therefore, the development of wireless accessories is one of the prerogatives of this technology.
Bluetooth stereo support:
Bluetooth stereo or A2DP (Advanced Audio Distribution Profile) - a Bluetooth profile or service designed for streaming music in stereo. Devices that support the A2DP profile allow you to listen to music using wireless Bluetooth headphones, thereby relieving you of the limitations of traditional wired stereo headsets.
PC connection:
By connecting the device to a personal computer, you can quickly and conveniently edit phone records or organizer notes, save important SMS messages or backup copies of the contents of the device on your PC, download various pictures, melodies, photos or video clips, access the Internet.
Depending on the characteristics of the device, connection to a PC is carried out using an interface cable, IrDA, Bluetooth or Wi-Fi modules.
Audio jack:
The type of connector for connecting external audio devices (wired headsets, headphones, speakers). Many modern smartphones use a universal connector such as USB Type-C or Lightning for audio output, charging and data transfer.
Posts
SMS:
SMS (Short Messages Service) or short text messages are an alternative way of exchanging information on cellular networks. Most of the devices support the reception and transmission of SMS messages in both English and Russian. Type the desired text, for example, "Honey, I'm at home. Kisses and I'm really looking forward to you", and within a few seconds it will be delivered to your specified mobile device.
In addition, on the basis of the SMS service, various SMS services are provided, from weather forecasts and exchange rates, to dating and downloading simple melodies or pictures.
MMS:
MMS (Multimedia Messaging Service) is a universal technology for exchanging multimedia messages, which is the development of the idea of \u200b\u200bshort SMS messages. In addition to regular text, an MMS message can contain color pictures and photographs, sound files of various formats, or short video clips. In addition, MMS messages can consist of several frames, representing a kind of animation.
Multimedia messages are sent using GPRS or EDGE packet data. You can send MMS messages both to a device compatible with this technology and to e-mail.
E-mail:
Built in e-mail client is an analogue of programs for working with e-mail on a personal computer, but in a slightly limited version. As a rule, the E-mail client allows you to send and receive emails, as well as small attachments in the form of files with pictures or melodies.
Alerts
Vibrating alert:
In situations where the use of sound alerts is not entirely appropriate, or completely useless, built-in vibration alert will inform you about an incoming call or other event with a slight tremor of the phone case. For example, at a lecture or meeting, near a busy highway, or at a noisy party.
Additional functions
Sensors:
Accelerometer (or G-sensor) - sensor of the device's position in space. As a primary function, the accelerometer is used to automatically change the orientation of the display image (vertical or horizontal). Also, the G-sensor is used as a pedometer, it can be controlled by various functions of the device by turning or shaking.
Gyroscope - a sensor that measures the angles of rotation relative to a fixed coordinate system. Able to measure angles of rotation in several planes at the same time. The gyroscope together with the accelerometer allows you to accurately determine the position of the device in space. In devices that use only accelerometers, the measurement accuracy is lower, especially when moving quickly. Also, the capabilities of the gyroscope can be used in modern games for mobile devices.
Light sensor - a sensor, thanks to which the optimal values \u200b\u200bof brightness and contrast are established for a given light level. The presence of the sensor allows to increase the operating time of the device from the battery.
Proximity sensor - a sensor that detects when the device is close to the face during a call, turns off the backlight and locks the screen, preventing accidental presses. The presence of the sensor allows to increase the operating time of the device from the battery.
Geomagnetic sensor - a sensor for determining the side of the world to which the device is directed. Tracks the orientation of the device in space relative to the earth's magnetic poles. The information received from the sensor is used in cartographic programs for orientation on the ground.
Atmospheric pressure sensor - sensor for accurate measurement of atmospheric pressure. It is part of the GPS system that allows you to determine the height above sea level and speed up the location.
Touch ID - fingerprint identification sensor.
Accelerometer / Geomagnetic / Gyroscope / Illumination / Approximation
Satellite navigation:
GPS (Global Positioning System - global positioning system) - a satellite navigation system that measures distance, time, speed and determines the location of objects anywhere on Earth. The system is designed, implemented and operated by the US Department of Defense. The main principle of using the system is to determine the location by measuring the distance to the object from points with known coordinates - satellites. The distance is calculated from the signal propagation delay time from its sending by the satellite to being received by the GPS receiver antenna.
Monoblock with flip (with a lid) - a classic type case with an additional lid that covers the main keyboard.
Folding (clamshell, book, frog) - this type of case consists of two halves that fold out together. Usually, the main and, if any, additional displays are located in the upper part, and the keyboard unit in the lower part.
Slider (sliding) - the body consists of two halves sliding apart relative to each other. Until recently, cases of this form factor were inherent in expensive fashion models.
Rotating (rotator) - perhaps the most unusual type of case, when the front half rotates 180 or 360 degrees relative to the back half. Due to its design features, it is rare.
Double slider - the body is similar slider, but the mechanism allows the halves to be moved apart in two opposite directions.
Display 5 ", 1280x720 Pix
* Specifications and package contents, including pre-installed or optional software, are subject to change by the manufacturer without prior notice.